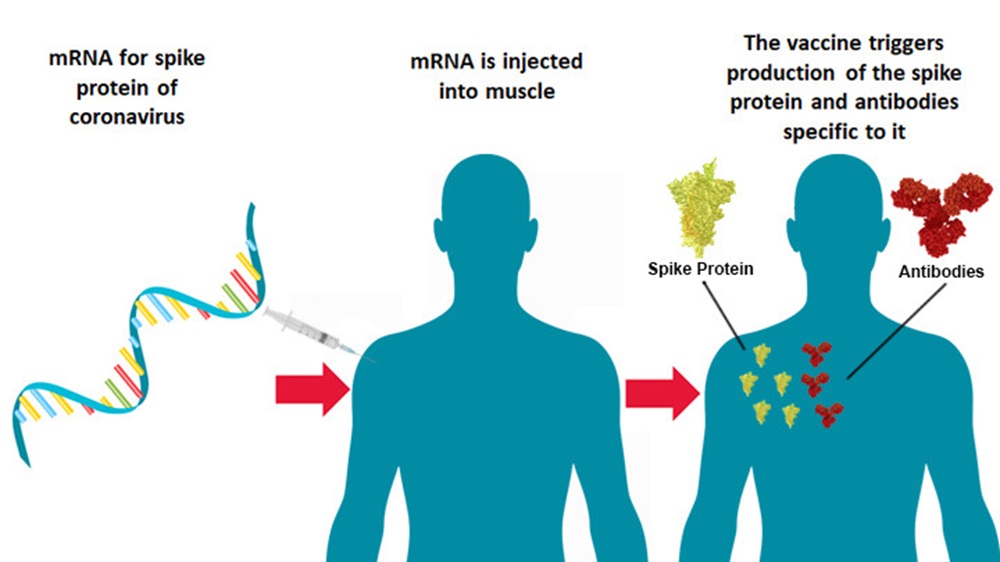
| The Global Cooperation Barometer indicates that international cooperation has “flatlined”, driven by heightened geopolitical tensions and instability, but positive momentum in climate finance, health and innovation offers hope. In an era of heightened volatility, leaders will need to embrace “disordered” cooperation and dynamic, solutions-driven decision-making to deliver tangible results and build trust. AI and other emerging technologies are reshaping the global landscape and driving upheaval. Concerted cooperation will be critical to harness benefits and minimize risks. Geneva, Switzerland, January 2025 – The World Economic Forum’s Global Cooperation Barometer offers a critical assessment of the state of global cooperation, showing a world grappling with heightened competition and conflict, while also identifying various areas where leaders can drive progress through innovative collaboration. Released amid geopolitical, technological and sociopolitical upheaval, the Forum’s flagship annual report underscores the urgency of addressing shared challenges and offers leaders guidance on what cooperation can look like in a shifting world. The Global Cooperation Barometer 2025, developed in collaboration with McKinsey & Company, uses 41 indicators to measure the current state of global cooperation. The aim is to offer leaders a tool to better understand the contours of cooperation broadly and along five pillars: trade and capital flows, innovation and technology, climate and natural capital, health and wellness, and peace and security. Now in its second edition, the Barometer draws on new data to provide an updated picture of the global cooperation landscape, with a particular focus on the impact of the new technological age. “The Barometer is being released at a moment of great global instability and at a time when many new governments are developing agendas for the year, and their terms, ahead,” said Børge Brende, President and CEO of the World Economic Forum. “What the Barometer shows is that cooperation is not only essential to address crucial economic, environmental and technological challenges, it is possible within today’s more turbulent context.” “This second edition of the Global Cooperation Barometer focuses on where cooperation stands today and what it can look like in the new technological age,” said Bob Sternfels, Global Managing Partner, McKinsey & Company. “Advancing global innovation, health, prosperity and resilience cannot be done alone. Leaders will need new mechanisms for working together on key priorities, even as they disagree on others, and the past several years have shown this balance is possible.” The latest edition of the Barometer highlights that global cooperation is at a critical juncture. The report’s analysis reveals that after trending positively for a decade and surpassing pre-pandemic levels, overall cooperation has stagnated. This has been driven by a sharp decline of the peace and security pillar of the Barometer over the past seven years, caused by mounting geopolitical tensions and competition which have significantly eroded global collective security. Levels of conflict and attendant humanitarian crises have increased in the past year to record levels, driven by crises including, but not limited to, the Middle East, Ukraine and Sudan. As the largely stable cooperative order that defined the post-Cold War period is giving way to a more fragmented landscape, solutions to pressing challenges – from climate action to technological governance – require collaboration. And despite the global security crises, the new findings indicate that collaboration has continued in various areas including vaccine distribution, scientific research, renewable energy development, and more – offering models for future cooperation. |
 |
