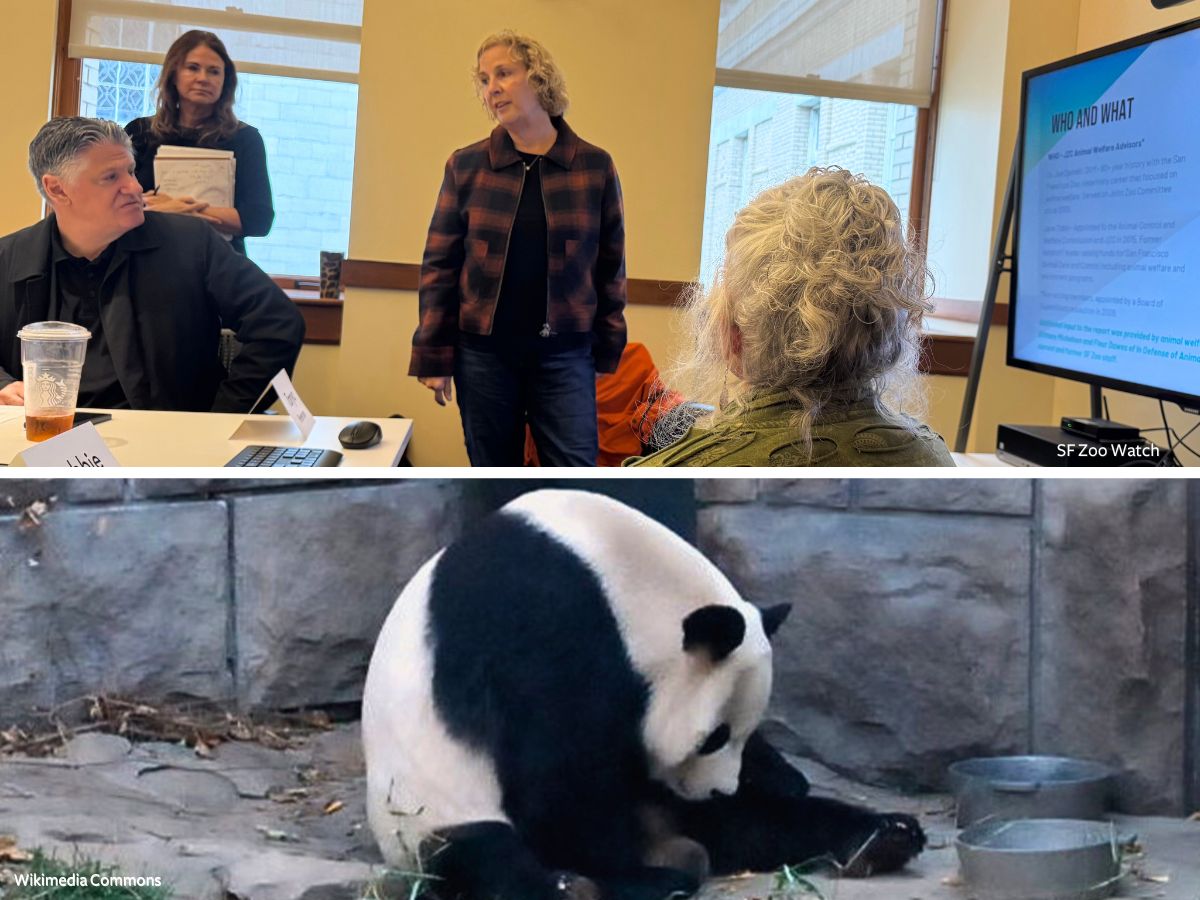

SAN FRANCISCO (November, 2024) — A report “daylighting” serious animal welfare, management and infrastructure failings at San Francisco Zoo was presented yesterday by the San Francisco Joint Zoo/Recreation and Parks Committee Animal Welfare Advisors, Jane Tobin and Joseph Spinelli DVM. The report contains a “complete list of habitat and welfare issues as well as facilities recommendations,” and critiques unsafe infrastructure, mismanagement, and misplaced priorities, while offering actionable solutions to address the zoo’s deep-rooted issues.
