If you have them should you keep them? Read on via this interesting article from our friends at Hagerty.
The nuts and bolts that make up our beloved automobiles have not changed that much over the last 150 years. But the tools needed to maintain them? Those have changed a lot. Software has cemented itself as part of a service technician’s day-to-day regimen, relegating a handful of tools to the history books. (Or, perhaps, to niche shops or private garages that keep many aging cars alive and on the road.)
How many of these now-obsolete tools do you have in your garage? More to the point, which are you still regularly using?
Spark-plug gap tool
Though spark-plug gap tools can still be found in the “impulse buy” section of your favorite parts store, these have been all but eliminated from regular use by the growing popularity of iridium and platinum plugs. These rare-earth metals are extremely resistant to degradation but, when it comes time to set the proper gap between the ground strap and electrode, they are very delicate. That’s why the factory sets the gap when the plug is produced.
These modern plugs often work well in older engines, meaning that gapping plugs is left for luddites—those who like doing things the old way just because. Nothing wrong with that; but don’t be surprised if dedicated plug-gapping tools fade from common usage fairly quickly.
Verdict: Keep. Takes up no real space.
Dwell meter

50 years ago, a tuneup of an engine centered on the ignition system. The breaker points are critical to a properly functioning ignition system, and timing how long those points are closed (the “dwell”) determines how much charge is built up in the ignition coil and thus discharged through the spark plug. Poorly timed ignition discharge is wasted energy, but points-based ignition systems disappeared from factory floors decades ago, and drop-in electronic ignition setups have never been more reliable (or polarizing—but we’ll leave that verdict up to you.)
Setting the point gap properly is usually enough to keep an engine running well, and modern multifunction timing lights can include a dwell meter for those who really need it. A dedicated dwell meter is an outdated tool for a modern mechanic, and thus most of the vintage ones are left to estate sales and online auction sites.
Verdict: Toss once it stops working. Modern versions are affordable and multifunctional.
Distributor wrench
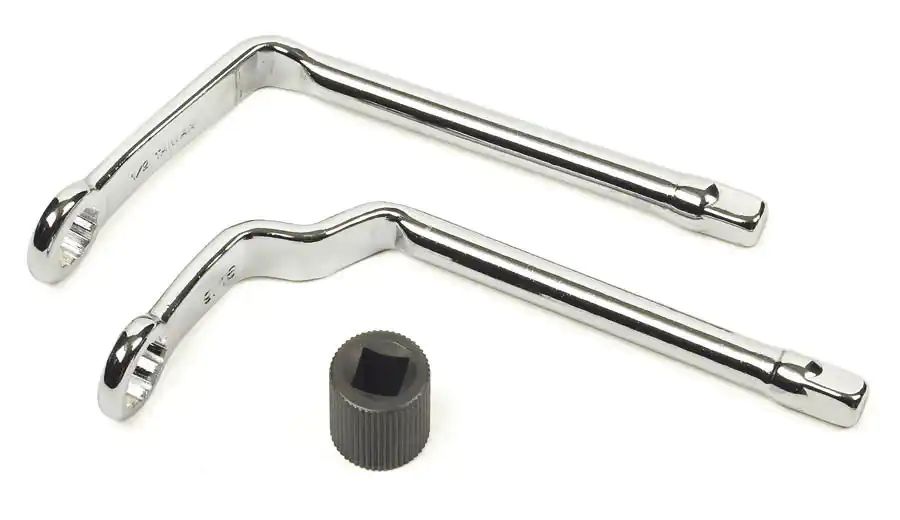

When mechanics did a lot of regular timing adjustments and tuning, a purposely bent distributor wrench made their lives much easier. However, much like ignition points, distributors have all but disappeared. Thanks to coil-on-plug ignition systems and computer-controlled timing, the distributor is little more than a messenger: It simply tells the computer where the engine is at in its rotation.
Timing adjustments have become so uncommon that a job-specific tool is likely a waste of space. If you’ve got room in your tool chest, keep yours around; but know that a standard box-end wrench can usually get the job done and is only fractionally less convenient than the specialized version.
Verdict: Keep if you have them. No need to buy if you don’t.
Pre-OBDII diagnostic scan tools
Prior to the required standardization of on-board diagnostic computers by the U.S. in 1996, a single car could host a wild mix of analog and digital diagnostic methods. OBDII, which stands for On-Board Diagnostic II, wasn’t the first time that a small computer was used to pull information from the vehicle via an electronic connection; it merely standardized the language.
Throughout the 1980s and early 1990s each OEM had its own version of a scan tool. Now those tools can be reverse-engineered and functionally spoofed by a modern computer, allowing access to diagnostic info tools that, at the time, were only available to dealers. Since many pre-OBDII cars are now treated as classics or antiques and driven far less frequently, the need for period-correct diagnostic tools is dropping.
Verdict: Keep. These will only get harder to find with time, and working versions will be even rarer.
Distributor machine
A distributor is simple in concept. Trying to balance the performance and economy of the ignition system, with the distributor attached to a running engine, and achieving proper operation starts to get pretty complicated. That’s where a distributor machine comes in.
A distributor is attached to the apparatus and spun at engine speed by an electric motor. This allows you to literally see how the points are opening and closing. You can also evaluate the function of vacuum or mechanical advance systems. These machines are still great but the frequency that this service is needed these days is few and far between, especially when trying to justify keeping a large tool around and properly calibrated.
Verdict: Keep, if you are a specialty shop or tool collector.
Engine analyzer

