All of modern life is a spectacle. Much of what contemporary man experiences in Western society is a false social construct mediated by images.
These mediated images create desires that can never be fulfilled; they create false needs that can never be met. “Many of our daily decisions are governed by motivations over which we have no control and of which we are quite unaware” (Berger 41). The constant spector of the mediated image creates an endless cycle of desire, consumption, and disinterest, fueling a banality in life that feeds the commodification of life.
Increasingly life itself becomes a commodity and the image more important than the reality it represents. This commodification infiltrates every aspect of human production, including the arts, and finds its pinnacle expression in the work of Damien Hirst. Hirst has carefully crafted a brand identity that has far surpassed the value of his art work in importance and worth. Working in tandem with former advertising executive turned art dealer Charles Saatchi, the spectacle of the Hirst image becomes the commodity. “Reality unfolds in a new generality as a pseudo-world apart, solely as an object of contemplation. The tendency towards the specialization of images-of-the-world finds its highest expression in the world of the autonomous image, where deceit deceives itself” (Debord
143).
No longer is the work of art itself a commodity, but rather the image of the artist (his/her/cis brand) that becomes the commodity.
It is this spectacle that drives the consumer to identify with a particular artist or brand. “The astronomical growth in the wealth and cultural influence of multi-national corporations over the last fifteen years can arguably be
traced back to a single, seemingly innocuous idea developed by management theorists in the mid-1980s: that successful corporations must primarily produce brands, as opposed to products” (Klein 4). The image has increasingly infiltrated and dominated the culture and the whole of society and has become “an immense accumulation of spectacles” (Debord 142).
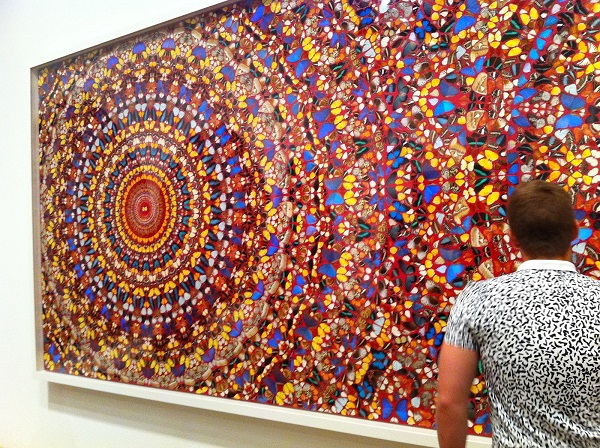

Where once the products of labor were the commodity, now it is the spectacle that has become the commodity.
A prime example of this spectacle is Damien Hirst’s sculpture, “For the Love of God.” The sculpture consists of a platinum skull covered with 8,601 diamonds. The sculpture valued at over $100 million usd/ $129.361,000 cad [exchange rate at time of publication] is clearly out of the reach of almost any collector. The sculpture itself is not the art product, rather it is the spectacle that is the product. “Mr. Hirst is a shining symbol of our times, a man who perhaps more than any artist since Andy Warhol has used marketing to turn his fertile imagination into an extraordinary business” (Riding, nytimes.com). Acknowledging that the sculpture is out of reach for the majority of collectors, Hirst offered screen prints costing $2000 usd/ $2,587 cad to $20,000 usd/ $25,870 cad ; the most expensive prints were sold with a sprinkling of diamond dust.

