Every so often, I engage in a particularly futile and depressing ritual—I shop for cars that I’ve foolishly let go. They’re cars that could have been feasible 10 years ago, but not today. I’ve been priced out of the market for virtually all of them. And while the market might be settling down at the moment, there are few signs of an out-and-out retreat to pre-pandemic pricing. Among cars from the 1970s through the early 1990s, there are precious few bargains. But go a little bit newer, where there’s even some depreciation yet to be done, and the picture gets more enticing. I’m talking cars from the 2000s to 2010s that are getting older, but still aren’t considered any kind of “classic” or “collectible” yet. Here are some highlights.
Fiat 500 Abarth

The 500 Abarth is the closest thing to a real hot hatch that Fiat has ever offered in the U.S., a market that is sadly short on real hot hatches. There were more interesting varieties of the Punto and Ritmo, but those were Euro-only cars that frankly weren’t very good compared to competition from Renault, Peugeot, VW, and Ford. As for the 500 Abarth, although it first arrived here in the early 2010s, the 160-hp pocket rocket feels more like a 1990s hot hatch. It’s crude, the ride is choppy, and a 10 year-old Fiat probably wears more like a 20 year-old VW. But it’s loud, analog-feeling, and fun. Most importantly, it’s cheap. Around $8000usd to $10,000usd/ $11,000cad to $13,700cad buys one with under 50,000 miles/ 80,467kms. That’s tons of fun per us or canadian dollar in a package that offers an old school driving experience in something that’s new enough to have most contemporary features and conveniences.
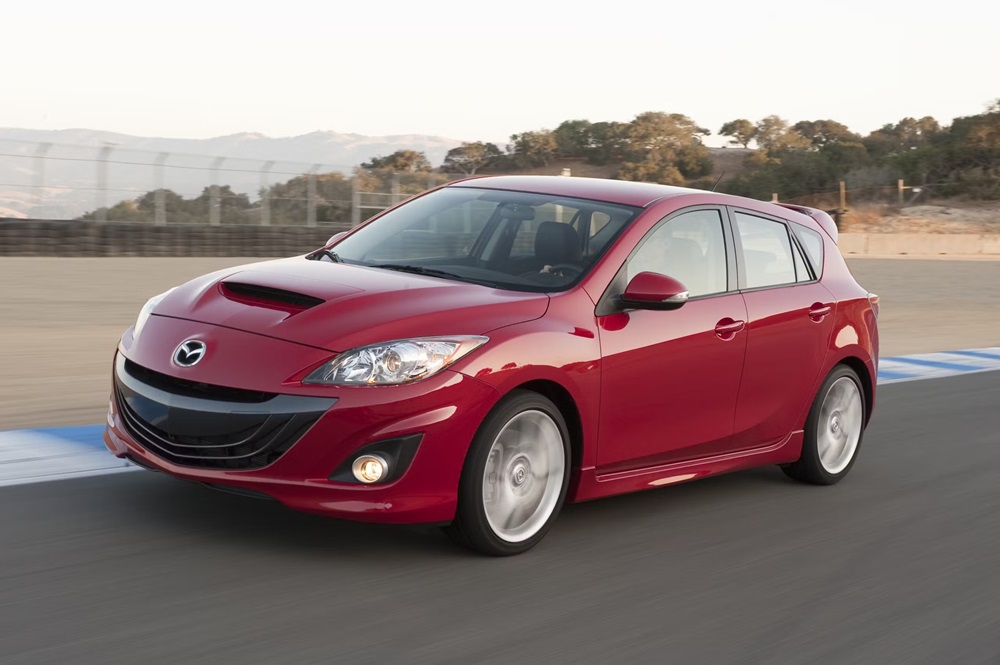
MazdaSpeed3