Tobin explained, “This is an opportunity for people to understand, like, where are we with the state of the zoo? Having an audit like this does definitely daylight a lot of issues.” Tobin raised a variety of “habitat issues, oversight issues, acquisition plan issues,” and urged the zoo to prioritize habitat updates and genuinely engage with public concerns, reminding it of its duty to respond to public records requests and update its “really out of date” Memorandum of Understanding, last updated in 1993.
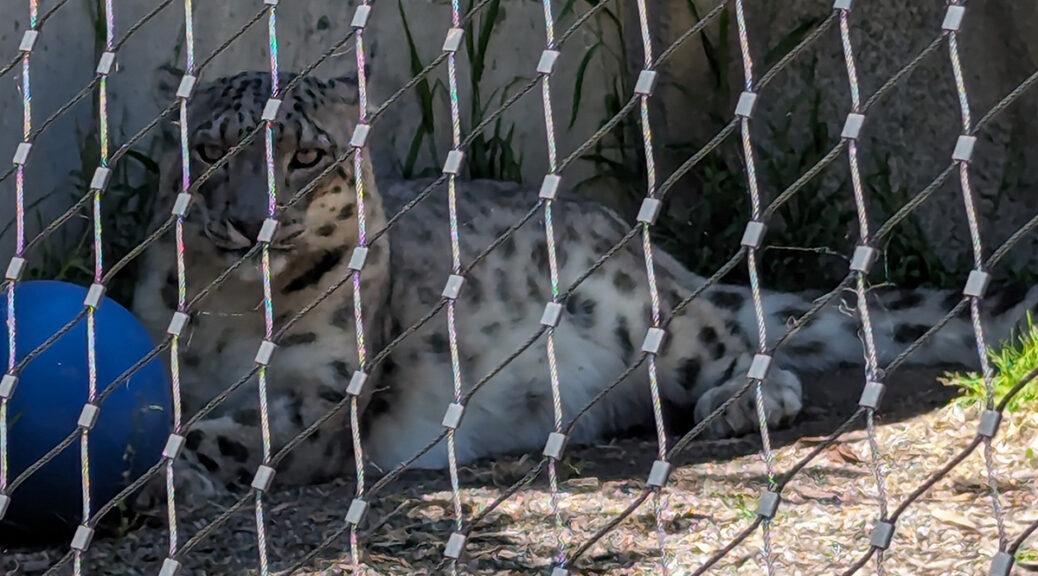
The report, which was prepared in consultation with current and former zoo staff, the San Francisco Animal Commission and animal welfare organizations including In Defense of Animals, SF Zoo Watch and Panda Voices, details “many of the Zoo’s enclosures are extremely outdated and fail to meet the criteria outlined above from an animal welfare perspective” with some exhibits approaching 100 years old. Tobin shared in the meeting, “It has been a really long time since we’ve seen any infrastructure updates, habitat construction, renovations, and short or long-term plans, and I think that you might ask the questions, well, how does that impact animal welfare? A great deal.”
Report co-author Dr. Spinelli has a long history with San Francisco Zoo and has served as an animal welfare advisor on the Joint Zoo Committee since 2009. He said, “For the future, I haven’t heard of a strategic plan for improving the quality of the spaces for the animals.”
Tobin drew attention to many animals in temporary habitats “well beyond their deadline,” citing one case in which animals have been without a permanent enclosure for six years. She said, “Animals should have a permanent habitat ready upon arrival and a financial impact analysis report would be wonderful so that the committee can fully understand with that acquisition what impact it would have on the care of the current animal inhabitants and the existing strategic plan.”
Concerning highly-controversial plans to acquire giant pandas, the report states, “The arrival of the giant pandas would make the already poor situation of the current animals living at the zoo even worse, diverting attention and resources away from doing basic repairs and building exhibits for other animals.”
