Spring means fresh flowers and sunny days, but it also brings seasonal health issues as the weather gets warmer: from Rosacea to Lyme disease.
Most likely, you or someone you know has been affected by Lyme disease, the most common tick-borne illness in North America with more than 300,000 cases diagnosed each year. In a timely new book, Conquering Lyme Disease(Columbia University Press), Columbia University Medical Center physicians Brian A. Fallon and Jennifer Sotsky reveal that despite the challenges to find a cure for this complex, debilitating disease, precision medicine and biotechnology are accelerating the discovery of new tools with which doctors will be able to diagnose it and treat patients.
“Through rapid genetic sequencing, scientists can identify many different strains of Borrelia burgdorferi as well as new tick-borne microbial infections, such as Borrelia miyamotoi, Borrelia mayonii, and the Heartland virus.” — Brian Fallon
Could groundbreaking technologies that rapidly increase our understanding and open up new pathways mean a cure for Lyme disease one day soon? The Global Search for Education is pleased to welcome Dr. Brian Fallon to find out how tech is tackling the ticks.
“Modern technology using Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) allows one to discover with great rapidity all microbes that may be present within a sample of fluid.” — Brian Fallon
Brian, how has technology improved the research process for tick borne diseases?
Consider the difference in price of genome sequencing between 20 years ago and today. In 2003, it had taken the Human Genome Project about 4 years and costs estimated between $500 million to 1 billion…by 2006 the cost for sequencing a single human genome had dropped to 14 million……today a whole human genome can be sequenced within days for less than $1,000. This is a tremendous advance.
Why is genome sequencing so important? Let’s look at human tick-borne diseases. When two different people are infected with Borrelia burgdorferi (the microbe that causes Lyme disease), one will resolve the disease quickly after a course of antibiotics while the other may develop a chronic relapsing remitting illness. Why? Because one person might have gotten a more persistent strain, while the other received a less invasive strain that stays localized to the skin. Additionally, the genetic differences in the human determines how the immune system responds to the invading microbe. Understanding the genetics of the infection and of the human host allows scientists to unravel the mysteries of tick-borne illnesses.
Through rapid genetic sequencing, scientists can identify many different strains of Borrelia burgdorferi as well as new tick-borne microbial infections, such as Borrelia miyamotoi, Borrelia mayonii, and the Heartland virus. When the genome of a microbe is sequenced, it provides a starting point for the study of pathogenesis, vaccine development, and treatment. Discovery of these new microbes inside ticks has been enormously helpful. A patient who has had typical symptoms of Lyme disease after a tick bite but has tested negative on the blood tests for Lyme disease might puzzle clinicians. They may criticize the insensitivity of the Lyme disease tests. However, when this same patient is tested for the newly discovered tick-borne infection, Borrelia miyamotoi, the diagnosis is then clear. Yes, the patient had a Lyme-like illness, but it wasn’t Lyme disease: it was Borrelia Miyamotoi disease.
Modern technology using Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) allows one to discover with great rapidity all microbes that may be present within a sample of fluid. This “discovery based” approach using “unbiased next generation sequencing” enabled a 14 year old boy to be rescued from a fatal infection within 48 hours (Wilson et al, NEJM, 2014). This boy had endured 3 hospitalizations over 4 months, had over 100 diagnostic tests, spent 44 days in an ICU for encephalitis of unknown etiology, had a brain biopsy, and had to be put into a medically induced coma to prevent damage from his ongoing seizures.
Eventually Dr. Charles Chiu at U.C.S.F. employed NGS analysis of more than 8 million sequences with a bioinformatics pipeline (SURPI) for the detection of all known pathogens. The cause of the boy’s meningoencephalitis was revealed as Leptospira santarosai. He had likely acquired it in Puerto Rico, as it is not present in the continental United States. He received the appropriate antibiotics and was discharged 2 weeks later to rehab. This same approach is especially useful for uncommon infections as they might not be suspected; for example, rare tick-borne viruses such as Powassan Virus or Heartland Virus can be rapidly detected using this discovery approach.

