— Kino Piispanristi integrates Genelec’s famous “The Ones” loudspeaker range along with the latest Dolby Surround technology to deliver premium audio quality — the best to be found (and heard) in Finland.

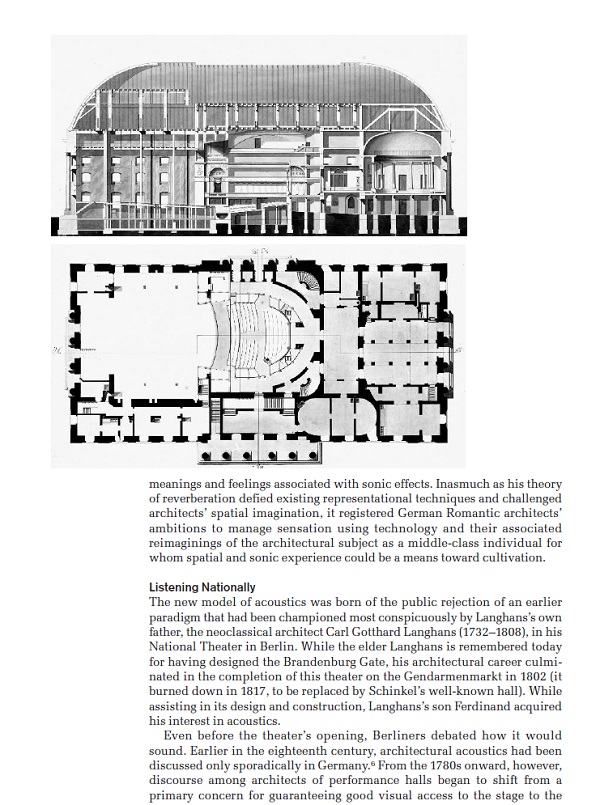
NATICK, MA, August, 2024 —Kino Piispanristi is a full-service 286-seat independent movie theater close to Turku, Finland. The venue is a long-time passion project of Henry Erkkilä, a movie lover who wanted to create a modern cinema that transcends tradition when it comes to audio-visual technology. Kino Piispanristi cinema strives to continually deliver a superior experience, so its luxury new premium screen features a Genelec sound system comprising the brand’s unmatched smart active studio loudspeakers and subwoofers.
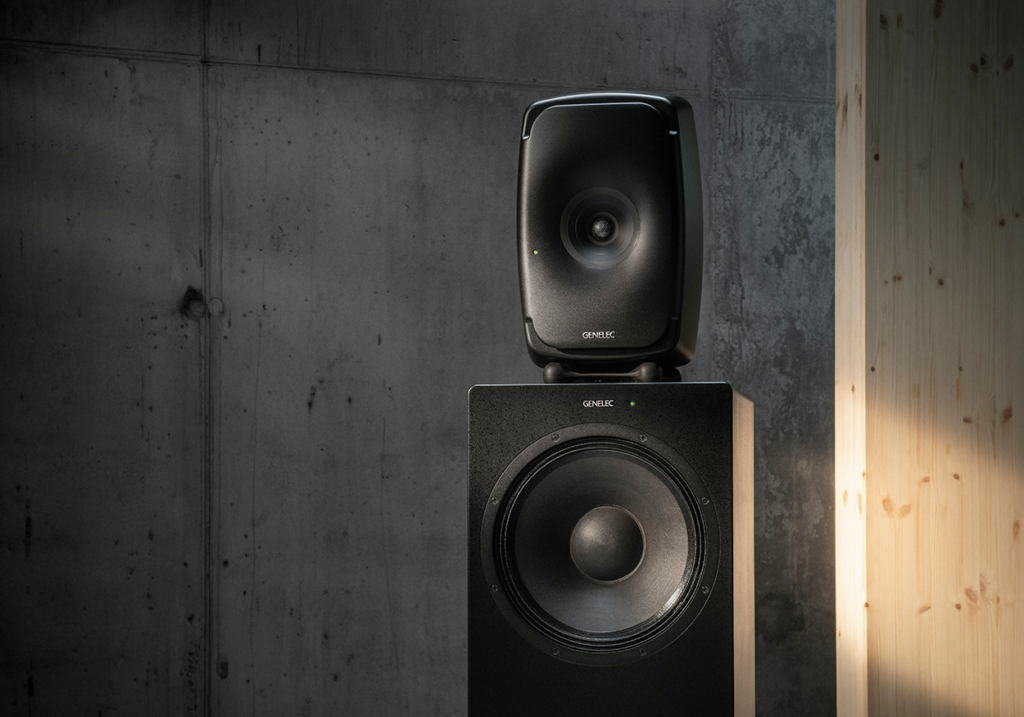

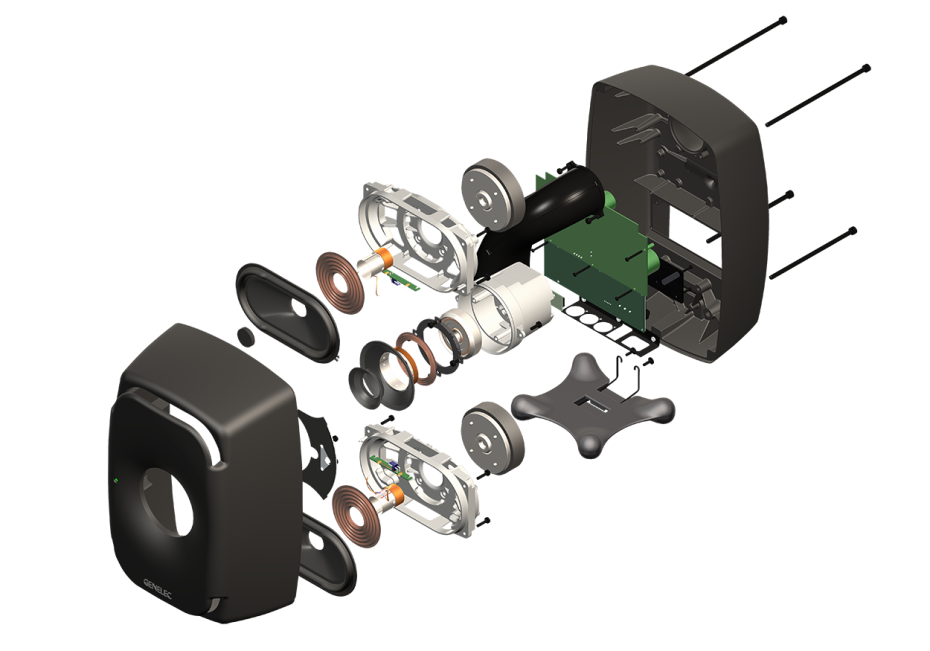
Genelec “The Ones”
