Art is, or it should be, about more than simply making marks on a surface or manipulating materials into pleasing–or indeed displeasing–shapes…. perhaps the avant-garde or kitsch. A true artist benefits immeasurably by knowing about the history that has created the universe they traverse.
Ever wonder what all that academic talk is that curators like to use so much? Do you find it pretentious or worse?
Art Theory informs in so many ways, tracing the paths that have led to a particular moment or movement. A foundational understanding of the schools of thought, the histories, the thinkers who have wrought the ground you stand on as an artist today enriches not only your own mind but your work as well.
One such thinker who made a significant impact on the art world in the 1940s was Clement Greenberg. In 1939, Greenberg published one of his seminal works Avant-Garde and Kitsch. The essay not only launched Greenberg to nearly overnight notoriety, it also sparked a major development in the art world as a whole.
The essay begins with the following statement:
“One and the same civilization produces simultaneously two such different things as a poem by T.S. Eliot, and a Tin Pan Alley song, or a painting by Braque and a Saturday Evening Post cover. “
Click on the following scan to open the full essay in PDF form-
Greenberg goes on to classify Avant-Garde as those things that are untouched by the decline of taste and meaning in a society (a poem by T.S. Eliot or a painting by Braque) while Kitsch is the title bestowed on the rest of the clutter that appeals to the masses and asks nothing in return other than their money (a Tin Pan Alley song or a Saturday Evening Post cover).
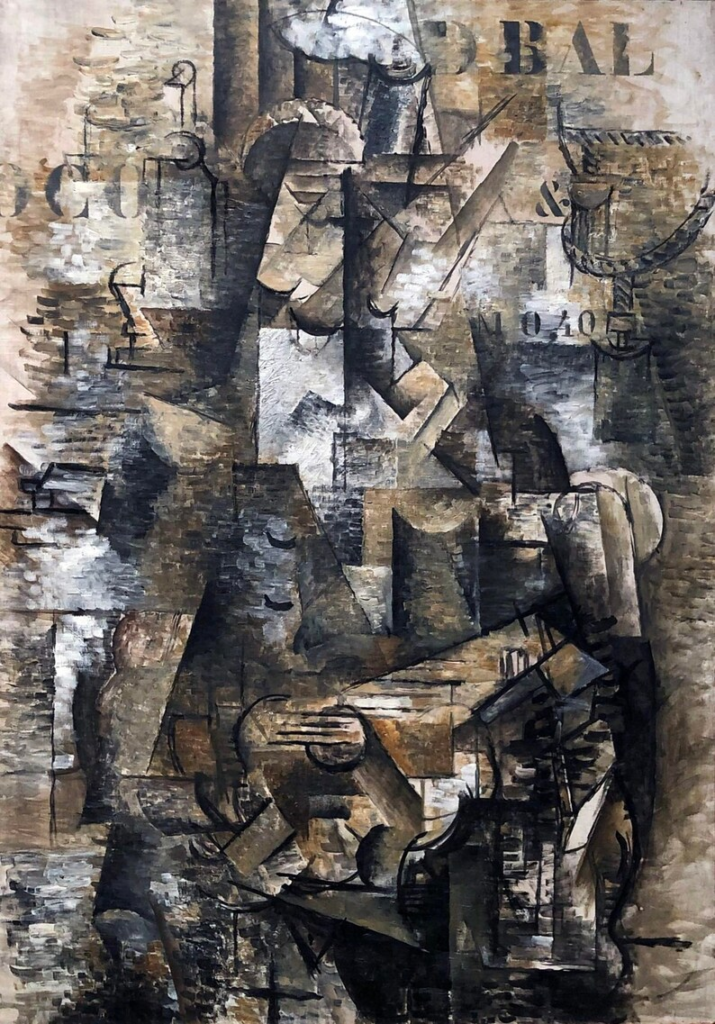

The Portuguese-Georges Braque-1911.
For Greenberg, Avant-Garde situated itself outside the influences of both capitalist and communist influences that were gradually dampening society’s ability to appreciate any depth of meaning.

Greenberg wrote several other important essays over the course of his life and career. He was a strong proponent of Modernism being the last best hope for the preservation of integrity in art. Jackson Pollock and Willem de Kooning were among those he deemed the saviors of art in their time.
Understanding who Clement Greenberg was and why his influence matters is just one piece of the complex puzzle of being a well-rounded artist. There are libraries worth of books out there that will break down every bit of art theory and history you ever need to know.
Of course, who has time to read all that? How can you know where to begin? Who and what are some of the most important influences that have shaped the art world as it stands today and how are you meant to sort them out from the crowd? For the Silo, Brainard Carey.