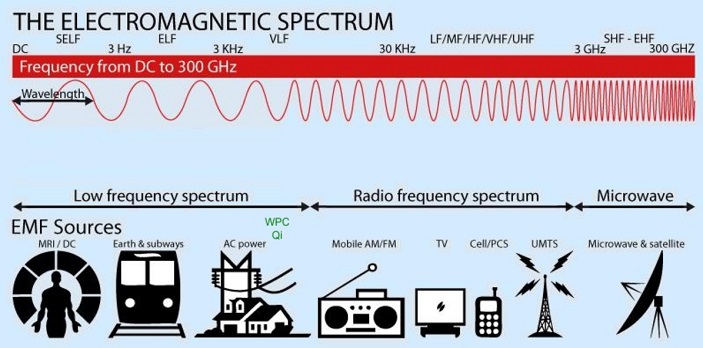
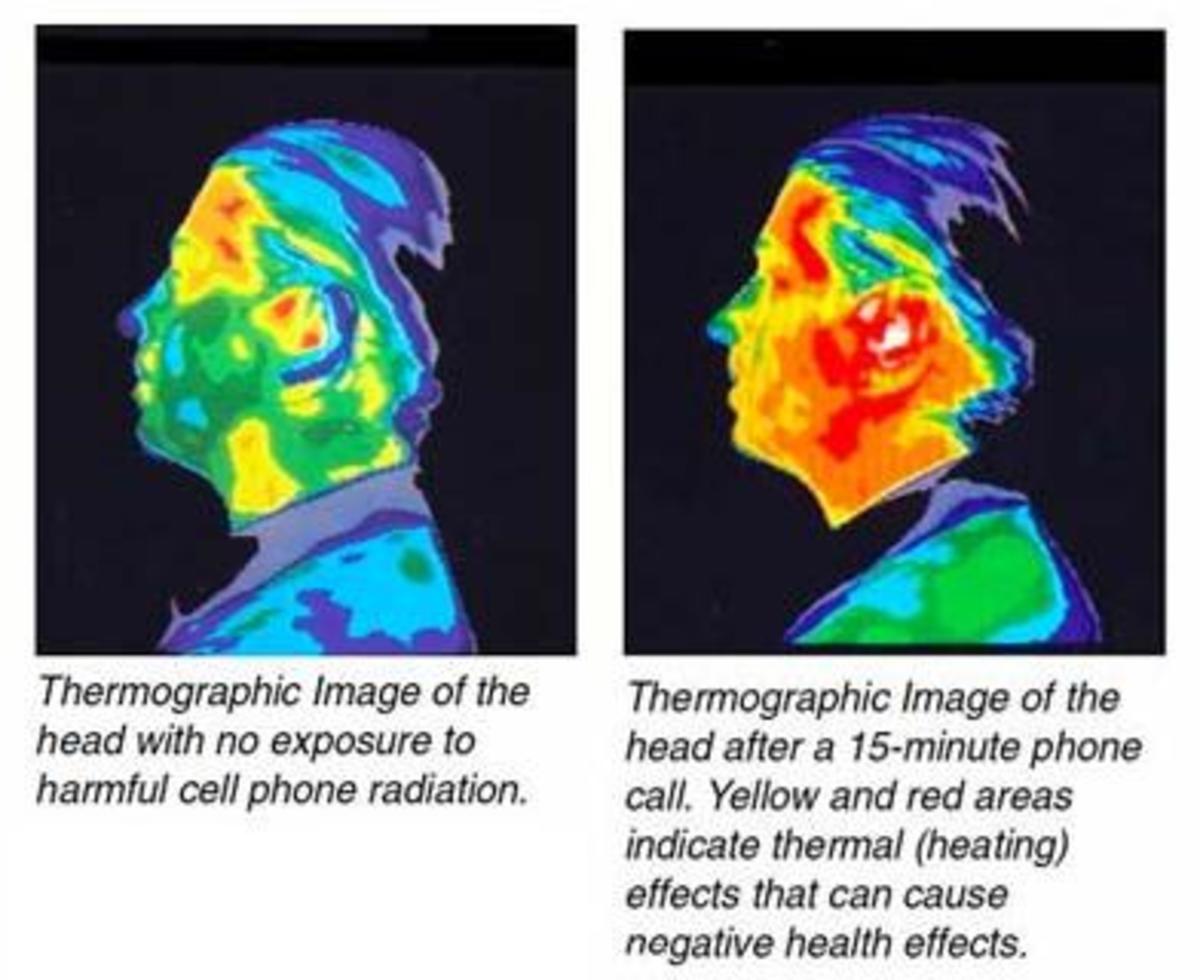
It occurs naturally in our environment, coming to us from the sun, from the soil and foods that we eat, and in the air that we breathe. It is omnipresent across a diverse cross section of industries. We tend to associate radiation with the nuclear industry, but the reality is that we come across radiation sources in numerous other areas: construction, health care, oil and gas, research, manufacturing, food processing – to name just a few.
