How well will you be spotted at sea by other ships, in rough and nasty weather? Our friends at Rolly Tasker asked three highly experienced ocean adventurers to give a unique insight into their thoughts on this.
How well will you be spotted at sea by other ships, in rough and nasty weather? As Rolly Tasker Sails are making sails for some of the world’s most ardent ocean sailors, this was a natural question to ask. Three highly experienced ocean adventurers give a unique insight into their thoughts on orange sails. The one thing they have in common? Serious ocean sailing and sails by Rolly Tasker Sails!

André Freibote: North Sea and Atlantic
André Freibote from Germany is sailing a Beneteau Oceanis 473 out of Bremerhaven on professional offshore sail training trips across the North Sea and out into the North Atlantic Ocean – in fact, he very nearly met up with Eric Aanderaa in Iceland in the 2024 summer! See his website “Segelpartner Nordsee” for more information on his cruising schedule and how you can join (in German language).


Eric Aanderaa: North Atlantic Ocean
Eric of course also offered his thoughts and needs no further introduction other than himself being Mr. No Bullshit Just Sailing. The crazy guy from Norway who sails from Haugesund out into the northern ocean no matter the weather or the season, on his Contessa 35, becoming a YouTube sailing star in the process.
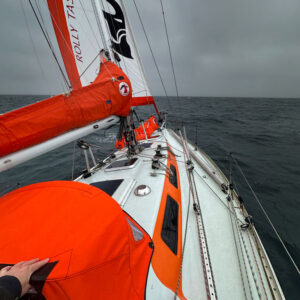

