Raw material: Wool. Operating mode: the hook.
Nice, France textile artist Stéphanie Lobry frantically fashions her art with an unexpected yet satisfyingly fitting leitmotiv: feminism.
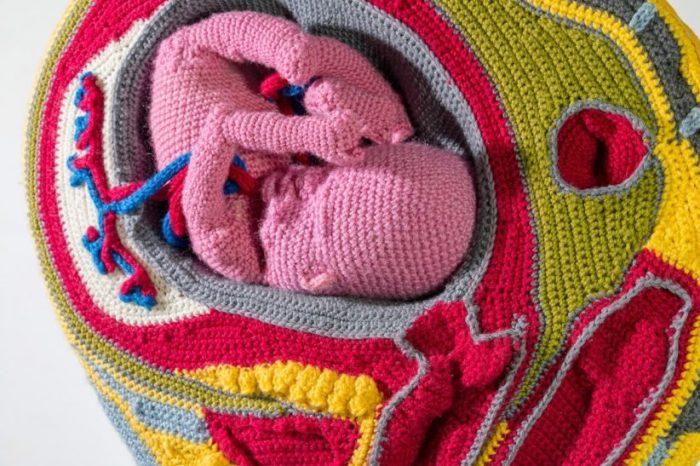
A Teacher when she’s not at the loft, where she created and exhibited her works, Stéphanie Lobry is busy hanging a crochet. Entitled 1.8 cubic meter, “parce c’est la taille qu’il fait”, lies in the piece, in the middle of a crowd of scattered bodies which share this small space with balls of yarn and needles.

If we pay attention to all red wires that surround and hang throughout her living room, we realize that they are, in fact, a gun.
“I wanted to divert the everyday objects. And to do so with needles and wool. No, no to knitting scarves for her daughters in some kind of ‘good housewife’ role, but rather to rediscover the woman inside, and then to discover humans in general.”
 Why crochet? Rolled cigarette in mouth, she passes a nonchalant hand into blond spiky hair. She thinks… “This practice is also ancestral, but has potential for feminist messages and aesthetics when it is diverted from its original use and put towards the service of art. I’ve always been very creative and a little hyper active yet the only compliment I could expect from that was to be commended for being a good mother…”. I got fed up.” Reduced once too often to the status of “the good historical female”, Stéphanie Lobry “lost it”and held her first exhibition.
Why crochet? Rolled cigarette in mouth, she passes a nonchalant hand into blond spiky hair. She thinks… “This practice is also ancestral, but has potential for feminist messages and aesthetics when it is diverted from its original use and put towards the service of art. I’ve always been very creative and a little hyper active yet the only compliment I could expect from that was to be commended for being a good mother…”. I got fed up.” Reduced once too often to the status of “the good historical female”, Stéphanie Lobry “lost it”and held her first exhibition.
Our compulsive crocheter remembers having hesitated….stalled somewhere between a choice of direction. Between science and art: “When I started my studies in molecular biology, my mother asked me if I was sure didn’t want to make fine art instead.” Would an academic focus on science bind her passions? In her artistic process, she discovered that there was in fact a synthesis manifested through the act of the creation, which after all, begins with the cells inside the brain. Fittingly, her art work began with a small croqueted skull which “immediately went to Gallery’. The creative process then dissected and took over other parts of the body.

