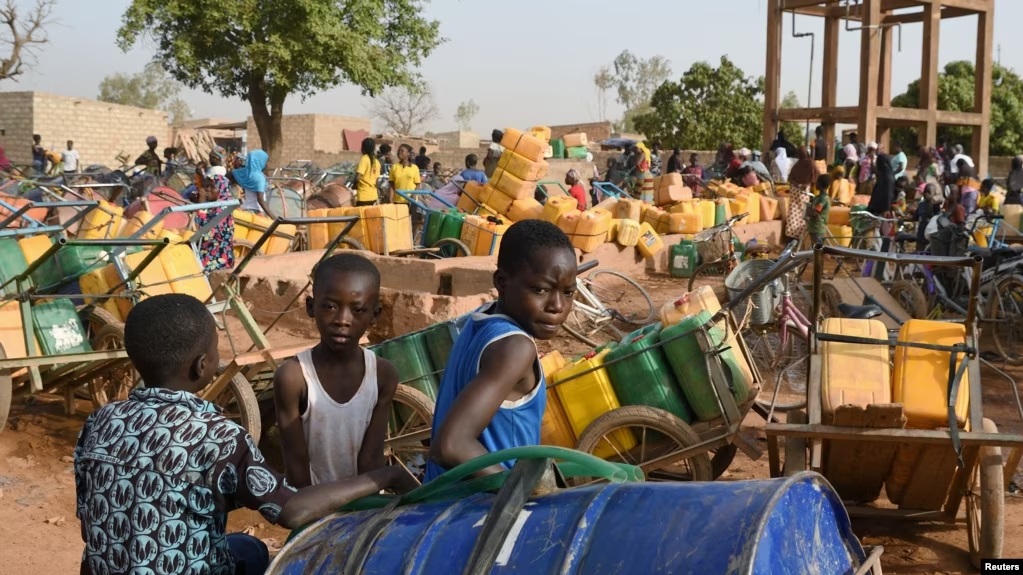
For the first time, Burkina Faso tops the list of the world’s most neglected displacement crises, according to a new report from the Norwegian Refugee Council (NRC). Redirection of aid and attention towards Ukraine has increased neglect of some of the world’s most vulnerable people.
The annual list of neglected displacement crises is based on three criteria: lack of humanitarian funding, lack of media attention, and a lack of international political and diplomatic initiatives. The crisis in the Democratic Republic of Congo ranks second, having appeared first or second on the list every year since its inception seven years ago. Colombia, Sudan, and Venezuela follow in this grim ranking.
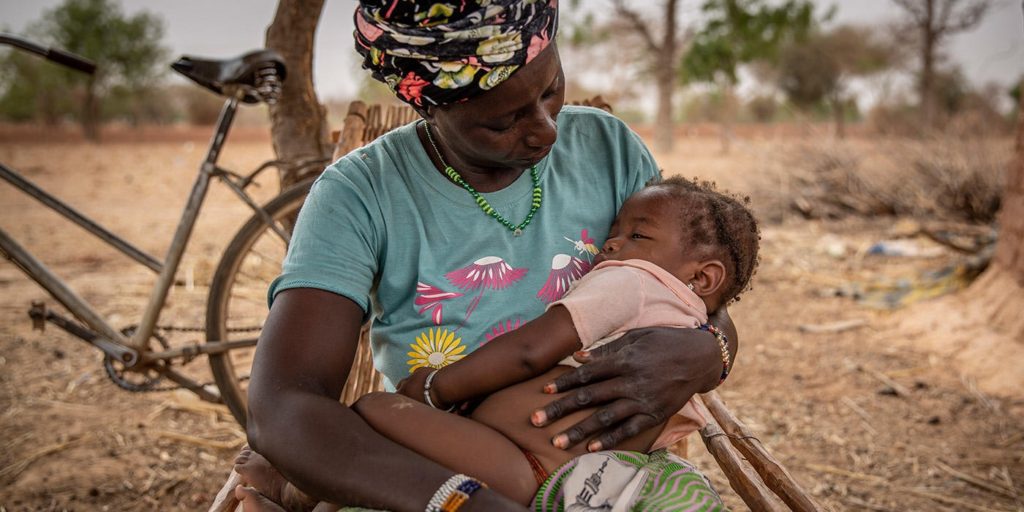

“Tell the world we have suffered. We have suffered a lot. Our neighbours have suffered. Our friends have suffered. Our relatives have suffered. We lost many. Most of them killed. I am thanking God because none of my family was left there, and we are all in safety. I do not want to return, but I am asking God for peace, for peace in this place,” says Halimata (35). Together with her family, she fled fighting in the east of Burkina Faso and sought safety in Kaya.
“Neglect is a choice – that millions of displaced people are cast aside year after year without the support and resources they so desperately need is not inevitable,” said Jan Egeland, NRC’s Secretary General.
