Minister Says He Was Taken Aback After Learning Deadly Viruses Were Shipped From Winnipeg Lab to Wuhan
Report first published via friends at The Epoch Times
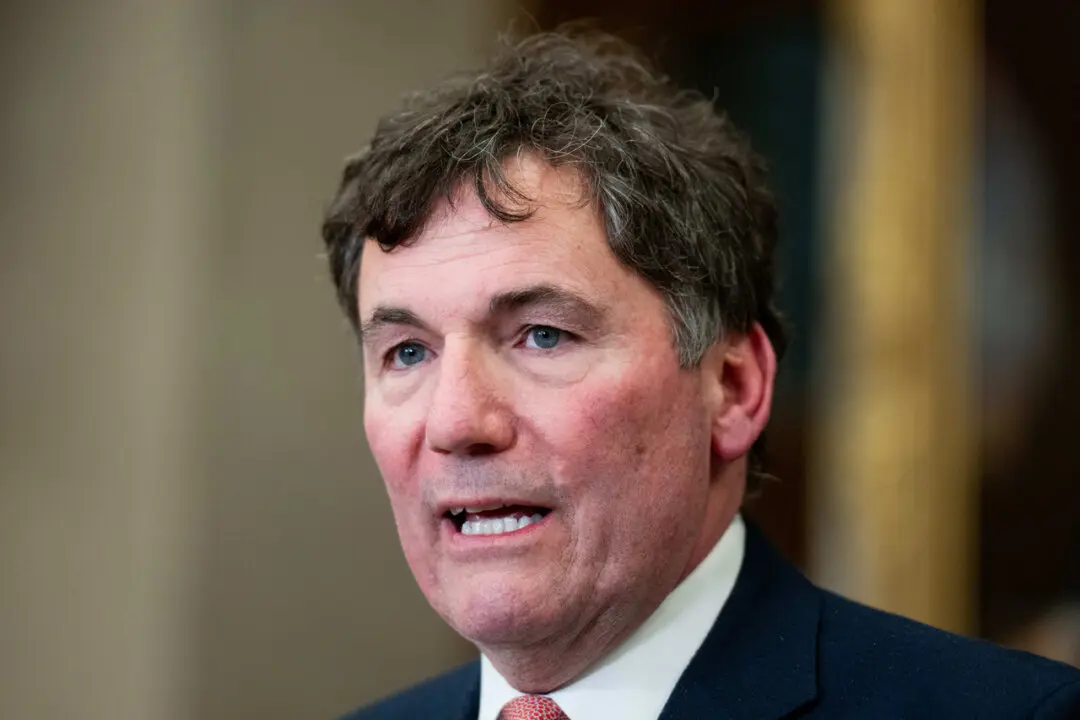

After learning that samples of deadly Ebola and Nipah viruses had been sent from Canada’s top-security lab in Winnipeg to China, Public Safety Minister Dominic LeBlanc said his reaction was similar to that of an MP who expressed incredulity upon learning of the move.
“I’m really concerned about the March 2019 incident where [Winnipeg lab scientists Xiangguo Qiu and Keding Cheng] were implicated in a shipment of live Ebola in Hanipah [Nipah] viruses on a commercial Air Canada flight. How the hell did that happen?” NDP MP Charlie Angus asked during a House of Commons Canada-China committee meeting on April 15.
In response, Mr. LeBlanc said, “When I saw that report, and publicly, I had the same reaction as you.”

A partly redacted national memo sent by the prime minister’s national security advisor to Prime Minister Justin Trudeau on June 29, 2017.
The minister deferred Mr. Angus’ question to the Public Health Agency of Canada, saying, “I don’t have any [information], but I had the same reaction as you, Mr. Angus.”
Mr. LeBlanc, who became minister of public safety in July 2023, was previously minister of intergovernmental affairs starting in July 2018.
The National Microbiology Laboratory (NML) in Winnipeg shipped 15 different strains of Nipah and Ebola viruses to the Wuhan Institute of Virology (WIV) in China on March 31, 2019. The package was sent from Winnipeg to Toronto and then on to Beijing via a commercial Air Canada flight.

Ms. Qiu and Mr. Cheng
The request to the NML management for the shipment of the viruses was facilitated by Ms. Qiu. The shipment was eventually approved by the NML management.
Ms. Qiu and Mr. Cheng, a married couple, were escorted out of the NML in July 2019 while under RCMP investigation. The couple were fired from their positions on Jan. 20, 2021, for having undisclosed ties to Chinese regime entities.
In 2021, in response to MPs’ questions about why the NML shipped virus samples to the Wuhan lab, laboratory management said the shipment followed all proper protocols and was in response to a letter from the Chinese lab indicating that they were to be used to understand their pathophysiology—the nature of infection—and the development of antivirals.