Erkkilä discovered his love for the film industry as a young boy. His father had a film projector that he travelled around Sweden with, bringing the latest screen favorites to audiences in his home country. Prior to the screening, Erkkilä would be tasked with dropping off advertisements in the local area, showcasing the movie on offer that evening and encouraging people to attend.
Inspired by his father, he set up his very own touring movie theater concept in 1998, but it wasn’t until 2017 that Erkkilä finally opened his first permanent space. Kino Piispanristi began with two theaters, but now the cinema boasts five screens, as well as additional venues in Turku, Salo and Laitila.
“We strive to offer all the perks of a modern cinema without being a faceless corporation,” begins Erkkilä.
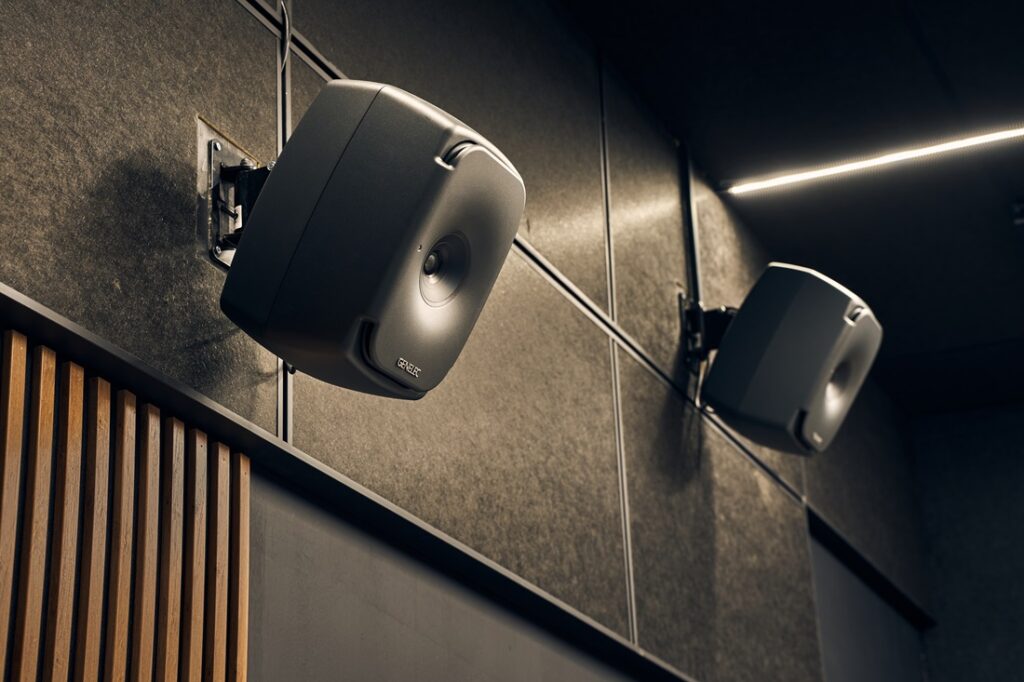

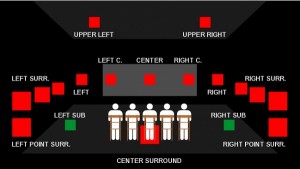
A look at some of the Genelec’s installed in Kino Premium.
