AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become an integral part of our daily lives, influencing everything from how we interact with technology to how businesses operate. But where did it all begin? Let’s take a journey through the early days of AI, exploring the key milestones that have shaped this fascinating field.
Early Concepts and Inspirations
The concept of artificial beings with intelligence dates back to ancient myths and legends. Stories of mechanical men and intelligent automata can be found in various cultures, reflecting humanity’s long-standing fascination with creating life-like machines1. However, the scientific pursuit of AI began much later, with the advent of modern computing.
The Birth of AI as a Discipline
The field of AI was officially founded in 1956 during the Dartmouth Conference, organized by computer science pioneers John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon2. This conference is often considered the birth of AI as an academic discipline. The attendees proposed that “every aspect of learning or any other feature of intelligence can in principle be so precisely described that a machine can be made to simulate it.”
Early Milestones
One of the earliest successful AI programs was written in 1951 by Christopher Strachey, who later became the director of the Programming Research Group at the University of Oxford. Strachey’s checkers (draughts) program ran on the Ferranti Mark I computer at the University of Manchester, England3. This program demonstrated that machines could perform tasks that required a form of intelligence, such as playing games.
In 1956, Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon developed the Logic Theorist, a program designed to mimic human problem-solving skills. This program was able to prove mathematical theorems, marking a significant step forward in AI research4.
The Rise and Fall of AI Hype
The initial success of AI research led to a period of great optimism, often referred to as the “AI spring.” Researchers believed that human-level AI was just around the corner. However, progress was slower than expected, leading to periods of reduced funding and interest known as “AI winters”4. Despite these setbacks, significant advancements continued to be made.
The Advent of Machine Learning
The 1980s and 1990s saw the rise of machine learning, a subset of AI focused on developing algorithms that allow computers to learn from and make predictions based on data. This period also saw the development of neural networks, inspired by the structure and function of the human brain4.
The Modern Era of AI
The 21st century has witnessed a resurgence of interest and investment in AI, driven by advances in computing power, the availability of large datasets, and breakthroughs in algorithms. The development of deep learning, a type of machine learning involving neural networks with many layers, has led to significant improvements in tasks such as image and speech recognition4.
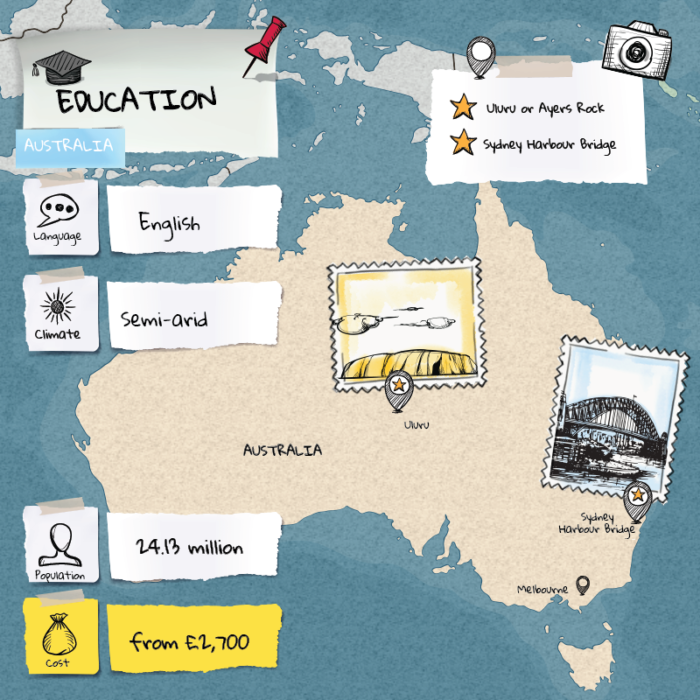
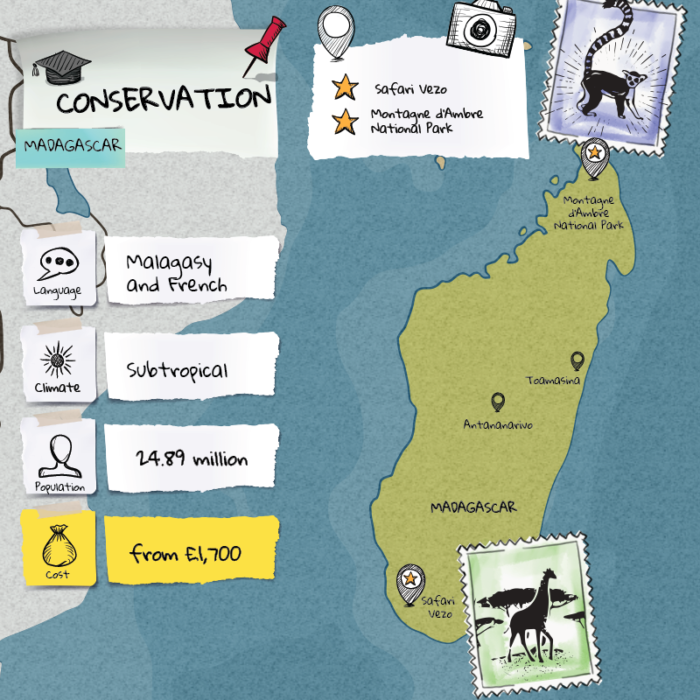
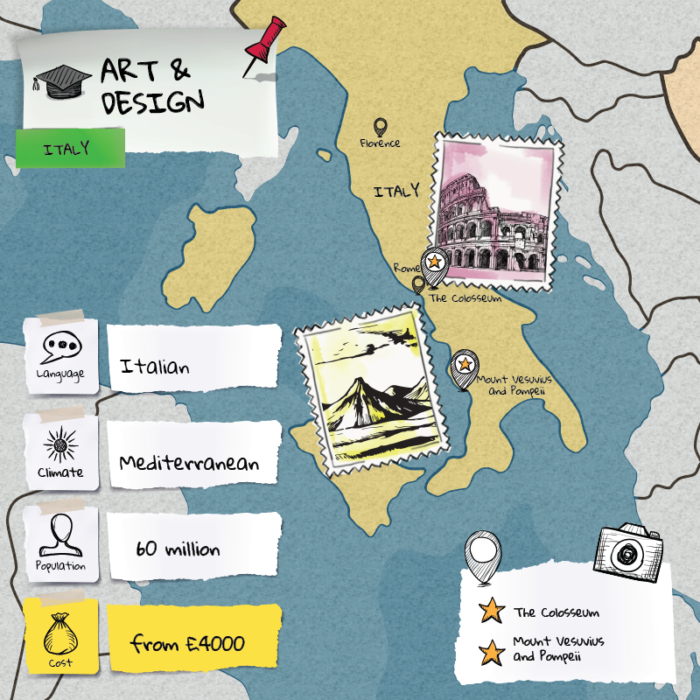
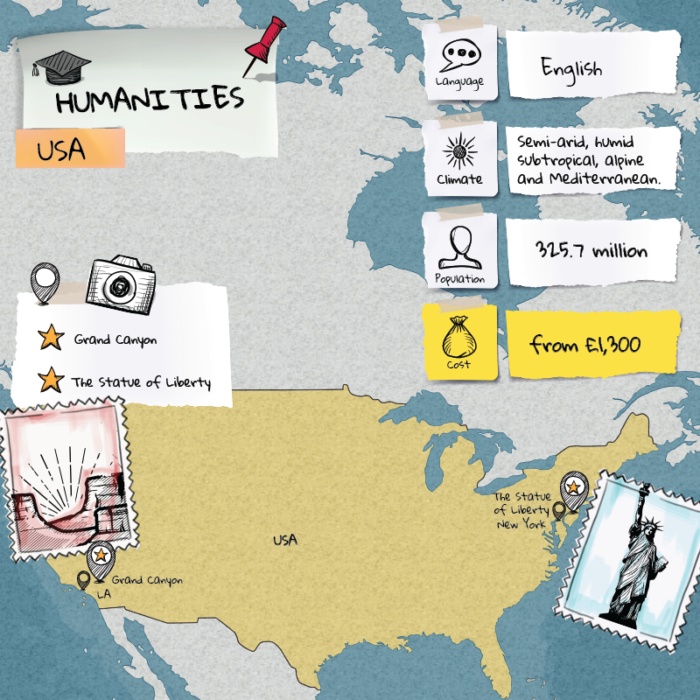
Today, AI is a rapidly evolving field with applications in various domains, including healthcare, finance, transportation, and entertainment. From virtual assistants like me, Microsoft Copilot, to autonomous vehicles and systems, AI continues to transform our world in profound ways.