“The powerful response to the suffering inflicted by the war in Ukraine demonstrated what the world can deliver for people in need. Political action for Ukrainians has been impactful and swift, borders kept open, funding plenty, and media coverage extensive. Those in power need to show the same humanity towards people affected by crises in places such as Burkina Faso and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.”
More than five times more articles were written about the Ukrainian displacement crisis last year than about all the world’s ten most neglected crises in total. For every dollar raised per person in need in Ukraine in 2022, just 25 cents were raised per person in need across the world’s ten most neglected crises.
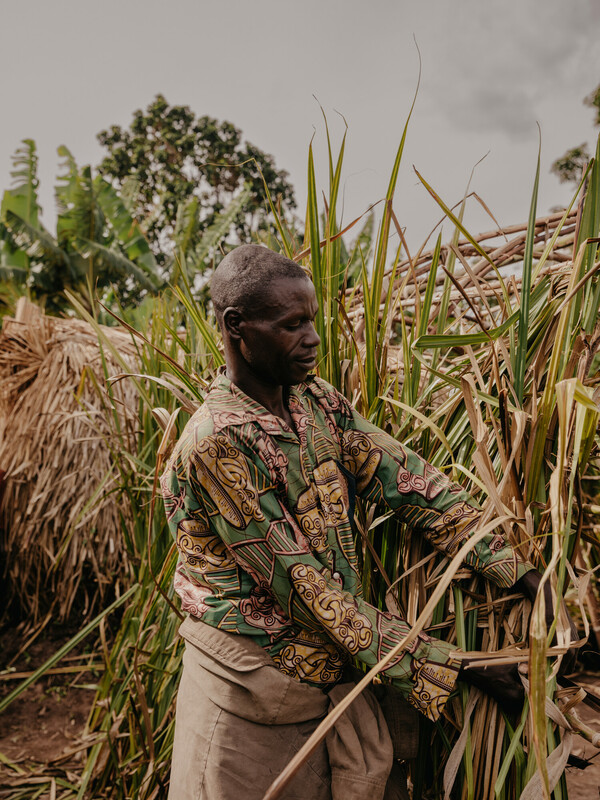

The Democratic Republic of Congo continued to make the list this year. Patient* 43, lives with his 6 children in the town of Bule, Djugu Territory, Ituri Province, DR Congo. ‘We fled in February 2021. We’ve moved around a lot, and now we are trying to build a new home. During the war, we’ve never had enough to eat, and we have no money to buy medicines if the children get sick. We used to live in a beautiful village, and had a big house. Now, all we have is this shelter. When it rains a lot, the water will come through the roof’. *Name changed for security reasons.
The repeated warnings of increased disparity due to the reallocation of resources to the Ukraine response have now become reality. The redirection of a large amount of aid money towards Ukraine and towards hosting refugees in donor countries means that many crises have seen a drop in assistance, despite growing needs. Total aid to Africa, where we find seven out of the ten most neglected crises, was 34 billion USD in 2022, representing a drop of 7.4 per cent compared to 2021.
The Ukraine crisis also contributed to an increase in food insecurity in many of the countries featured in the report, worsening already dire crises, and increasing the number of people in need.
“The world has failed to support the most vulnerable, but this can be reversed. The lives of millions of people suffering in silence can improve, if funding and resources are allocated based on need, not geopolitical interest, and media headlines of the day,” said Egeland. “Last year the gap between what was needed and what was delivered in humanitarian assistance was 22 billion USD. This is a huge sum of money, but no more than Europeans spend on ice cream a year. We need donors to increase support and new donor countries to step up to share responsibility.”
Burkina Faso’s decline since the crisis broke out five years ago has been swift and devastating. More than 2 million people have been forced to flee their homes, and nearly a quarter of the population now requires humanitarian aid. Across the country, 800,000 people are living in areas under blockade by armed groups where they have no access to even basic services. The situation is increasingly dire with some people forced to eat leaves to survive.