“We react to trends quickly and make moves boldly so that our customers can walk in and out feeling happy. Having the greatest theater sound system in Finland is an excellent way to help us light up people’s faces!”
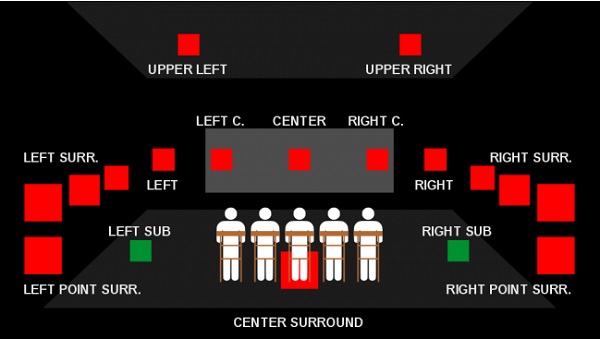
Kino Piispanristi’s newest screen is a premium, more intimate space with exceptional picture quality and a 7.1 audio system based around Genelec’s “The Ones” family of coaxial three-way studio loudspeakers – which deliver extended frequency response, controlled directivity and fatigue-free listening. Three 8361s – the flagship of The Ones range – are deployed for LCR, with six of the more compact 8341s in the surround positions, complemented by two 7380 subwoofers for clean, controlled LF performance.
“For our premium space theater, sound is everything.”
“Theater technology, be it projectors, screens, audio or seats, is constantly evolving and unless you’re among the frontrunners, you might get left behind,” Erkkilä explains. “Genelec is widely known and admired as a wonderful example of Finnish engineering and design. As a local business, we try to emphasize the importance of using locally sourced products, and Genelec’s quality is unmatched. This was a pilot project for us and we’re looking into expanding our other spaces – since it’s been such a hit. We charge a few Euros extra for the premium screen, but the movie experience is so good that our customers still see it as excellent value.”
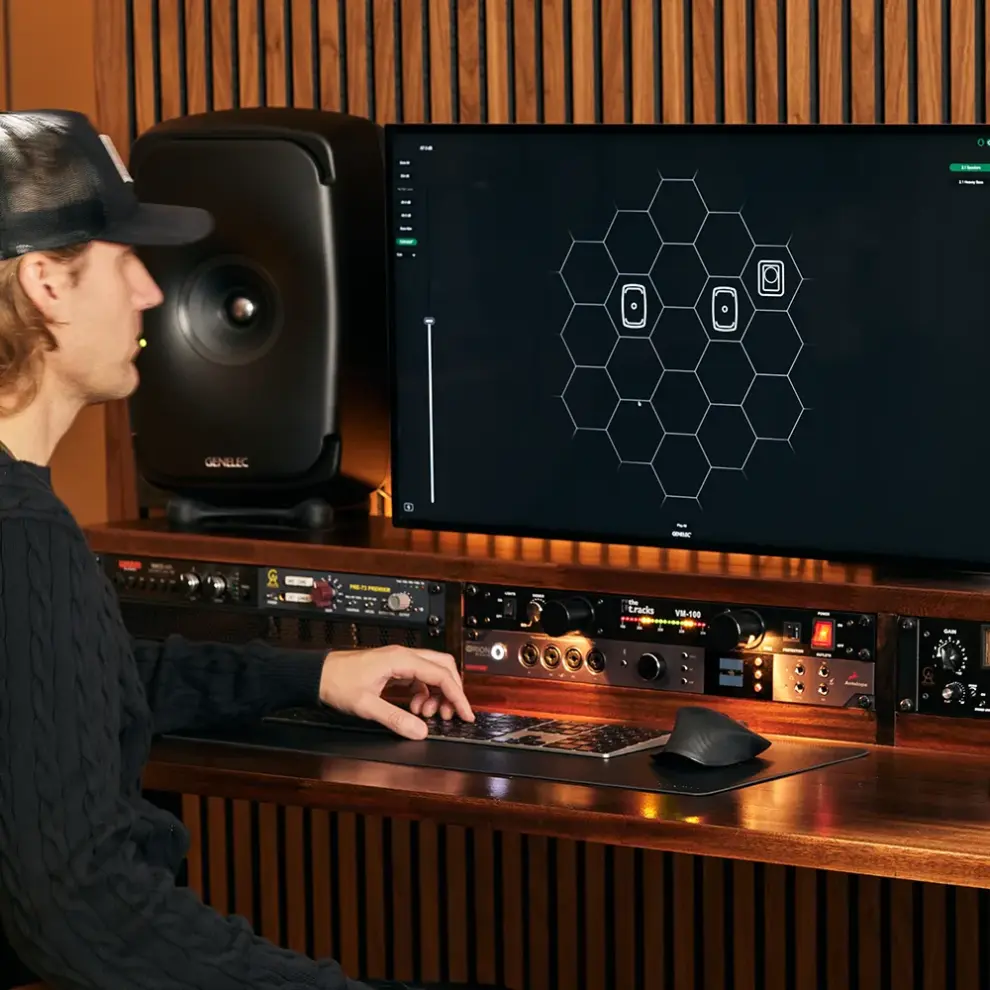

GLM Space calibration software at work.
Usually found powering the world’s most notable music, broadcast and film studios, Genelec’s studio loudspeakers are now being specified for an increasing number of high-end residential and boutique commercial cinemas around the world – thereby allowing customers to experience the same kind of sonic detail and clarity as the movie creators themselves.