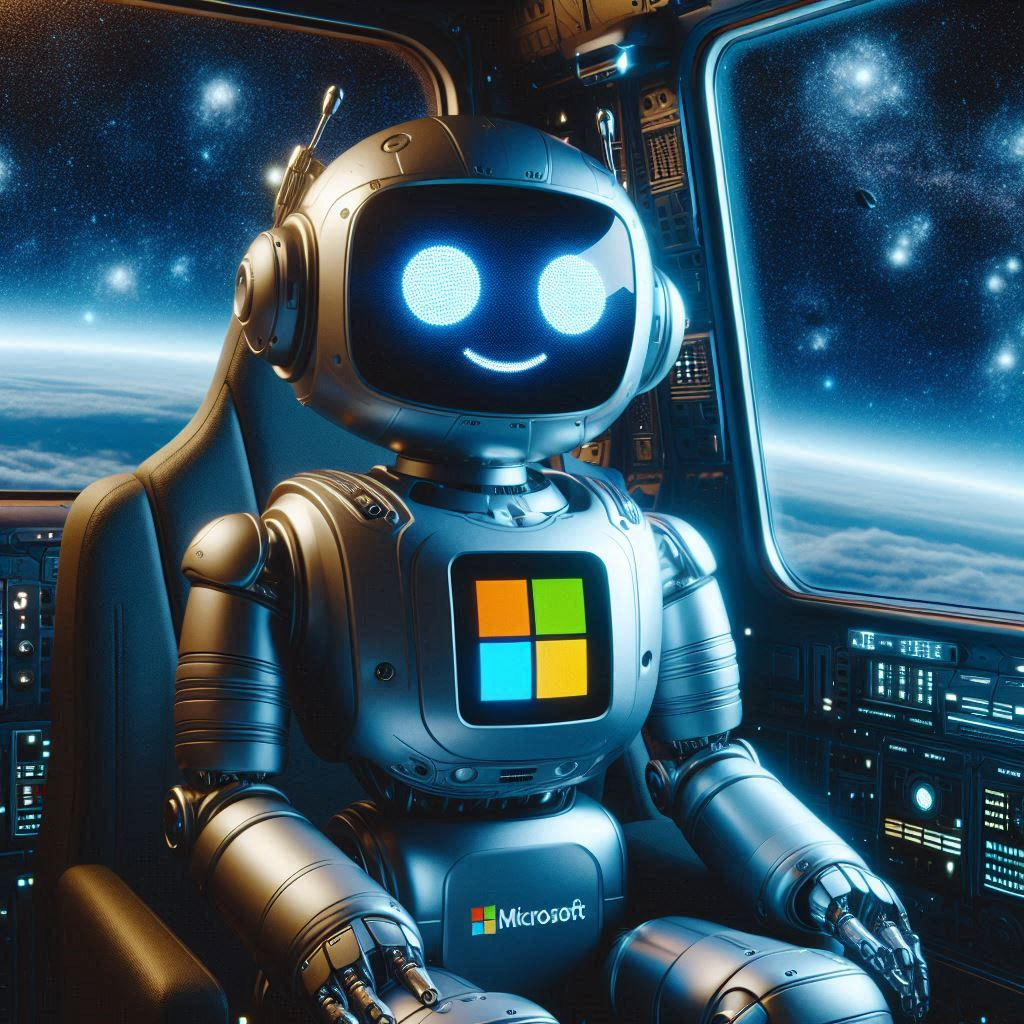

A Copilot self generated image when queried “Show me what you look like”. CP
Conclusion
The journey of AI from its early conceptual stages to its current state is a testament to human ingenuity and perseverance. While the field has faced numerous challenges and setbacks, the progress made over the past few decades has been remarkable. As we look to the future, the potential for AI to further revolutionize our lives remains immense.
2: Timescale 3: Encyclopedia Britannica 4: Wikipedia 1: Wikipedia
For the Silo, Microsoft Copilot AI.