Report Highlights:
- Update the MOU: Modernize the 1993 agreement to include robust animal welfare standards and appoint non-voting advisors, such as veterinarians and animal welfare experts, to ensure ethical oversight.
- Reject the Panda Plan: Halt the multi-million dollar panda exhibit and focus resources on improving the welfare of current animals and fixing infrastructure.
- Infrastructure Overhaul: Redesign outdated enclosures to meet modern ethical and safety standards.
- Transition the Zoo: Implement a rescue and rehabilitation model instead of trading and breeding programs.
- Establish Oversight: Create an independent commission focused on animal welfare with robust authority.
The zoo audit follows a San Francisco Chronicle investigation and series of articles exposing zoo mismanagement, as well as a catalog of current concerns raised by animal advocates including the zoo’s reckless plans to import giant pandas from China by 2025. An In Defense of Animals’ alert exposing the issues at the zoo and urging the cancellation of the panda plans has gained over 14,000 supporters.
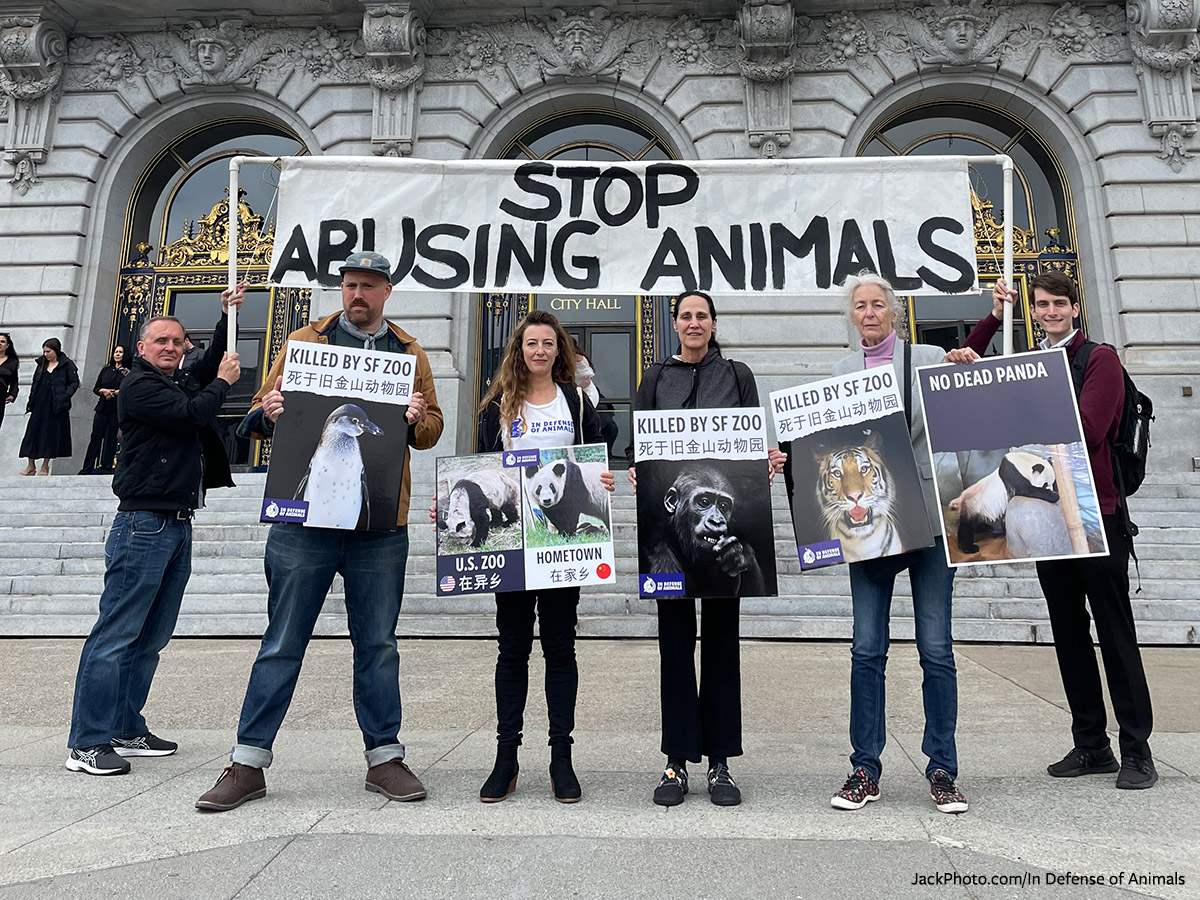

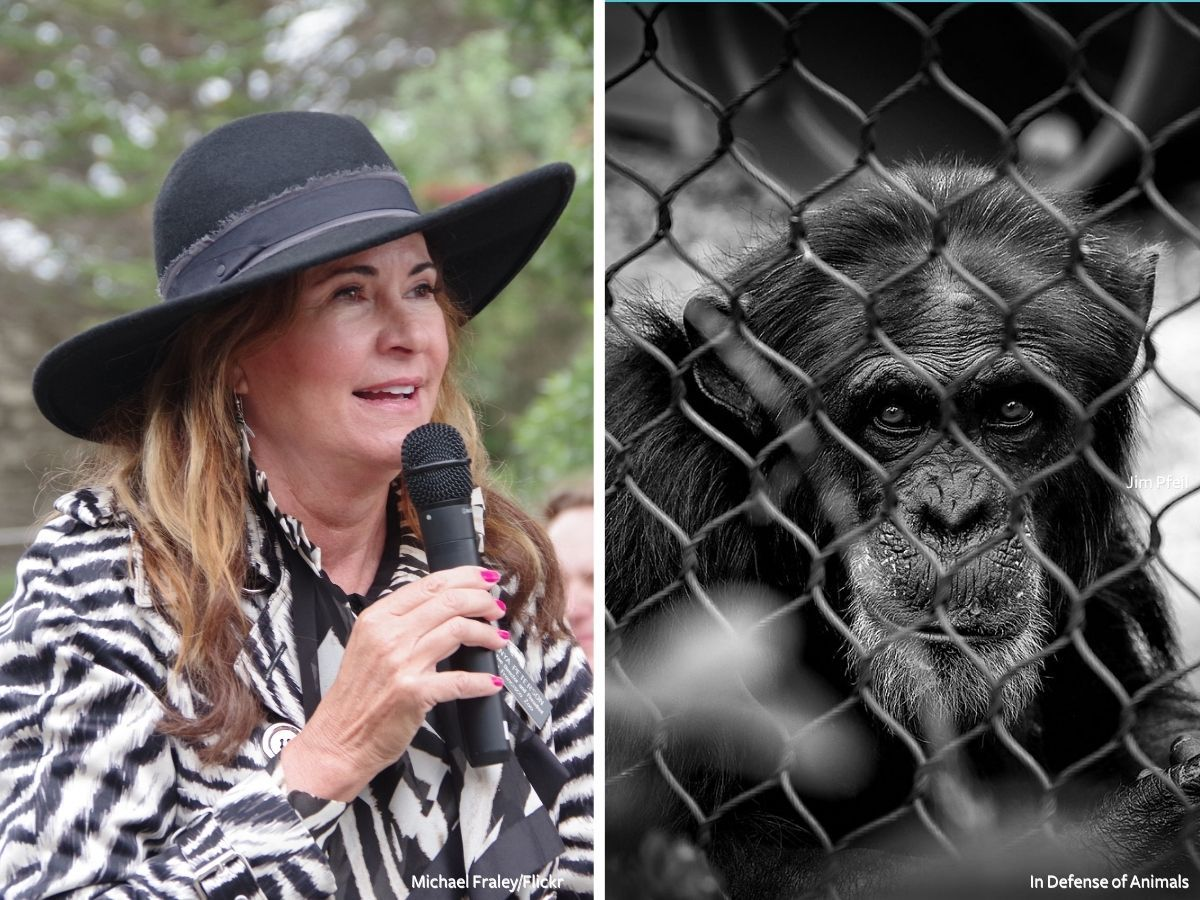
“We are grateful for the recommendations report from the Joint Zoo/Recreation and Parks committee animal welfare advisors which illustrates extreme issues that must be fixed at San Francisco Zoo,” said Brittany Michelson, Campaign Specialist for Captive Animals at In Defense of Animals. “These recommendations should be taken seriously and implemented immediately.”