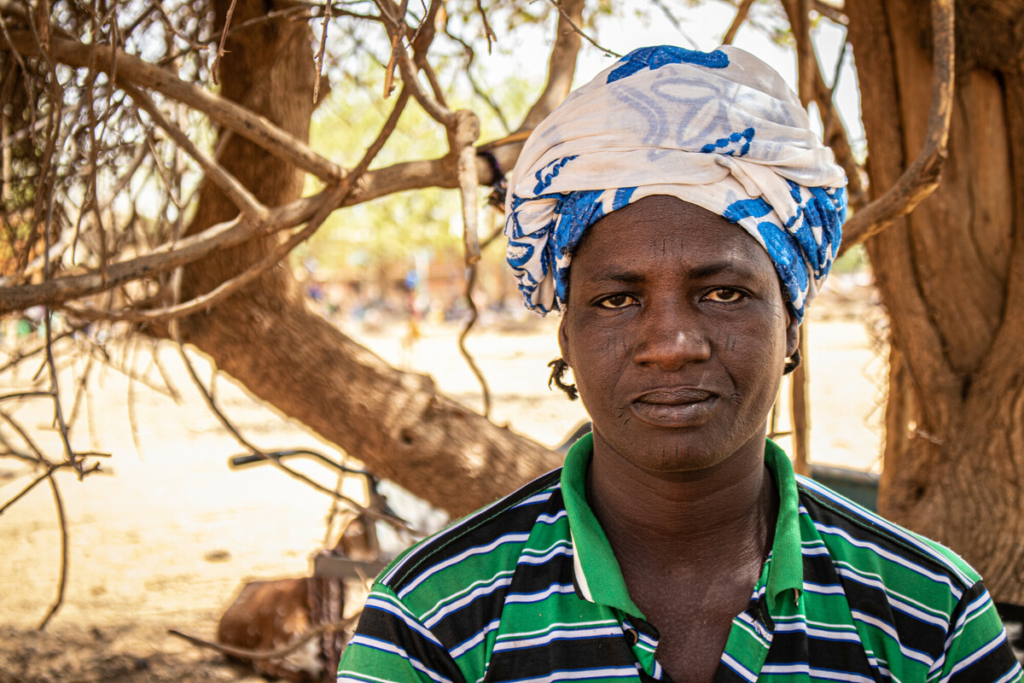

Maïga Abibou is an Internally Displaced Person (IDP) from Wapassi in the North region of Burkina Faso. Because of rampant insecurity in Wapassi, she made her first move with her family to Naoubé, a village in the Center North. A few months later, she fled again with her family to Louda, a village located a few kilometers from Kaya. There, she has been living with dozens of other families out in the open for over a month while hoping to get shelters soon before the rainy season begins in Burkina Faso. “We want the world to know about our difficulties, about what is worrying us now. We fled from far away to come here. This is our second escape. We could not bring anything with us. We moved with our carts; we were in the bush and there were no vehicles,” Abibou said.
“We must do more to end the suffering in Burkina Faso before despair becomes entrenched and it is added to the growing list of protracted crises. That this crisis is already so deeply neglected shows a failure of the international system to react to newly emerging crises, as it also fails those lost in the shadows for decades. Ultimately, greater investment in diplomatic solutions is needed if we hope to pull crises off this list,” said Egeland. For the Silo, Jessica Wanless. Featured image: FILE – Children wait for their turn to buy water from a privately-owned water tower, amid an outbreak of the coronavirus disease, in Taabtenga district of Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso, April 3, 2020.
Facts and figures:
- Each year, the Norwegian Refugee Council (NRC) publishes a list of the ten most neglected displacement crises in the world. The purpose is to focus on the plight of people whose suffering rarely makes international headlines, who receive no or inadequate assistance, and who never become the centre of attention for international diplomacy efforts. The report is available here.
- The neglected displacement crises list for 2022 analyses 39 displacement crises based on three criteria: lack of funding, lack of media attention, and lack of international political and diplomatic initiatives. Full details on the methodology can be found in the report.
- The full list in order this year is: Burkina Faso, DR Congo, Colombia, Sudan, Venezuela, Burundi, Cameroon, Mali, El Salvador, Ethiopia.
- Burkina Faso has appeared on this list for the previous four years. It ranked second on last year’s report, seventh in 2020, and third in 2019.
- DR Congo is a textbook example of a neglected crisis. It has topped the list three times (2021, 2020 and 2017). It previously ranked second on the list in 2019, 2018 and 2016.
- Colombia and El Salvador appear in this report for the first time this year.
- The total funding to the Burkina Faso humanitarian response plan was 339 million USD in 2022, of the 805 million USD requested – making the response just 42 per cent funded (OCHA).
- In 2022, 3.5 million people were in need of humanitarian assistance in Burkina Faso – by the end of the year this has skyrocketed to 4.9 million people. This is a 40% increase and nearly equal to 1 in 4 Burkinabè (OCHA).
- There are almost 2 million internally displaced people in Burkina Faso (IDMC).
- 800,000 people are living in 23 blockaded towns and cities in Burkina Faso, unable to access aid regularly. Half of them are in the city of Djibo (Access Working Group).
- The average humanitarian appeal was just over half funded in 2022, while the Ukraine appeal was almost 90% funded (OCHA).
- The gap between the total humanitarian appeals by the UN and partners and the money actually received amounted to 22 billion USD in 2022 (OCHA).
- Total aid to Africa was USD 34 billion in 2022 (overseas development assistance, including development aid and humanitarian), representing a drop of 7.4% compared to 2021 (OECD).
- Collectively the world’s most powerful donor countries used more of their aid on the reception of refugees at home than on overseas humanitarian assistance in 2022 (OECD).
- The European Ice Cream Market was estimated to be valued at $21.7 Billion in 2021 (Research and Markets).
- 212 USD was raised per person in need inside Ukraine, while 52 USD was raised per person in need across the world’s ten most neglected crises in 2022 (OCHA).
- In total, 375,000 articles were written in the English media about the world’s ten most neglected displacement crises last year, according to statistics from Meltwater. In comparison, 1.98 million articles were written in English about the displacement crises in Ukraine during the same period (Meltwater).