An Ariane of modern times
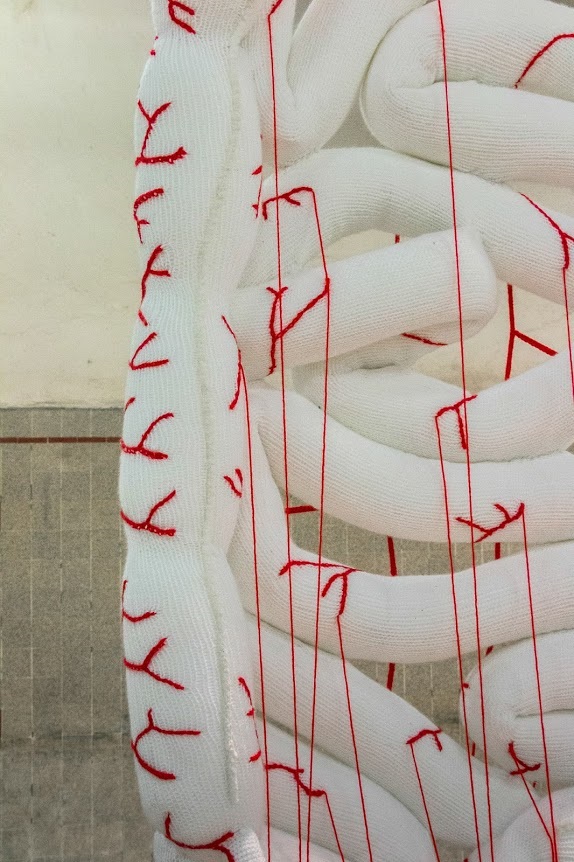
Sweeping my gaze around her workshop, it stops suddenly on the croqueted heart, “it was a participatory project I created shortly after Charlie.” Surely a way to re – unite people, to reconnect, “everyone needed it.” The artist put out a call using social media, letting all participants know that their name would be displayed at the bottom of the finished work. In a few weeks, she received 763 balls of wool, from more than 120 donors, scattered to the four corners of the world, from Paris to Noumea, the Chile, the Belgium and the Greece.
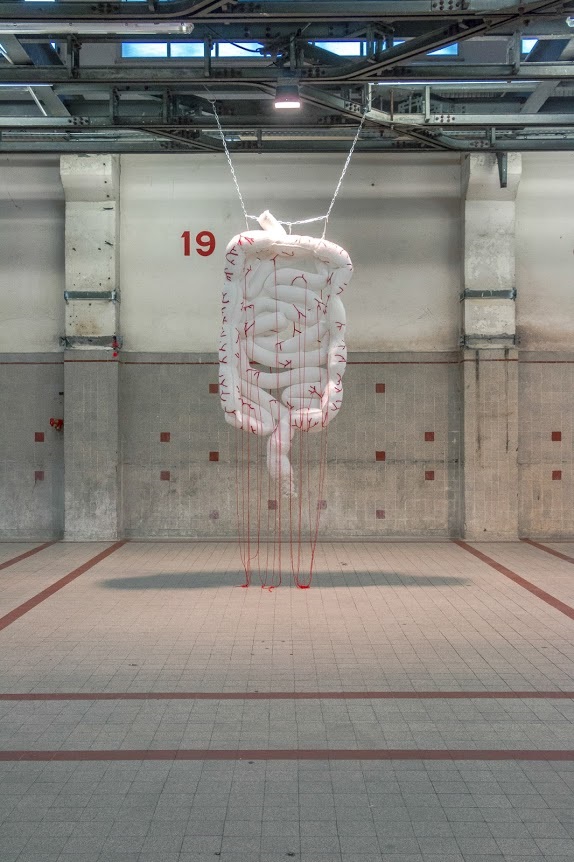

A Runaway success requires a lot of hard work.
It takes almost a month to sort the fabrics and create a ball that weighs more than 40 kg. As for the hook… 45 days are necessary for the realization of a typical piece of finished work: “the ball weighed a ton! I couldn’t do more than five knots without being exhausted.” It is a technique so grueling and time-consuming, but I feel like I’m really at the beginning, I still have a lot to say.” She seems to have found her way alright and is brimming with ideas to express her commitment.
Worried perhaps about her peers who see their emancipation sometimes as endangered, this knitter doesn’t fail to hang onto a hint of conviction to her works. I remember especially this sort of determined representation that she had given at the Théâtre National de Nice, last May, dressed in a full suit. Knitted of course. Delivering metaphors spun into all of her creations. For the Silo, Marine de Rocquigny originally for Art and Facts www.artandfacts.fr
*photos by Florian Lévy
Stéphanie Lobry accroche l’œil au crochet avec son cœur. Ledit, intitulé 1,8 mètre cube, « parce c’est la taille qu’il fait », gît dans la pièce, au milieu d’une foule d’organes éparpillés, partageant ce petit espace avec les pelotes de laine et les aiguilles.
