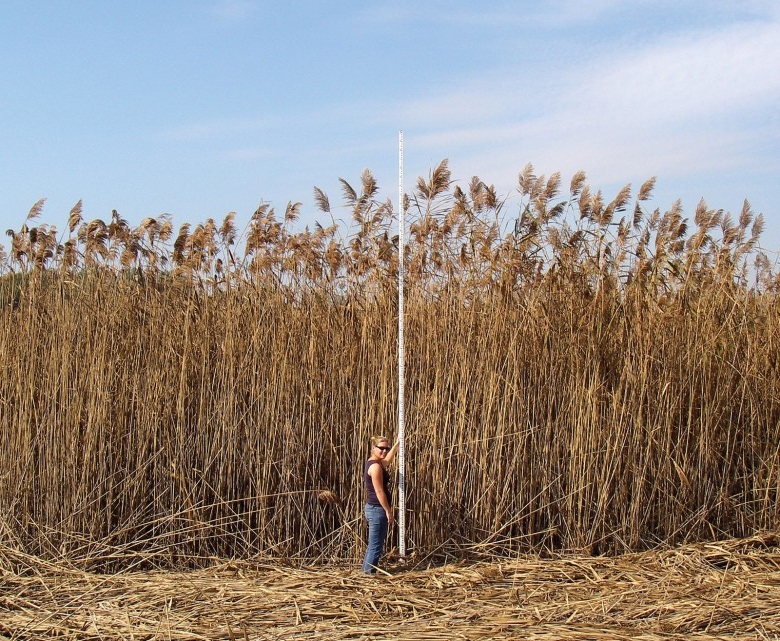
Phragmites is likely the largest invasive plant threat facing Ontario today. It has taken over our wetlands, invaded our ditches and can get a foothold just about anywhere. It’s the monster that keeps coming back – we can’t let our guard down.
Phragmites was first found locally in the Long Point wetlands 20 years ago.
Spraying of glysophate started at Long Point and Rondeau Provincial Parks in September 2016, and has proven 99.7 per cent successful. When the phragmites is dead, the seed bank of native species, like cattails, will reactivate. Although spraying works, it must be followed up by rolling or cutting and burning. On Long Point Bay, there is a combination of private, provincial and federal wetlands. Much of the private wetlands are in the hands of hunt clubs, most of which have been active in controlling phragmites.
The Crown Marsh and the Turkey Point beaches are provincial holdings.
The Canadian Wildlife Service land, which comprises most of the point itself and the Big Creek marsh, are federal. I recently attended the meeting of the Long Point Phragmites Action Alliance – a local group dedicated to fighting this invader. They donated $20,000 toward continuing spraying in the Long Point Crown Marsh last year. Their annual fundraiser, Rocking the Point, will be August 24th.
My office worked tirelessly to ensure phragmites were sprayed last fall at Turkey Point beach after several years of inaction by the previous government. This spring the dead plants were flattened and burned. The Ministry of Natural Resources and Forestry is working with a number of conservation partners to coordinate prevention, control, research and management activities to help address this serious threat in recognition of the importance of the prevention, early detection, early response and eradication of invasive species.
This year the Ontario government is investing over $2 million in invasive species programs and education, and will be investing $850,000 in the centre to support ongoing research and management. Based in Sault Ste. Marie, the centre brings together government, academia, industry and Indigenous communities and organizations to conduct research, response planning, management and habitat restoration.
Early detection is especially important because once invasive species become established it is extremely difficult to remove them, potentially causing long-lasting damage to our environment.
For federal lands, thanks to the actions of MP Diane Finley, the Nature Conservancy of Canada (NCC) will receive $375,000 over the next three years to aid in the removal and prevention of phragmites growth in sensitive ecosystems. Recently, we saw another win for the ongoing control of phragmites with the Ontario Trillium Foundation’s significant contribution of $90,000 to NCC to purchase a boat to control this invasive. Now in its fourth year, the partners have effectively controlled phragmites in over half the coastal wetlands at Long Point and Turkey Point.
With the help of the Ontario Trillium Foundation funds, NCC will be able to continue monitoring the shorelines for phragmites – catching remnant populations before they spiral out of control. Early detection and constant monitoring and control are key to successfully eradicating those devastating invaders and returning the marshes and shorelines to havens for turtles, birds and waterfowl. Although $2 million has been spent on phragmites control in the area, we must be vigilant as the monster will return. For the Silo, Toby Barrett MPP for Haldimand-Norfolk.
Supplemental- The Ontario Phragmites Working Group.
Featured image- Phragmites Great Lakes region photo by Janice Gilbert 2007