Karl Marx argued that the value of the commodity arose from its relationship with other commodities; its ability to be exchanged for other commodities. Marx used the the production of a table to illustrate his thesis:
“…by his activity, man changes the materials of nature in such a way as to make them useful to him. The form of wood, for instance, is altered if a table is made out of it. Nevertheless the table continues to be wood, an ordinary, sensuous thing. But as soon as it emerges as a commodity, it changes into a thing which transcends sensuousness.” (Marx 122)
Hirst’s diamond encrusted skull remains mere diamonds, valuable yes, but still diamonds. However, when coupled with the spectacle of Damien Hirst’s identity, the skull becomes a fetishized commodity capable of selling screen-prints valued in the thousands. The argument can be made that diamonds on their own carry value, and could be commodities themselves, however that doesn’t account for the fact the Hirst was able to sell prints of the skull for over $2000 usd/ $2,587 cad. Nor do the diamonds alone account for the spectacle surrounding the art work; it is Hirst’s brand, his image that creates the spectacle.
“The mystical character of the commodity does not therefore arise from its use-value. Just as little does it proceed from the nature of the determinants of value” (Marx 123). The value of a commodity arises from its spectacle, its ability to be desired. In Marx’s day that desire was its ability to be traded for other commodities; today that value is derived from its association to a brand, an identity, a spectacle. “Art reflects the illusory way in which society sees itself, it reflects the bourgeoisie’s aesthetic ideas as if they were universal” (Osborne 79).
The spectacle feeds itself through the mediating of the image to create desire for status and recognition, through associations.
“The ends are nothing and development is all – though the only thing into which the spectacle plans to develop is itself” (Debord 144). The spectacle’s main objective is self perpetuation. Its aim is totality. It must be noted that Hirst himself did not even create the work of art, but rather employed a studio full of jewelers to execute the sculpture, and printers to produce the prints.
Hirst exemplifies the bourgeoisie capitalist employer who retains ownership over the fruit of the employees’ labor. He is in many ways more akin to a captain of industry than he is to the romantic notion of an artist. “In the early twenties, the legendary adman Bruce Barton turned General Motors into a metaphor for the American family, something personal, warm and human” (Klein 7). Hirst has also turned himself into a metaphor, however, metaphors aren’t always true. This falsehod is at the heart of the issue. The spectacle isn’t concerned with what is true, rather it is concerned with what can be made to appear true. It is this appearance of truth that makes a commodity valuable. This fetishism of the commodity is why gold and silver have value, it is because people gave them value. It is the reason Damien Hirst, or any other brand, has value, because people gave it value.
Damien Hirst cannot be blamed for commodifying art, he is simply following a long tradition of turning objects and products into commodities. The fact that his commodity is his own image doesn’t seem to matter. “Hirst is just playing the game. It is a game played by collectors and dealers at art fairs throughout the year; it is a game finessed as never before by Sotheby’s and Christie’s; it is a game in which, in the words of Nick Cohen, a rare British journalist to trash Mr. Hirst’s publicity coup, ‘the price tag is the art’ ” (Riding .nytimes.com).
That final statement beautifully summarizes the commodification of art, ‘the price tag is the art.’ The fact that the art is obscenely priced, and out of the reach for the majority of collectors, the fact that it is made of diamonds, a precious stone known as the blood stone because of its association with brutal and oppressive regimes, merely adds to its allure, to its spectacle. Damien Hirst is merely playing the game, like many before him. He is a part of the growing culture
industry that sells image. Images are the new commodity fetish. Images are the new mysterious commodities exchanged for more the more durable and enduring commodities. The bourgiousie sell their images, which have no real value, to the public which consumes them, in exchange for goods of real value.
“The $200 billion usd/ $270 billion cad culture industry – now North America’s biggest export – needs an every-changing, uninterrupted supply of street styles, edgy music videos and rainbows of colors. And the radical critics of the media clamoring to be ‘represented’ in the early nineties virtually handed over their colorful identities to the brand masters to be shrink-wrapped.” (Klein 115)
Nick Cohen said of Hirst, “[he] isn’t criticizing the excess, not even ironically … but rolling in it and loving it. The sooner he goes out of fashion, the better.” What Cohen fails to realize is that the spectacle is a fashion. And when one image goes out of fashion, another takes its place. Hirst may indeed go out of fashion, but another art brand will take his place, perpetuating the commodification of the arts in increasingly bombastic ways.

Perhaps art has always been a commodity?
In the past patrons would hire artists to paint them into scenes from the gospels. Patrons could be seen on the outskirts of paintings piously praying, thus creating an image of themselves as good and pious Christians. By association with the sacred art, the patron was creating a mediated image. Rulers did this all the time. The Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius is a perfect example. Its a mediating image that communicates power and authority.
But none of these examples reach the level of spectacle and fetishism that is Damien Hirst. While art may have been a commodity in the past, it was never commodified. In other words, while the art itself may have been exchanged for other goods, the artist himself was not treated as a commodity. The art of the past may have served a purpose, it may have contained a mediated message, but it was still a product, and it was the product that was valued, not its brand identity.
The commodification of art creates a unique problem in history. If it is the spectacle that matters, and the artist’s identity that has value, then what value is left in the art itself?
What then separates art from ordinary objects? Is there any aesthetic emotion that remains in the work of art itself, or does the aesthetic emotion dwell completely within the spectacle? These are questions that cannot easily be answered, and ultimately will require the lens of history to answer completely. But they are a pressing concern, for when art is commodified, it may cease to be art and instead become celebrity, product, or worse, advertising. For the Silo, Vasilios Avramidis
Works Cited
Berger, Arthur Asa. Seeing is Believing: An Introduction to Visual
Communication. New York, NY: McGraw Hill, 2008. Print.
Debor, Guy. “Showing Seeing: A Critique of Visual Culture.” The Visual Culture
Reader. Ed.Nicholas Mirzoeff. New York, NY: Routelage, 1998. 142-144. Print.
Klein, Naomi. No Logo, No Space, No Choice, No Jobs. New York, NY: Picador, 2000.
Print.
Marx, Karl. “Showing Seeing: A Critique of Visual Culture.” The Visual Culture
Reader. Ed.Nicholas Mirzoeff. New York, NY: Routelage, 1998. 122-123. Print.
Riding, Alan. Alas, Poor Art Market: ‘A Multimillion Dollar Headcase.’ The New York
Times. June 2007, Damien Hirst and the Commodification of Art http://www.visual-studies.com/interviews/moxey.htm