Pourquoi le crochet ? Cigarette roulée au bec, elle passe une main nonchalante dans ses blonds cheveux en bataille. Elle songe… « Cette pratique aussi ancestrale soit-elle, prend des allures féministes quand elle est détournée de son utilisation pour se mettre au service de l’art. » Car c’est bien avec une volonté libératrice et féministe qu’elle s’est lancée il y a maintenant sept ans : « J’ai toujours été très créative et un peu hyper active pourtant le seul compliment que je pouvais espérer c’était d’être une bonne mère de famille… J’en ai eu marre. » Réduite une fois de trop au statut de BMF, Stéphanie Lobry « pète les plombs » et organise une première exposition.
Alors que les curieux s’aventurent dans ses appartements, elle les reçoit en nuisette, repassant chemise après chemise, la main collée à son fer. Et si l’on prête attention à l’ensemble de fils rouges qui l’entourent et parcourent son salon, on s’aperçoit qu’ils forment, en fait, un pistolet. « J’ai voulu détourner les objets du quotidien. » Elle se munie dès lors d’aiguilles et de laines. Non, pas pour tricoter des écharpes à ses filles en bonne femme d’intérieur, mais plutôt pour redécouvrir l’intérieur de la femme, puis de l’humain en général.
Rencontre logique. La crocheteuse compulsive se souvient avoir longtemps hésité entre la science et l’art : « Quand j’ai commencé mes études en biologie moléculaire, ma mère m’a demandé si j’étais sûre de ne pas vouloir plutôt faire les Beaux-Arts. » Alors autant entreprendre une reconversion qui pourrait lier ses passions et ses connaissances. Dans sa démarche artistique, elle revient donc à la genèse de la création, qui commence avec des cellules. Elle commence avec un petit crâne « tout de suite parti en galerie », puis dissèque et reprend toutes les parties du corps. Du neurone au pied. Du sexe aux poumons.

Une Ariane des temps modernes
En balayant du regard son atelier, elle s’arrête sur le cœur, « c’était un projet participatif que j’ai crée peu après Charlie. » Surement une façon de re-fédérer les gens, de renouer les liens, « tout le monde en avait besoin. » L’artiste lance alors un appel sur les réseaux sociaux, tous les participants verront leur nom affiché au bas de l’oeuvre. En quelques semaines, elle reçoit 763 pelotes de laines, provenant de plus de 120 donneurs, dispersés au quatre coins du monde, de Paris à Nouméa, en passant par le Chili, la Belgique ou la Grèce. Succès fulgurant. Travail titanesque en perspective. Il lui faut près d’un mois pour trier les tissus et constituer une pelote de plus de 40 kilos. Quant au crochet… 45 jours nécessaires à la réalisation de l’organe démesuré. « Les aiguilles étaient énormes et la pelote pesait une tonne ! Je ne pouvais pas faire plus de cinq nœuds sans être épuisée.
Une technique épuisante donc et laborieuse que la « quinqua » ne compte pas abandonner de si tôt: « J’ai l’impression que je ne suis vraiment qu’au tout début, j’ai encore beaucoup de choses à dire. » Sorte d’Ariane des temps modernes. Elle semble avoir trouvé sa voie grâce au fil et regorge d’idées pour exprimer son engagement. Inquiète au sujet de ses consœurs qui voient leur émancipation parfois en péril, cette tricoteuse ne manque pas d’accrocher un soupçon de conviction à ses œuvres. On se souvient notamment de cette représentation qu’elle avait donnée au Théâtre National de Nice, en mai dernier, enfermée dans une combinaison intégrale tricotée comme dans sa condition féminine, attendant qu’on tire sur les fils pendants pour la délivrer. Une cause qui lui tient à cœur, une métaphore filée sur l’ensemble de ses créations.
Marine de Rocquigny pour Art and Facts www.artandfacts.fr