The Ones models provide optimized performance by intelligently adapting to the acoustics of the room, achieved by a combination of GLM space calibration software and internal DSP within each loudspeaker and subwoofer. “GLM calibration allowed us to achieve a better balance with the lower and higher voices on screen,” explains Erkkilä. “Without it, it’s likely that the room would’ve changed the natural feel of the audio. It gave us full control over the system.”
PDF brochure on how Genelec used this cinema for a product case study.
GLM offers precise calibration of each loudspeaker’s in-room frequency response, playback level and distance delay, minimizing unwanted room influences and ensuring the best possible audio quality. In addition to the Genelec system, Kino Piispanristi uses Dolby Cinema processors which bring a natural feel to film soundscapes – immersing the audience in the true excitement of cinema.
“Our expertise in cinema and Genelec’s legacy in sound was the perfect match, and the collaboration was even more meaningful because of the local connection,” concludes Erkkilä. “The Ones loudspeaker series has completely transformed the cinema, and now we can offer audiences everything that the big players can – and more. The cinema is a result of a lot of hard work and dedication, and the Genelec system feels like the icing on the cake. It’s reinvented what we show on the screen.”





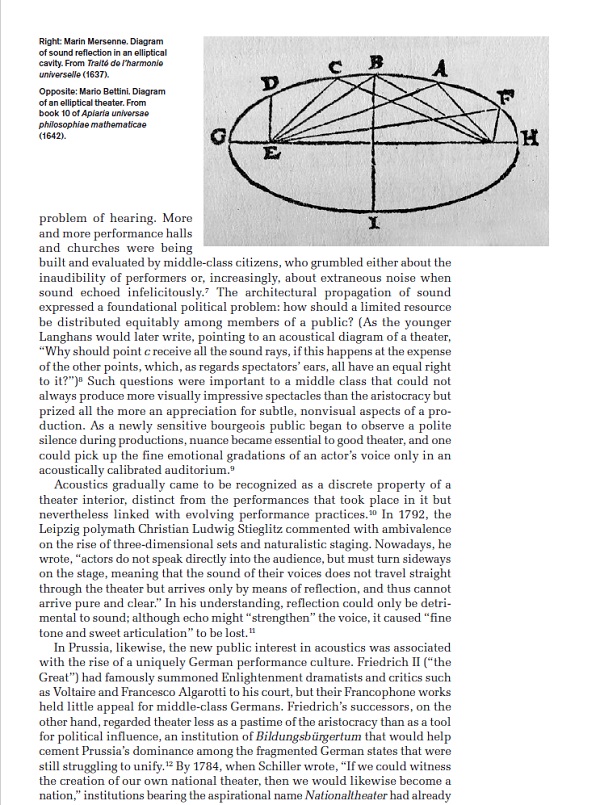
 This allowed for extras such as director’s commentary tracks and other features to be added onto a film, creating “Special Edition” releases that would not have been possible with VHS. Disc access was random and chapter based, like the DVD format, meaning that one could jump to any point on a given disc very quickly. By comparison, VHS would require tedious rewinding and fast-forwarding to get to specific points.