How has big data impacted the way advocacy groups support research?
A patient-generated source of Big Data is LymeDisease.org. This California based organization developed a survey called “My Lyme Data” that patients could fill out on the web about their clinical history and lab tests and treatments. In a short period of time, they had data on 10,000 patients whom they track over time. With this information, they provide a more comprehensive clinical view of the bulk of patients who are diagnosed with persistent symptoms despite treatment for Lyme Disease (aka Chronic Lyme Disease).
“In geographic areas where medical professionals are scarce, AI technologies will play an increasing role in improving patient care by allowing differential diagnoses to be generated and treatment options suggested through AI-based systems accessed through the internet.” — Brian Fallon
Jobs in all professions are being automated. Do you believe AI technologies will only assist doctors or will they replace physicians in some tasks? What does this mean for doctors, nurses, and the future of medicine?
While AI technologies will go a long way to assist health care providers to provide better care, its application to medical care is still just beginning. One can anticipate, however, that in geographic areas where medical professionals are scarce, AI technologies will play an increasing role in improving patient care by allowing differential diagnoses to be generated and treatment options suggested through AI-based systems accessed through the internet.
The general public has more access to information than ever before about Lyme disease from websites, medical organizations, articles and social media. Everyone can be their own “expert” or even their own “doctor.” Can you speak about the pros and cons of online health data in the era of fake news?
This obviously is a huge area of concern. Individuals used to turn to their physician or to the medical information books, such as the Merck Manual. Now, they turn to the web.
In a recent survey of patients who used the web to obtain health information (Doherty-Torstrick 2016), we learned that more than half of the 730 patients reported they experienced increased distress as a result of checking the web. We also learned from this survey that individuals who did not have a health education were more likely to spend more time on the web and were thus prone to develop more anxiety than those who were better educated from a health perspective. While some of the information they find may be accurate, other information may be well-intentioned but ill-informed, misleading, and even harmful.
“Researchers can rapidly screen thousands of drugs to determine which agents have the strongest ability to kill Borrelia spirochetes. This is possible because of the development of high throughput assays, which have proven more effective than the standard agents in eradicating both the stationary phase Borrelia and its more drug-tolerant persister-forms.” — Brian Fallon
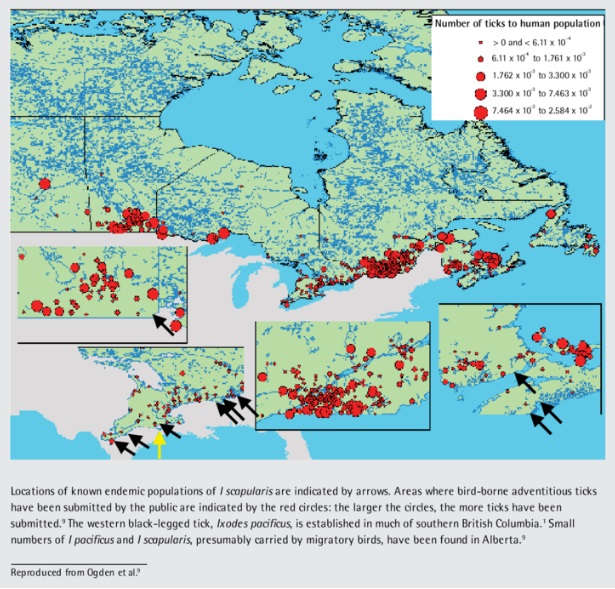
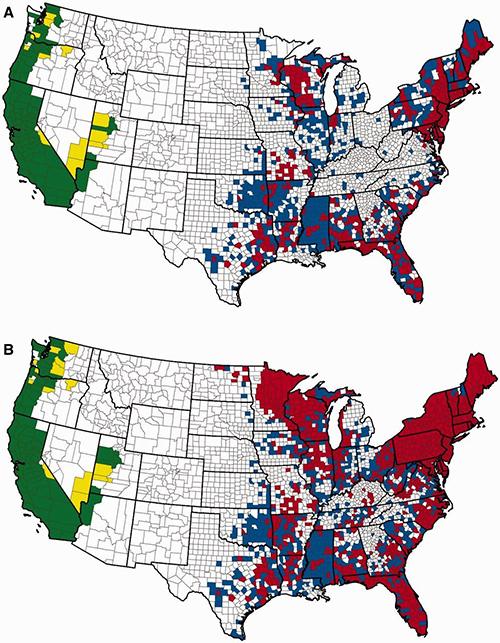
Look into the future. What are the technologies you are most excited about in terms of helping to find cures for Lyme disease and improve patients quality of life?