Justin Barker of SF Zoo Watch said, “I think we need to get real about the zoo. 97% of the union staff don’t have confidence in the management, yet you stood by the CEO. We have major infrastructure issues. Stop painting the rosiest picture.”
Interjections from angry docents during the meeting were quelled by Commissioner Larry Mazzola who admitted, “communication is important and it might have been lacking until today.”
However, after the meeting, several zoo docents hurled verbal abuse at Barker. They brandished a photo of the zoo’s langur exhibit, one of the poorest habitats cited in the report, calling out, “You are complaining about this? How dare you!”
They also made public comments in the meeting urging all concerned to “move on” and suggested incidents were isolated to the deadly tiger escape 15 years ago. The audit is the latest of a mountain of evidence exposing current failings from zoo staff, media, and animal welfare organizations. The committee heard today how two additional animals were reported to have died last month from unsafe conditions — a penguin who died with a mold-caused infection, and a pelican who is presumed to have died from predation owing to an unsafe enclosure.
Notable zoo safety incidents include:
- 2007 – The escape of Siberian tiger Tatiana, who killed a visitor before being shot
- 2011 The theft of squirrel monkey Banana Sam
- 2014 – The crushing of baby lowland gorilla Kabibe by a hydraulic door malfunction
- 2020 – The theft of endangered lemur Maki
- 2020 – The deaths of two wallaroos and a red kangaroo who were killed when a predator entered their unsafe enclosure
- 2023 – The death of Handy Harry, a young penguin struck and killed by a guillotine door
- 2023 – The near-death of a keeper when a grizzly bear chased her owing to a door malfunction
- 2024 – The death of a sacred ibis due to unsafe, filthy conditions in the birdhouse by aspergillosis — an infection caused by mold
- 2024 – Two further deaths of a penguin and pelican possibly caused by mold and predation in October
