Like other authors who write about innovation, I love Thomas Edison stories. He was an inventive genius and found the code to serial innovation more than 120 years ago.
That code is still in use by companies like IDEO who’ve learned his lessons and both improved upon them and added to them. But the basic core is still the same.
Less well known is Edison’s entrepreneurial side. He put financiers, government officials, politicians and inventors like himself together in an inspired coalition that built the first electrical grid in New York City. After all, what good is a light bulb if you don’t have a source of electricity to power it?
But his inventions were not always successful, nor were his attempts to market and sell them.
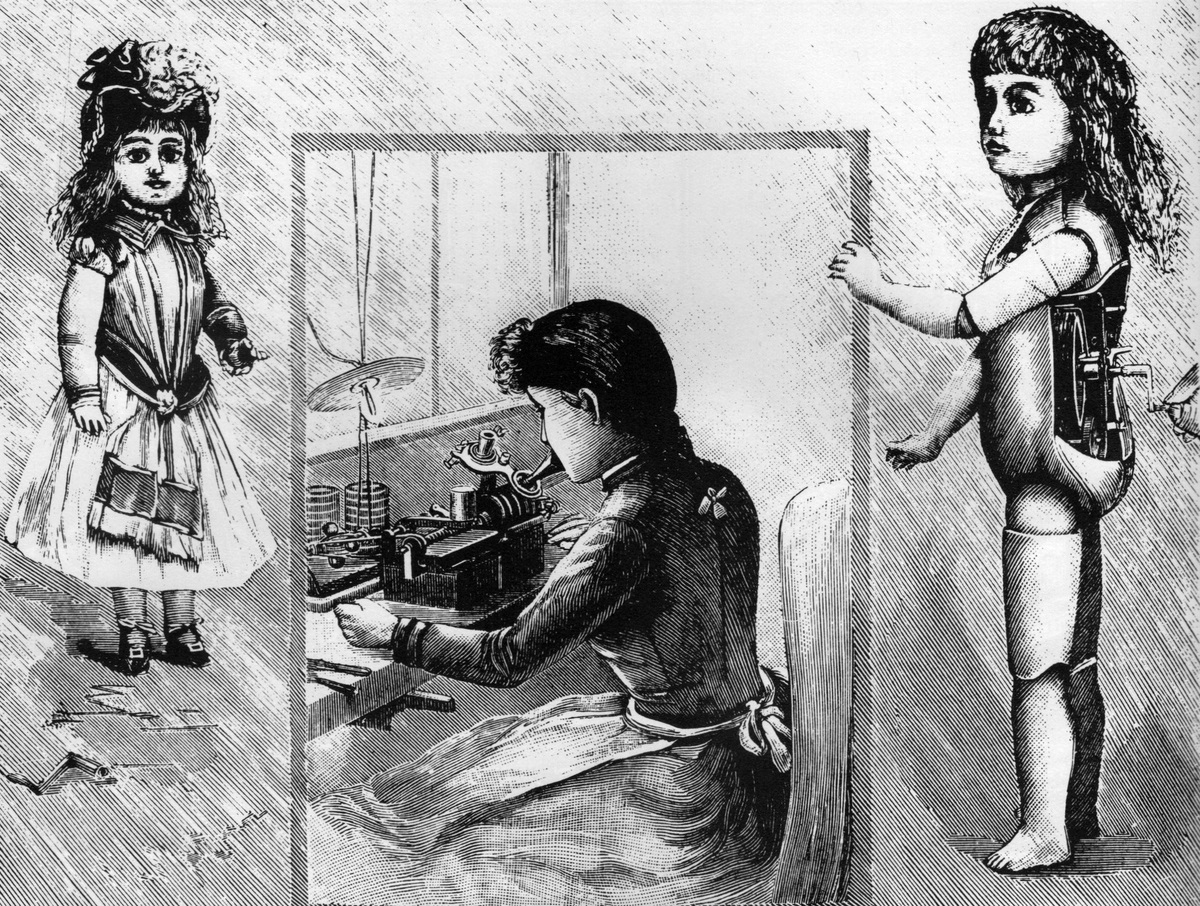
For example, very few people today know about Edison’s talking doll. Expected to sell during the 1890 Christmas season, she was a marketing failure.
Creepy even for the 19th Century
I think she looks like the “Bride of Chucky” and is more than a little spooky. Talking, animated objects are commonplace today, but Edison was the first to have the idea and execute it.
What gave her voice was a tiny version of the phonograph – another of his inventions. He thought it would be novel to make a talking doll and hoped it would catch on. The doll market was already thriving, so a talking doll could potentially reach the top of the heap.
But not all of Edison’s creativity turned into cash, and his Bride of Chucky was a dismal failure. The little talking machine went inside the doll with the handle protruding from her back. Edison produced 2,500 of the dolls but only 500 sold. They were $10 each — two weeks of the average pay back in 1890 – and many of those sold were returned for quality problems.
Edison quickly turned his back on her.
I particularly like this story because it shows the critical difference between innovation and entrepreneurship. Great ideas are not always great opportunities. Opportunities possess five characteristics that differentiate them from great ideas:
Durability – They keep creating value over time.
Sustainability – The organization has the willpower, manpower and resources to sustain the idea through failure, rethinking and reformulation.
Defensibility – The potential return on investment makes it worth the time, resources and risk that accompany all new ventures, thus making it worth doing this over doing something else.
It creates value – It creates value for the person willing to reach into their pockets for money to pay for the intangible form and thus it creates value for the company.
It is compelling – The Innovation is differentiated in some critical way that makes a customer segment just have to have it.
Entrepreneurs differ substantially from innovators because they have the discipline to determine whether a great idea is also a great opportunity. This takes a lot of work, failure, rethinking and, most of all, passion to get you through all of this vetting. Many innovators lose interest after the idea stage and don’t understand that innovation without value creation may be fun – but it’s also folly.
Edison, like many other inventors, fell in love with his baby and he built a bunch of them, assuming a slam dunk in the market. In fact, these dolls were not just spooky looking, they were big and heavy and cost a lot of money.
Edison’s enthusiasm for his ability to make a talking doll was not counterbalanced by the discipline necessary to determine whether the idea was just that or a real opportunity. He was so eager to produce them that he didn’t ask if the market wanted such an invention and at what price.
I am sure that Edison was OK with failure, as he once said that he had not failed in his efforts to create the light bulb, but rather found a thousand ways that didn’t work. For the Silo, Neal Thornberry, Ph.D.
Supplemental- Bride of Chucky http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0144120/