With radiation being everywhere in our lives, it is not surprising that it garners a lot of attention, curiosity and, often, worry.
With more than 15 years as a career radiation protection professional, I’ve had to respond to many occupational radiation safety questions — some have related to regulations and compliance, others to potential health effects of exposure and ways to minimize such exposure. In all cases, it is best to rely on well established radiation physics concepts and scientific data, where available.
While there is not much that we can do to escape natural background radiation exposure, we do want to avoid any unnecessary exposure to high levels of radiation, such as the potential hazard due to elevated radon (a radioactive gas) in our homes and workplaces.
Radon testing of homes is the simplest first step you can take to protect yourself and your family from radon gas, but all too often we do not make the time to educate ourselves and make this a priority. Workplaces are required to have a radiation protection program in place that is appropriate for the type of radiation and potential risk in their industry. But it takes time and investment to develop these programs, and it requires the commitment of both employers and workers to put these programs into practice.
Our challenge is that radiation and its associated risks are not always well understood.
On the one hand, we do not wish to alarm anyone unnecessarily, yet we want to make sure that the public, workers and employers are aware of the steps they need to take to stay safe. Remember, we are talking about an “invisible” hazard that very rarely causes ill health effects in the short-term. Additionally, the existing radiation protection models are built on what we call the linear no-threshold concept, which, in simple terms, is based on studies of the atomic bomb survivors from the Second World War in Japan and other high-exposure situations, and extrapolates the information to the potential health effects of low exposures.
An agency of the World Health Organization (WHO) recently published a study on the health effects of low-level exposure to radiation that provides data to support the validity of the linear no-threshold model. We encourage all who read the study (available at The Lancet Haematology) to not get alarmed and to keep the study conclusions in perspective.
It suggests that extended exposure to low level of radiation increases the risk of developing leukemia.
A frightening statement, but we have to keep in mind that the increased risk is small, in line with what we have estimated based on the modeling concepts. This boils down to two things: first, it is important that we continue to apply the ALARA principle — “As Low as Reasonably Achievable” — to all our of interactions with radiation; and second, that we continue to view the numbers associated with radiation and risk in the proper context. The study points to a “small increase” of risk of dying from cancer from low levels of radiation exposure.
Let’s put this into perspective.
If we extrapolate this study’s conclusions for nuclear workers to persons living near Canadian nuclear plants, people are 6,000 times more likely to die in a car accident, than to die from leukemia due to doses received from reactor plant emissions. Yet most of us think nothing of driving to work, driving our kids to school, or driving to visit friends and family. The radiation risk is there, but it is significantly smaller than the risks we accept every day, often without even thinking or worrying about them.
More research is required on the health risks from low-level radiation exposure, and there are efforts underway around the world to make it happen. At the Radiation Safety Institute, we will be looking forward to hearing about more study results. In the meantime we invite all people who are interested in the subject of radiation safety, who have a question or a concern, to reach out to our Free Information Service at 1-800-263-5803 or by e-mail at info@radiationsafety.ca. Let’s keep the conversation going. For the Silo, Laura Boksman Chief Scientist at the Radiation Institute of Canada.