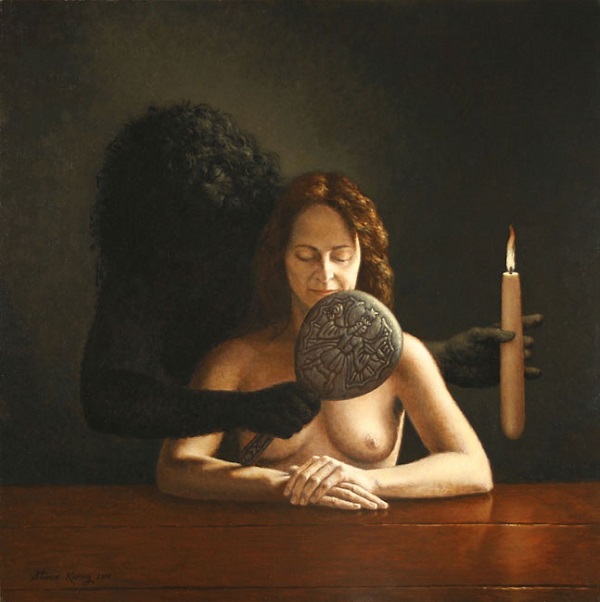
[You may know him from the movies “What The Bleep Do We Know” and “Down The Rabbit Hole” – Two great introductory documentaries on Quantum Physics you really owe it to yourself to see. Let the Silo introduce you to a welcomed, new contributor- Dr. Amit Goswami – Author, Speaker and Scientist. Ed.]
“I am very excited about one of my recent books- Quantum Creativity. The main message of this book is this: If you are interested in creativity and in thinking quantum, you have the basics of what it takes to be creative, in fact, to be extraordinary in your creativity.
Quantum physics is the physics of possibilities. Quantum physics says reality is both possibility and actuality.
The objects of the universe are possibilities, quantum possibilities; they become objects of actuality in our experience when we observe because we have chosen actuality from the possibilities proffered. This two-level complementary reality is an important aspect of our consciousness. The unmanifest, (psychologists call it the unconscious, spiritual traditions call it the transcendent) is the realm where consciousness processes possibilities (unconscious processing) but without awareness, without subject-object separation.
The manifest (psychologists call it the conscious, spiritual traditions call it the immanent) is the domain of actualities that consciousness processes with awareness, with subject-object split.
Quantum thinking consists of this two-level processing—both unconscious and conscious. Quantum thinking understood in this way liberates you, anyone, from any assumed ordinariness. With its help, anyone can be creative.
Creativity was difficult for people of the olden days because they had to pursue it blindly, they did not know how human creativity works; they assumed it is all mystery, all arts. And today, lots of people shortchange their creativity because of their faulty mechanistic worldview.
The truth is, we cannot discuss the relevant issues of human creativity without a lot of make-belief within our current mechanistic worldview based on the metaphysics of scientific materialism—everything is matter moving in space-time and material interaction.
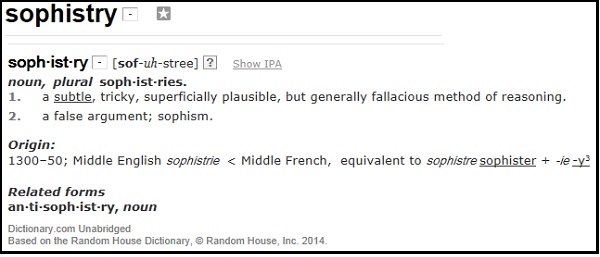
The science of creativity that the protagonists of a mechanistic worldview talk about, and which today you read about in the media, is about machine creativity. To a large extent it is sophistry, about how determined machines can somehow appear to be creative.
It is self-evident that human creativity requires consciousness as a causal entity with free will, freedom to choose.
It is self-evident that human creativity requires the capacity to process meaning, that human creativity involves affects (agony and ecstasy), and that human creativity begins with intuition.
Dealing with human creativity requires a worldview in which consciousness is causally potent, in which not only our physical experiences but also our experiences of thinking, feeling and intuition are validated. Quantum physics, properly interpreted, gives us that worldview. Engaging the two level complementary reality of quantum physics gives human creativity all its wonderful and mysterious attributes that material machines moving in a one-level space-time reality cannot possibly simulate.” For the Silo, Dr. Amit Goswami.