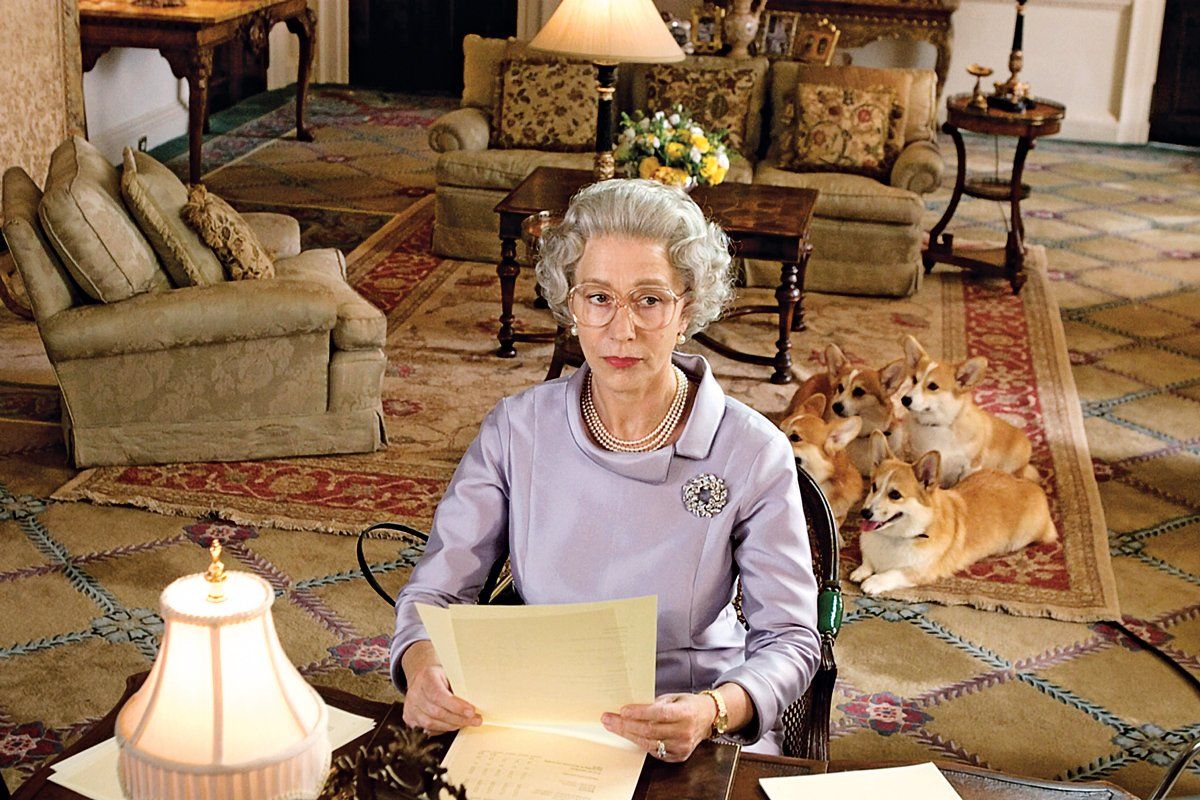
As the world mourns the passing of Queen Elizabeth II, we undoubtedly acknowledge the scope of her public service for over 70 years. She is one of the most recognized and famous people on the face of the earth.
My parents travelled to England when I was young and could (hope to) catch glimpses of the Royal Family, including the Queen, outside Buckingham Palace. My family, one could say, became Royal Watchers. Years later, I’d be hired by former MPP Toby Barrett UE who I quickly learned harbored profound respect for Queen Elizabeth II.
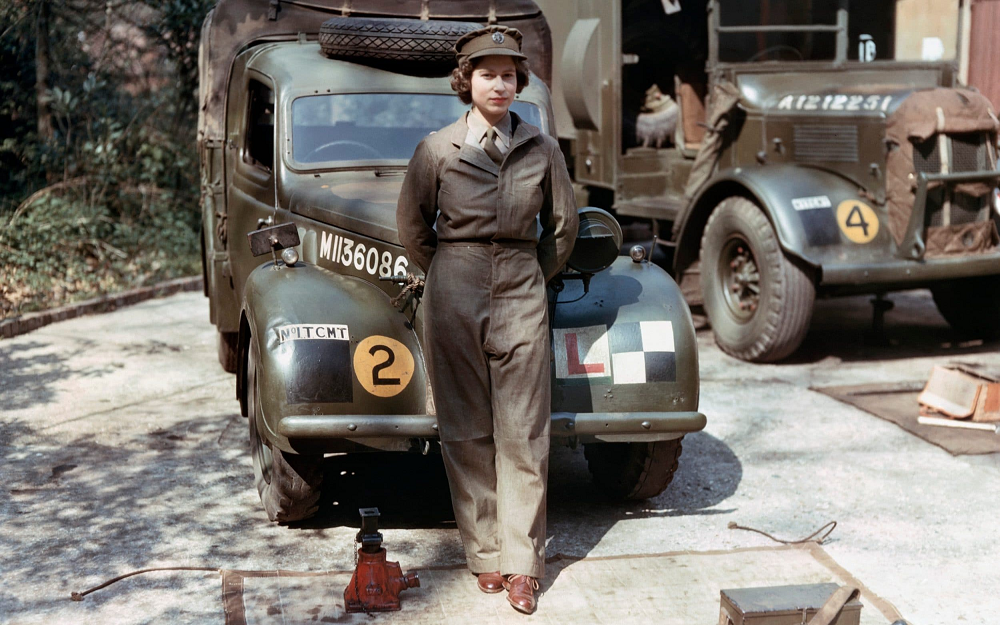
Shortly after officially becoming our longest reigning Monarch, Toby penned a newspaper column that began with: “Queen Elizabeth II is the only British Monarch in history properly trained to change a spark plug!” As Toby said at the time, the statement exemplified the character of our Queen.
