More than half of Canadians DO NOT support the federal government’s mandate to require all new cars sold in Canada to be electric by 2035, a recent Ipsos poll finds.
Canadians across the country are “a lot more hesitant to ban conventional cars than their elected representatives in Ottawa are,” said Krystle Wittevrongel, research director at the Montreal Economic Institute (MEI), in a news release on Oct. 3.
“They have legitimate concerns, most notably with the cost of those cars, and federal and provincial politicians should take note.”
The online poll, conducted by Ipsos on behalf of the MEI, surveyed 1,190 Canadians aged 18 and over between Sept. 18 and 22. Among the participants overall, 55 percent said they disagree with Ottawa’s decision to ban the sale of conventional vehicles by 2035 and mandate all new cars be electric or zero-emissions.
“In every region surveyed, a larger number of respondents were against the ban than in favour of it,” MEI said in the news release. According to the poll, the proportion of those against the ban was noticeably higher in Western Canada, at 63 percent, followed by the Atlantic provinces at 58 percent. In Ontario, 51 percent were against, and in Quebec, 48 percent were against.
In all, only 40 percent nationwide agreed with the federal mandate.
‘Lukewarm Attitude’
Just 1 in 10 Canadians own an electric vehicle (EV), the poll said. Among those who don’t, less than one-quarter (24 percent) said their next car would be electric.


A research report released by Natural Resources Canada (NRCan) in March this year suggests a trend similar to that of the Ipsos poll’s findings. The report indicated that only 36 percent of Canadians had considered buying an EV in 2024—down from 51 percent in 2022.
“Survey results reveal that Canadians hold mixed views on ZEVs [Zero-Emission Vehicles] and continue to have a general lack of knowledge about these vehicles,” said the report by EKOS Research Associate, which was commissioned by NRCan to conduct the online survey of 3,459 Canadians from Jan. 17 to Feb. 7.
The MEI cited a number of key reasons for “this lukewarm attitude” in adopting EVs, including high cost (70 percent), lack of charging infrastructure (66 percent), and reduced performance in Canada’s cold climate (64 percent).

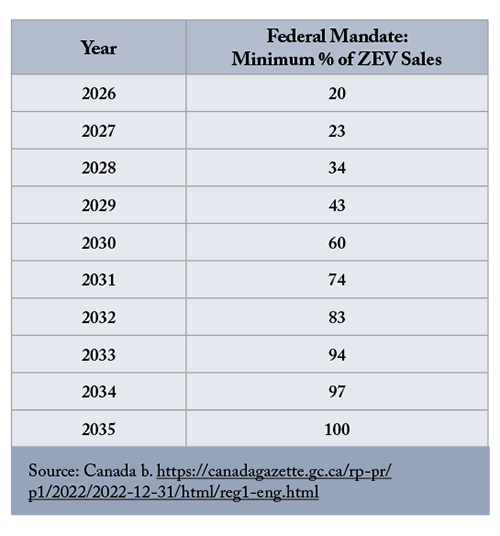
Canada’s shift from gas-powered vehicles to EVs is guided by federal and provincial policies aimed at zero-emission transportation. The federal mandate requires all new light-duty vehicles, which include passenger cars, SUVs, and light trucks, sold by 2035 to be zero-emission—with interim targets of 20 percent by 2026 and 60 percent by 2030.
Some provincial policies, such as those in Quebec, are even stricter, including a planned ban on all gas-powered vehicles and used gas engines by 2035.
‘Unrealistic’
The MEI survey indicated that two-thirds of respondents (66 percent) said the mandate’s timeline is “unrealistic,” with only 26 percent saying Ottawa’s plan is realistic.
In addition, 76 percent of Canadians say the federal government’s environmental impact assessment process used for energy projects takes too long, with only 9 percent taking the opposite view, according to the survey.
A study by the Fraser Institute in March said that achieving Ottawa’s EV goal could increase Canada’s demand for electricity by 15.3 percent and require the equivalent of 10 new mega hydro dams or 13 large natural gas plants to be built within the next 11 years.
“For context, once Canada’s vehicle fleet is fully electric, it will require 10 new mega hydro dams (capable of producing 1,100 megawatts) nationwide, which is the size of British Columbia’s new Site C dam. It took approximately 10 years to plan and pass environmental regulations, and an additional decade to build. To date, Site C is expected to cost $16 billion,” said the think tank in a March 14 news release.
On April 25, Prime Minister Justin Trudeau announced that Canada since 2020 has attracted more than $46 billion cad in investments for projects to manufacture EVs and EV batteries and battery components. A Parliamentary Budget Officer report published July 18 said Ottawa and the provinces have jointly promised $52.5 billion cad in government support from Oct. 8, 2020, to April 25, 2024, which included tax credits, production subsidies, and capital investment for construction and other support.
On July 26, a company slated to build a major rechargeable battery manufacturing plant in Ontario announced that it would halt the project due to declining demand for EVs.
In a news release at the time, Umicore Rechargeable Battery Materials Canada Inc. said it was taking “immediate action” to address a “recent significant slowdown in short- and medium-term EV growth projections affecting its activities.”
For The Silo, Isaac Teo with contribution from the Canadian Press.