Declassified intelligence documents show that Ms. Qiu also sent antibodies and other materials to China without prior approval.
Shipments included antibodies for the China National Institute for Food and Drug Control, as well as small amounts sent to laboratories in the United Kingdom and the United States for testing.
The documents show that Ms. Qiu discussed the shipment of Ebola and Nipah with WIV employees in July 2018, and initially suggested that a formal agreement is not necessary as “no one owns the IP.” She also expressed “hope there is another way around” rather than issuing a formal agreement.
The documents also show that Ms. Qiu signed on to a project at WIV involving research on Ebola, and that some of the virus strains that were shipped from NML were meant for this project. Ms. Qiu had asked that the project remain a secret to her Canadian management as WIV was in the process of requesting the transfer of the virus strains from NML, the documents say.
Researchers work in the National Microbiology Laboratory in Winnipeg, Man., where the ZMapp antibody “cocktail” was created to fight Ebola. PHOTO BY HANDOUT
The Wuhan lab has been involved in synthetic biology research on the deadly Nipah virus, according to testimony from a U.S. scientist. Synthetic biology involves creating or redesigning biological entities and systems.
“The Nipah virus is a smaller virus than SARS2 [the virus causing COVID-19] and is much less transmissible,” Dr. Steven Quay, a Seattle-based physician-scientist, told a U.S. Senate subcommittee hearing on Aug. 3, 2022. “But it is one of the deadliest viruses, with a greater than 60 percent lethality” and 60 times deadlier than SARS2, he said. “This is the most dangerous research I have ever encountered.”
Chinese Talent Recruitment
During the April 15 House committee meeting, Mr. LeBlanc acknowledged revelations from the declassified documents that Ms. Qiu was involved in China’s Thousand Talents Program. The program was recognized by U.S. authorities as China’s efforts to “incentivize its members to steal foreign technologies needed to advance China’s national, military, and economic goals.”
It is clear that “elements from a Chinese-sponsored recruitment program were involved” at the Winnipeg lab, Mr. LeBlanc said. “It is well known that such programs are one way that China seeks to incentivize academics to participate in activities that exploit advancements in Canadian technologies.”
China is using the programs “to improve its military and intelligence capabilities, as well as the economic competitiveness all at the expense of Canada’s national interest,” the minister said.
He declined to address concerns raised by Conservative MP Michael Cooper regarding the delay in removing Ms. Qiu from the NML, saying it should be addressed to the health minister whose department is in charge of the Public Health Agency of Canada, which in turn oversees the NML.
Although concerns about the two were first raised in 2018, they weren’t fired until three years later. For The Silo, Andrew Chen. Omid Ghoreishi and Noé Chartier contributed to this report
Supplemental– Bio-warfare experts question why Canada was sending lethal viruses to China.
Supplemental- Canada sent untested ebola vaccine to World Health Organization.










 Historical records reveal that missing persons have occurred in North America for hundreds of years and what connects these cases is both frightening and confusing. David has discovered geographical connections that include- national park locations, urban locations near bodies of water, boulder fields, mountain elevations and other seemingly ‘safe’ locations.
Historical records reveal that missing persons have occurred in North America for hundreds of years and what connects these cases is both frightening and confusing. David has discovered geographical connections that include- national park locations, urban locations near bodies of water, boulder fields, mountain elevations and other seemingly ‘safe’ locations. David’s research has shown that oddly, many missing persons in these cases are highly intelligent and healthy individuals that include doctors, scientists and marathon runners. In other cases the victims are hunters or seasoned hikers- people who would actually be most likely to prevent outdoor mishaps.
David’s research has shown that oddly, many missing persons in these cases are highly intelligent and healthy individuals that include doctors, scientists and marathon runners. In other cases the victims are hunters or seasoned hikers- people who would actually be most likely to prevent outdoor mishaps.





 Trade networks, however, were not durable. The contributors discuss the establishment and decline of great trading network systems, and how they related to the expansion of civilization, and to different forms of social and economic exploitation. Case studies focus on local conditions as well as global networks until sixteenth century when the whole globe was finally connected by trade.
Trade networks, however, were not durable. The contributors discuss the establishment and decline of great trading network systems, and how they related to the expansion of civilization, and to different forms of social and economic exploitation. Case studies focus on local conditions as well as global networks until sixteenth century when the whole globe was finally connected by trade.