Elizabeth learned to change a spark plug at 18 (during the Second World War) after joining the British Army Women’s Auxiliary Territorial Service. She served as an army truck mechanic and as an ambulance and army truck driver.
Elizabeth carried an incredible responsibility throughout her life, beginning at a young age. Upon taking the throne in 1952, she witnessed enormous social change. At 25, Elizabeth became Queen, and was officially crowned at her coronation two years later.
During her reign, Queen Elizabeth visited Canada more than any other country – 22 times. She must have had a special place in her heart for our country and its people, as she was known to refer to Canada as home. From the outpouring of sentiments, the feeling was indeed mutual.
On September 8th, the Queen’s children travelled to Balmoral, near Aberdeen, after physicians placed her under medical supervision. Later in the day Thursday, news spread that the Queen had passed away peacefully in the afternoon. A sad, solemn day.
Queen Elizabeth II officially made Liz Truss Britain’s prime minister two days before her passing. Truss would become the 15th prime minister to meet with the Queen. The meeting was at Balmoral Castle, in the Scottish countryside, where Boris Johnson first arrived to begin the power transfer. The first prime minister the Queen met with during her reign was Winston Churchill – a leader I often quote.
Last Thursday, Prime Minister Truss described Queen Elizabeth II as the rock on which modern Britain was built and continued by saying that she had “provided us with the stability and strength that we needed.” In times of adversity, the Queen has steadied nations with her strength and stoicism – the embodiment of a true leader.
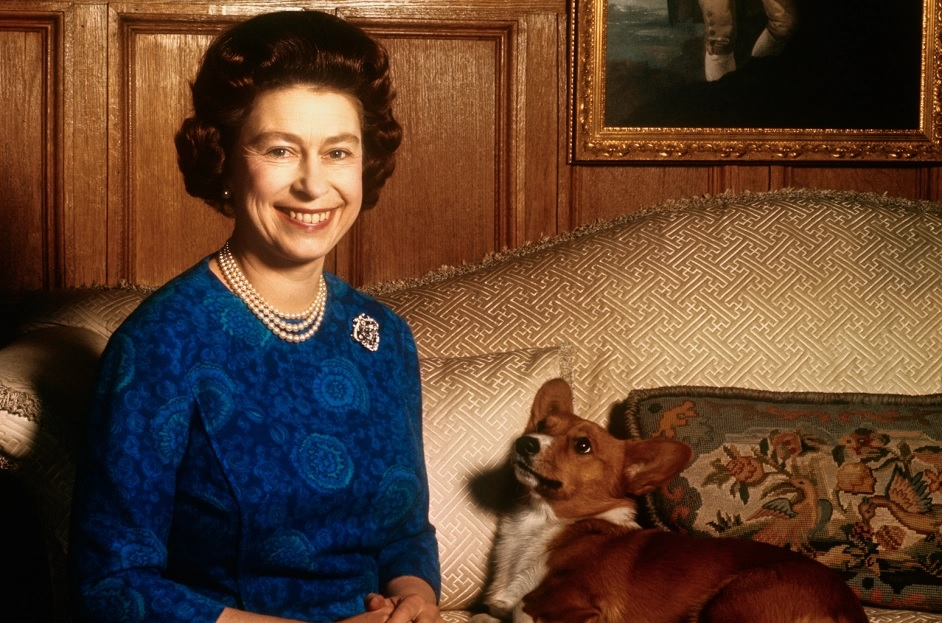

Succession plans have long been in place, and the Queen’s son, Charles III, will become King. As an aside, I met Prince Charles and Camilla a few years back at a function in Toronto. It was a cheeky meeting and one I will never forget.
While we all come to grips with the passing of a lady who impacted our lives in ways, we did not realize, Britain is preparing to usher in a new era in the nation’s fascinating history. Britain, Canada and the Commonwealth will undoubtedly embrace the King and offer him loyalty and devotion, exactly as Her Majesty would have wished.
For the Silo, by Bobbi Ann Brady MPP Haldimand-Norfolk