Researchers can rapidly screen thousands of drugs to determine which agents have the strongest ability to kill Borrelia spirochetes (Feng 2014). This is possible because of the development of high throughput assays, which have identified new antibiotics that have proven more effective than the standard agents (doxycycline, amoxicillin) in eradicating both the stationary phase Borrelia and its more drug-tolerant persister-forms. While it cannot be assumed that what is true in the lab setting will translate to efficacy in humans, biotechnology advances have enabled the identification of new therapeutic agents, offering much hope for a wider array of treatment options for patients in the future.
Another major advance is “big data” conducted by biomedical information engineers trained in biostatistics and computer science. Internet search engine queries are being monitored to predict outbreaks of infectious disease. Unanticipated side effects of drugs and their interactions can be detected through analyzing millions of digital medical records from patients who have taken a particular drug. One can examine whether patients given an antibiotic did better when treated for longer or shorter periods, or whether patients with a pre-existing autoimmune disease are more likely to develop complications from a new onset Tick-borne infection than those without a history of autoimmune problems.

The blacklegged ticks, I. pacificus, (depicted here), and I. scapularis, are known vectors for the zoonotic spirochetal bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi, which is the pathogenic bacteria responsible for causing Lyme disease. The ticks, inoculated with the bacterium when they bite infected mice, squirrels and other small animals, subsequently pass the pathogens to their human victims when they obtain a blood meal.B. burgdorferi bacteria can infect several parts of the body, producing different symptoms at different times. Not all patients with Lyme disease will have all symptoms, and many of the symptoms can occur with other diseases as well. If you believe you may have Lyme disease, it is important that you consult your health care provider for proper diagnosis.
The first sign of infection is usually a circular rash called “erythema migrans”, or EM. This rash occurs in approximately 70-80% of infected persons and begins at the site of a tick bite after a delay of 3-30 days. A distinctive feature of the rash is that it gradually expands over a period of several days, reaching up to 12 inches (30 cm) across. The center of the rash may clear as it enlarges, resulting in a bull’s-eye appearance. It may be warm but is not usually painful. Some patients develop additional EM lesions in other areas of the body after several days. Patients also experience symptoms of fatigue, chills, fever, headache, and muscle and joint aches, and swollen lymph nodes. In some cases, these may be the only symptoms of infection.
Our Lyme and Tick-borne Diseases Research Center, located at the Columbia University Irving Medical Center (CUIMC) in New York City, is right next door to an international data resource. CUIMC is the coordinating center of a public health information initiative which includes medical records from approximately 400 million people drawn from eighty health-care organizations from around the world. This represents a unique opportunity to ask questions, generate hypotheses and get answers about Tick-borne diseases. When discovery is optimized, medical care is enhanced.
For the Silo, David Wine/CM RubinWorld.
Brian Fallon, MD, MPH is the Director of the Lyme and Tick-Borne Diseases Research Center at the Columbia University Irving Medical Center and the author with Jennifer Sotsky of Conquering Lyme Disease: Science Bridges the Great Divide, published in 2018 by Columbia University Press.