Back in the days of the Zoom Zoom tagline, Mazda fielded the incredibly entertaining MazdaSpeed3. Offered from 2007-13, it’s a four-door hatch with 263 hp and 280 lb. ft. of torque. It’s exactly the kind of car enthusiasts and auto journalists beg manufacturers for, but rarely head to a dealership and actually buy. Everyone who tested a Speed3 back in the day found the car fun, especially those of us who were entertained by the torque-steer. Car and Driver wasn’t, comparing driving the car to a game of tug-of-war. But, affordability and perfection don’t often go hand-in-hand, so for $10,000usd to $12,000usd/ $13,700cad tp $16,400cad at current prices you could do far worse than the powerful and practical Speed3.
C5 Corvette
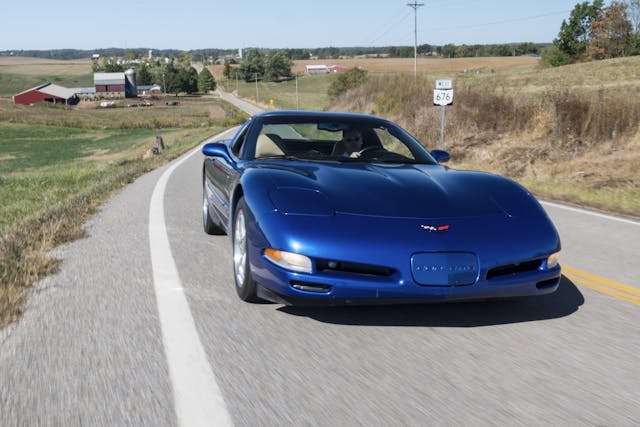

If hot hatches aren’t your jam, there’s always the bargain Corvette of the moment, the 1997-2004 C5. While some variants, most notably the Z06, sailed beyond true affordability in the last several years, a base manual C5 with somewhere between 75,000 and 100,000 miles/ 120,000km and 160,934km can still be had in the $13,000usd to $15,000usd range/ $17,760cad – $20,490cad. That’s a huge bargain for what was an utterly clean sheet design, one of the few in Corvette history, and more performance than almost anything in this price point. Interiors are standard 2000s GM, but livable. And the styling, over a quarter-century after it was introduced, is aging quite nicely.
2003-08 BMW Z4
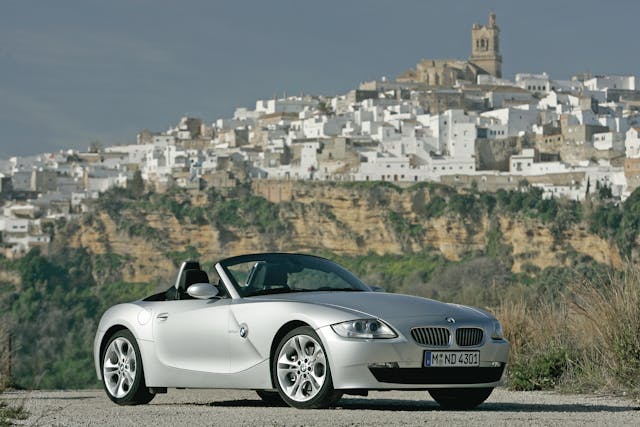

The 2003-08 Z4 is a bit like the C5 Corvette in that it wasn’t universally loved when new, but is aging well. Available in 2.5- and 3.0-liter six-cylinder forms, the Z4 was larger and more practical than its predecessor, the Z3. Its odd surface detailing and Kamm-tail also look better now than they did 20 years ago. The Z4’s list of maladies is well-known at this point—the VANOS variable valve-timing system can give trouble (it’s often the solenoids), as can the cooling system. These are pricy repairs, but with nice cars available in the $9000usd to $12,000usd/ $12,300cad to $16,400cad range, if you budget $2000usd-$3000usd/ $2,730cad-$4,100cad to sort things out, these can still be a compelling deal in semi-modern convertible German sports car.

2012 Mercedes-Benz SLS AMG CoupePalm Coast, Florida
2005-2014 Ford Mustang

You could argue that the 2005 Mustang was the first one to really look like a Mustang since maybe 1973. The brilliant Sid Ramnarace-designed S197 Mustang managed to look the part without being foolishly retro, a hard balance to achieve. Special editions, and certainly the Shelby versions of the S197 are not cheap, but a lightly optioned V-8 coupe or convertible is still one of the best cheap V-8 pony cars out there. Being a Mustang, there are always plenty on the market to choose from at any given time, and a decent manual transmission car can be had in the $12,000usd to $14,000usd/ $16,300cad to $19,130cad range. For the Silo, Rob Sass/Hagerty.
Featured image: Mazda/Guy Spangenberg