Pat Lawless: on Golden Globe Race
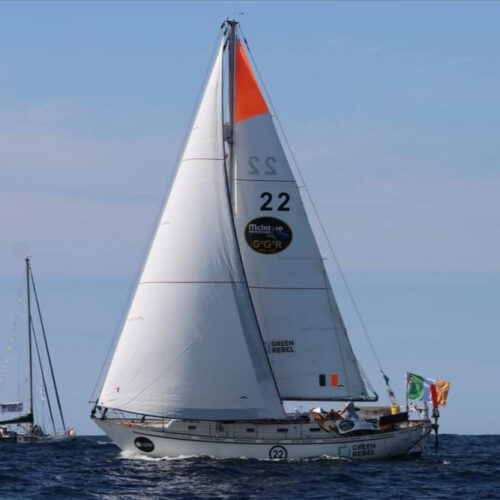
The vastly experienced professional seaman and sailor Pat Lawless from Ireland, who is currently preparing his Saltram Saga 36 to compete, for the second time, in the non-stop, single-handed around-the-world retro “Golden Globe” race (GGR) that will start in 2026. Needless to say, he will again put his trust into Rolly Tasker Sails. Find out more about Pat on his website.
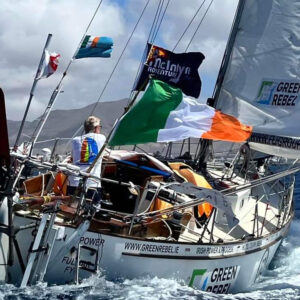
So, are sails in bright orange a good idea to increase visibility of your boat? We know that many storm sails are made in orange for this reason, but what about your standard sails?
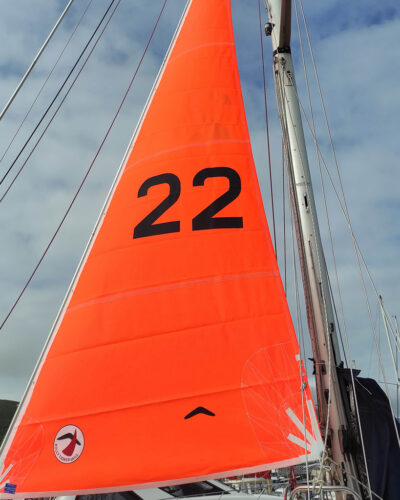
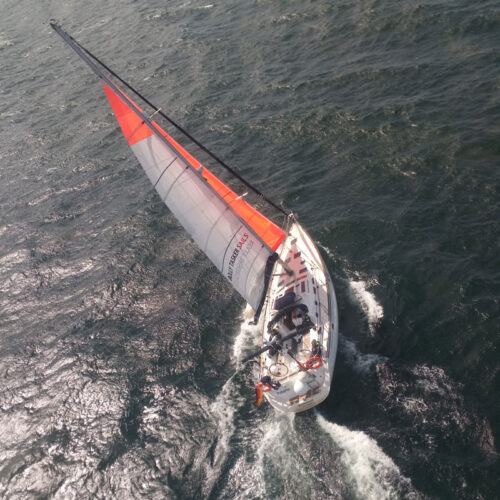
“Orange colours stand out from sea and sky far away. It will definitely make it easier for other traffic to spot you. It will also make it much easier to find you in a distress situation”, says Eric. “In all cases orange is the most visible colour of them all, I believe.” Pat is yet looking at colour choices for his new sails for the GGR: “I have been thinking about safety orange sails for a while. The Notice of Race for the Golden Globe Race says all the sails have to be the same colour with safety yellow or orange at the top of the mainsail. That means that all the sails can be safety orange or yellow. I know from using an orange storm jib and having a bright orange spray dodger that it’s easy on the eyes. Probably better than White. Am I brave enough to go all orange sails?” Finally, André is quite clear on the subject: “The situation will arise when you just can’t be orange enough at sea!”
And this despite AIS and radar?
“AIS is actually clear in the information, giving name, call sign, course, speed and so on. However, if a sailing yacht is detected by radar in poor visibility, the lookout on a commercial vessel should be diligent. Here on the North Sea, we have already received radio messages along the lines of: “Fantastic, how well we can see you, sailing yacht Polaris!” It is imperative, so it seems, to be seen by eye and not only rely on radar or AIS, although all commercial ships and some fishing vessels receive and send AIS signals and rely mostly on AIS and radar for their lookout. However, visual contact also is extremely important.
Pat confirms this: “In the Golden Globe Race we don’t have a plotter or other modern equipment. We do have an AIS transmitter, and active radar reflector. Any ships I spoke to while at sea all said that they saw me a long way off, no problem.”
Would you have the entire sail in orange or just a patch or the top part?
Eric says: “I like to have at least the top part orange, as its the highest point on the boat, letting the sails easily be spotted in between big wavetops.”
André: “The upper area of the mainsail and all the sails on the cutter stay are completely orange. Since the cutter stay is on a furling system, the UV protection of the sails is also in orange to ensure better visibility even when furled.”
What about other parts of the boat?
Eric: “I have painted the sides of the rooftop in orange, changed my blue sprayhood to orange and changed the cutter sail-bag to orange. This way the boat will be much more visible.”
Pat also plans to brighten up his boat in a similar way: “In storms the hull is so important. I will put an orange stripe over the white about 150mm just under the gunnel and the same on the top of the cabin sides. This should stand out with the white underneath it. I had about 3sq meters of safety orange on the deck in the GGR 2022. This will be freshened up when I apply the stripes. Apart from that, the Saltram Saga 36 is a good dry boat. I don’t use dodgers on the lifelines. In the Southern Ocean they are wind pollution in the wrong place and sometimes block areas of sight. My spray dodger will be safety orange. But in storms, it will be folded down.”
André, on the other hand, seems happy for now with his orange sails: “At the moment I am not planning to change any other parts on board to orange. However, I could see my lazy bag for the mainsail in orange.”
Will orange sails, sprayhoods or dodgers not be too bright on the eyes in fair weather and sunshine?
Eric has taken this potential problem into account: “The sails in orange are not quite as intense as the bright signal colour painted on deck. Still, the sails will be visible from far away.” André believes that this will not be an issue at all: “Never too bright!”
How Orange Will You Be?
How orange would you dress up your boat for ocean sailing or offshore passages? Pat is still in the decision-making process: “My quandary is mainly about the colour of the sails. I need to make a decision early in 2025. While sailing in the longest, loneliest, sporting event in the world, I need to be seen as easy as possible. The sails are the biggest area of the boat most of the time.” But will he really have all sails completely in orange? At Rolly Tasker Sails, we offer suitable sail-cloth in “Storm Orange”. However, if you want to go for specific types of sail fabric, the solution will probably come down to having orange sail tops or patches.
The View From the Bridge
It’s always good to see also the other perspective, so we spoke to a commercial Captain, Master Mariner Reemt Remmers, about visibility of yachts at sea. He fully confirms the fact that orange sails are a true safety factor for yachts at sea, especially in rough weather with limited visibility. Which is when, according to him, there will often be an extra lookout on the bridge.
Orange, AIS and Radar
Orange, incidentally, is also the signal colour for ship’s lifeboats. Obviously not without reason. And if a ship’s officer from the bridge spots an orange object somewhere out there, this officer will then instantly be on full alert. AIS, on the other hand, is just as important. There will be times in ship’s routine when only one officer will be on the bridge who will rely on AIS and radar. Obviously, also at night, these technologies are essential to remain visible.
Between these two, Reemt Remmers also confirms that yachts are often easier to spot and identify on AIS rather than by radar. In heavy seas especially, the radar signal response from a yacht can be quite weak and might not be noticed by the watch-keeping officer. An AIS signal, on the other hand, will be clearly seen and also contains all essential information about the type of boat and her movements in a clear and precise way. For the Silo, Sven Cornelius.