Even a casual enthusiast can see there is a lot more information that can be gleaned from a running engine than whatever readouts might be on the dash. Enter the engine analyzer, a rolling cabinet of sensors and processors designed to fill in the data gaps between everything that is happening in a car and what its gauges report.
An engine analyzer is essentially a handful of additional instruments packaged into a small box hanging around the bottom of your tool drawers. It can also house a lot of sensors in a giant cabinet, which was likely wheeled into the corner of the shop in 1989 and left to gather dust. Now engine analyzers can be found listed online for as cheap as $200usd/ $287cad.
The funny thing is that many of the sensors in these engine analyzers are often the same systems that come built into modern dynamometer tuning systems. In a dyno, the sensors allow the operator to see more than max power; they also show how changes to an engine’s tune affect emissions. Maybe engine analyzers didn’t disappear so much as change clothes.
Verdict: Toss. The opportunity cost of the space these take up can be tough for most home garages. Sensors went out of calibration decades ago so the information you might get from one is dubious at best.
Most pneumatic tools (for home shops)
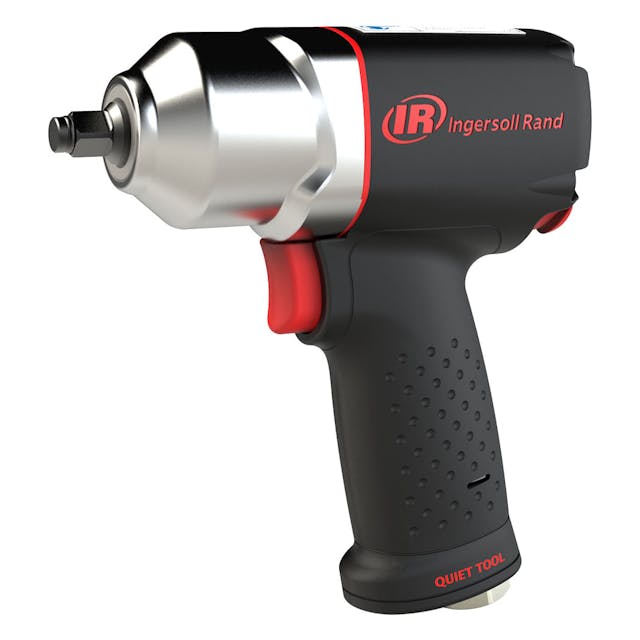

Air tools hold an odd place in the hearts of many gearheads. For many years the high-pitched zizzzz and chugging hammers of air-driven die grinders and impact drills were the marks of a pro. Or, at least, of someone who decided that plumbing high-pressure air lines around the shop was easier than installing outlets and maintaining corded tools. Air tools are fantastic for heavy use, as they are much easier to maintain and can be rebuilt and serviced.
Those tools can really suffer in lack of use, though, since pneumatic tools rely on seals and valves, neither of which deal well with dry storage. Battery tools have caught up to air tools for most DIY folk. No more air lines or compressors taking up space in the shop—and requiring additional maintenance—and, in return, a similarly sized yet more agile tool.
Verdict: Keep, if you already have the compressor. Don’t have one? Invest in battery tools.
Babbitt bearing molds/machining jigs
Every engine rebuild has to have bearings made for it in some fashion. Today’s cars use insert bearings that are mass-produced to surgical tolerances for a multitude of applications. If you wanted—or more accurately needed—new bearings in your Model T circa 1920, you needed to produce your own … in place … inside the engine. Welcome to Babbitt bearings.
The process is a true art form, from the setup of the jigs to the chemistry of pouring molten metal and machining the resulting orbs to actually fit the crankshaft and connecting rods. Now there are newly cast blocks for your T that replace the Babbitt with insert bearings. Since those antique Ford engines just don’t get abused the way they used to, and lead fairly pampered lives, they need rebuilding far less often than they did in-period. Modern oils also do a better job of protecting these delicate bearings. Since they are less and less in demand, the tooling and knowledge to make Babbitt bearings are difficult to find, and precious when you do.
Verdict: Keep. It’s literally critical to keeping a generation of cars alive.
Split-rim tire tools

Among the realm of scary-looking tools that have earned their infamy, split-rim tools hold court. The concept is simple: The rim is sectioned, allowing it to contort into a slight spiral that can be “screwed” into a tire. (This is almost the reverse of a modern tire machine, which stretches the tire around a solid wheel rim.) When tires needed tubes, both tire and rim were relatively fragile, and the roads were rough, split rims were popular—and for good reason. Now the tooling for drop-center wheels is ubiquitous and shops often won’t take on split-rim work. Success is hard to guarantee, even if techs are familiar with split rims—and they rarely are.
Verdict: Keep. No substitute for the right tools with this job.
These tools might not make much sense in a dealership technician’s work bay, but that doesn’t mean they should disappear forever. Knowing how to service antiquated technology is as important as ever, whether using old tools or new ones. If you’ve got any of these items, consider it your responsibility to document what the tool does and how to safely use it. Keeping alive the knowledge of where our modern tools came from is powerful.
For the Silo, Kyle Smith.