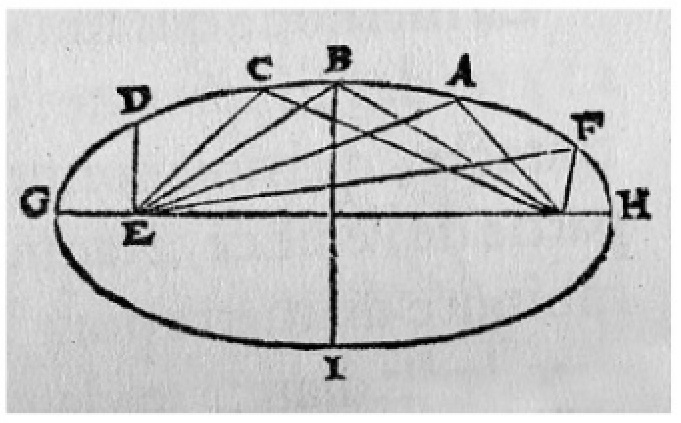
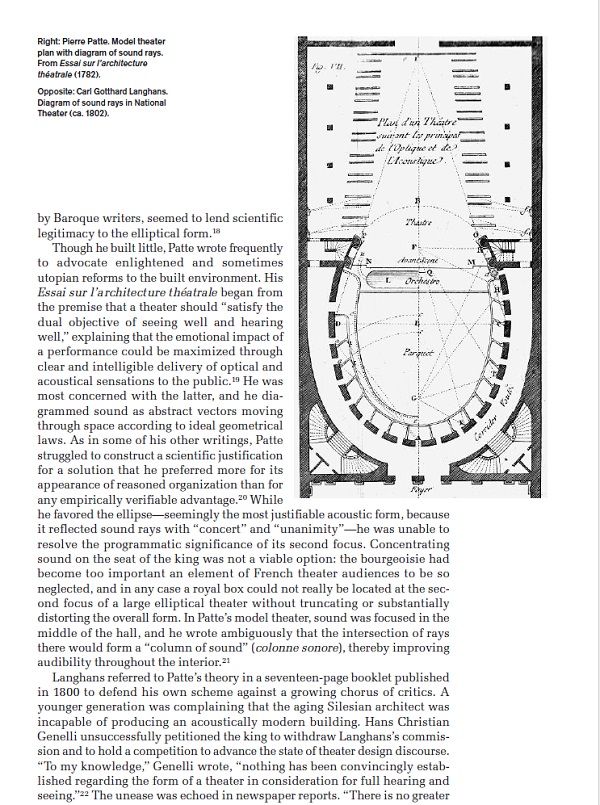
This allowed for extras such as director’s commentary tracks and other features to be added onto a film, creating “Special Edition” releases that would not have been possible with VHS. Disc access was random and chapter based, like the DVD format, meaning that one could jump to any point on a given disc very quickly. By comparison, VHS would require tedious rewinding and fast-forwarding to get to specific points.

 Another important innovation for Laserdisc was the fact that it was the very first home video format to offer Dolby Digital Surround Sound- often referred to as AC-3 on Laserdisc jackets and hardware. Many fans of Laserdisc are still enjoying this feature because some movies such as the Alien AC-3 LD were released with their original cinema surround mix on the AC-3 Laserdisc and those mixes are unavailable on today’s modern formats such as Blu-ray or UHD Blu-ray. Many early LD players can even be modified to turn them into AC-3 LD players.
Another important innovation for Laserdisc was the fact that it was the very first home video format to offer Dolby Digital Surround Sound- often referred to as AC-3 on Laserdisc jackets and hardware. Many fans of Laserdisc are still enjoying this feature because some movies such as the Alien AC-3 LD were released with their original cinema surround mix on the AC-3 Laserdisc and those mixes are unavailable on today’s modern formats such as Blu-ray or UHD Blu-ray. Many early LD players can even be modified to turn them into AC-3 LD players.