| Notably, peace and security have declined sharply in recent years, but other pillars of the Barometer have remained resilient and reveal emerging opportunities for international cooperation, Innovation and technology. While geopolitical competition is rising in regard to certain frontier technologies such as semiconductors, overall global cooperation on technology and innovation advanced in 2023, in part due to digitization of the global economy. This helped drive the adoption of new technologies, a strong ramp-up in the supply of critical minerals – and a related drop in price of lithium batteries – and a rebound in student mobility. However, rapid disruption from emerging technologies such as AI is reshaping the global landscape, raising the possibility of a new frontline of geostrategic competition or even an “AI arms race”. Cooperative leadership and inclusive strategies will be key to harness its vast potential while tackling risks. Climate and natural capital: Cooperation on climate goals improved over the past year, with increased finance flows and higher trade in low-carbon technologies such as solar, wind and electric vehicles. Yet, urgent action is required to meet net-zero targets as global emissions continue to rise. Greater global cooperation will be essential to scale up technologies and secure the financing needed to meet climate goals by 2030. Health and wellness: Some health outcomes, including life expectancy, continued to improve post-pandemic, but overall progress is slowing compared to pre-2020. While cross-border assistance and pharmaceutical R&D have declined, and cooperation on trade in health goods and international regulations stalled, various health metrics including child and maternal mortality remain strong. Given rising health risks and ageing populations, leaders should invest in global cooperation to bolster public health and sustainable health systems. Trade and capital flows: Metrics related to the flow of goods and services, trade, capital and people had mixed outcomes in 2023. Goods trade declined by 5%, driven largely by slower growth in China and other developing economies, while global fragmentation continued to reduce trade between Western and Eastern-aligned blocs. Despite this, global flows of services, capital and people showed resilience. Foreign direct investment surged, particularly in strategic sectors like semiconductors and green energy, while labour migration and remittances rebounded strongly, surpassing pre-pandemic levels.Looking ahead, leaders will need to find ways to work together, even as competition increases, as tangible results will be crucial to maintain public trust and support. The report concludes by underscoring the urgent need for adaptive, solutions-driven leadership to navigate a turbulent global landscape. By pivoting towards cooperative solutions, leaders can rebuild trust, drive meaningful change and unlock new opportunities for shared progress and resilience in the complex years ahead. About the Global Cooperation Barometer Methodology The Global Cooperation Barometer – first launched in 2024 – evaluates global collaboration across five interconnected dimensions: trade and capital, innovation and technology, climate and natural capital, health and wellness, and peace and security. The Barometer is built on 41 indicators, categorized as cooperative action metrics (evidence of tangible cooperation, such as trade volumes, capital flows, or intellectual property exchanges) and outcome metrics (broader measures of progress like reductions in greenhouse gas emissions or improvements in life expectancy). Spanning 2012–2023 and indexed to 2020 to reflect pandemic-era shifts, the Barometer normalizes data for comparability (e.g., financial metrics relative to global GDP and migration metrics to population levels) and weights it equally within and across pillars. About the Annual Meeting 2025 The World Economic Forum Annual Meeting 2025, taking place in Davos-Klosters from 20 to 24 January, convenes global leaders under the theme, Collaboration for the Intelligent Age. The meeting will foster new partnerships and insights to shape a more sustainable, inclusive future in an era of rapidly advancing technology, focusing on five key areas: Reimagining Growth, Industries in the Intelligent Age, Investing in People, Safeguarding the Planet, and Rebuilding Trust. Click here to learn more. |