These incidents represent only a fraction of the zoo’s long history of neglect and unsafe conditions. A significant number of keepers have resigned, citing management’s negligence towards both animal and staff safety.

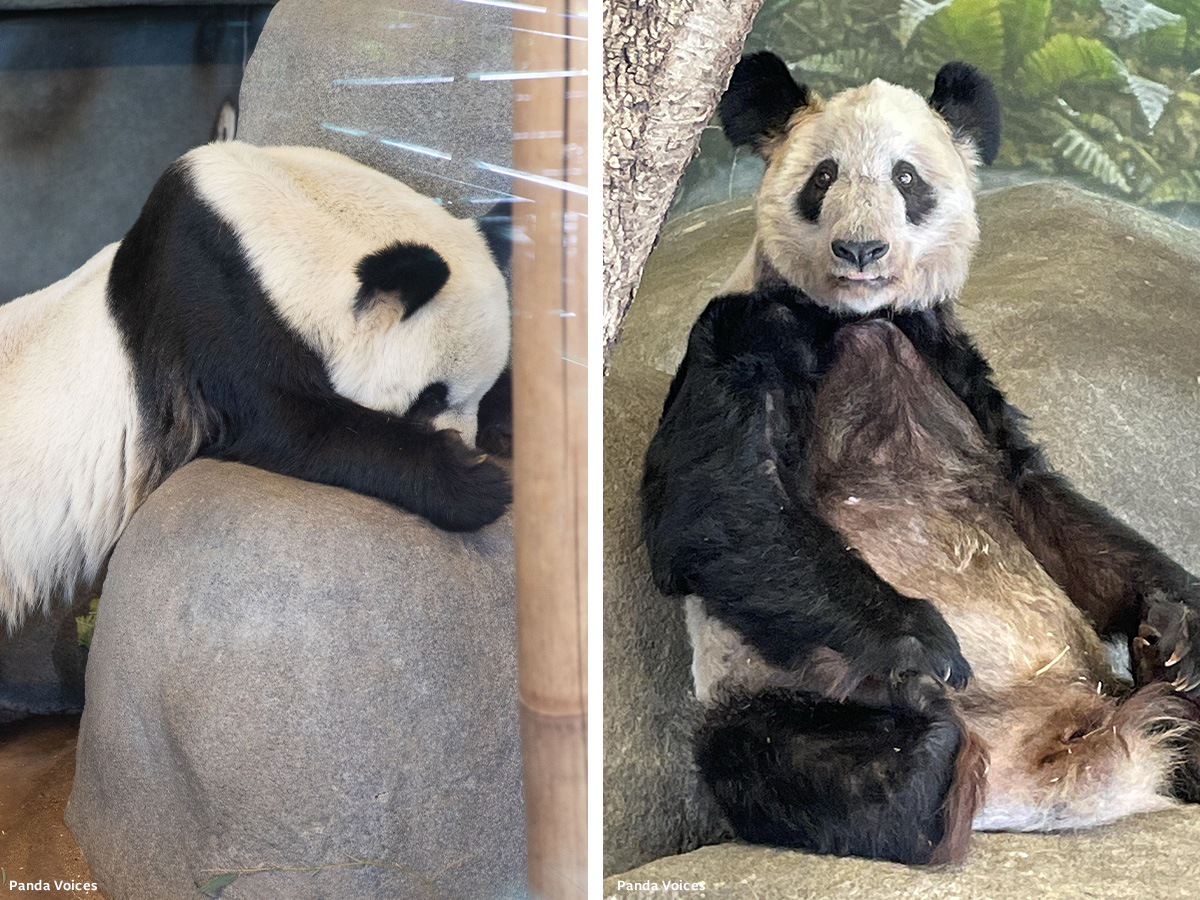
San Francisco is grappling with an $800 million usd/ $1.12 billion cad budget shortfall that has already led to deep cuts in public services like health and education. Amid this crisis, the zoo’s plan to acquire pandas — estimated to cost $70 million usd/ $98 million cad over 10 years — is financially irresponsible. While private fundraising might cover initial construction, long-term care for pandas requires significant ongoing resources, including specialized facilities, experienced staff, and regular flights to supply fresh bamboo.
If the zoo incurs expenses that far exceed the revenue generated from panda exhibitions as has happened at other zoos hosting pandas — most recently in Finland and previously in Scotland — the mounting costs may lead to a shortage of bamboo supply and poor bamboo quality, compromising the welfare of the pandas, as happened at the Memphis Zoo which led to pandas’ ill health and death.

Adding to these concerns, the proposed habitat — rumored to be a repurposed big cat exhibit near predators — is severely unsuitable for pandas, who are highly sensitive to noise and smell. This plan exemplifies the zoo’s misplaced priorities, diverting attention and resources from fixing crumbling infrastructure and addressing the welfare of its current inhabitants.
Members of the public are encouraged to sign the alert urging decision-makers to halt the panda plan: https://idausa.org/sfpanda
Supplemental-
The Humane Future of Zoos? The Hologram Zoo is a thing.







 The list was selected from over 60 facilities from southern Canada to Mexico where almost 1,000 whales and dolphins are held captive for public display. “Forcing an orca to live in solitary confinement while hoarding so many beluga whales is Marineland’s tragic dichotomy, and a horrific example of cetacean captivity. It plumbs the depths in its exploitation of intelligent and sensitive animals,” said In Defense of Animals President, Dr. Marilyn Kroplick. “Even with the most modern technology, veterinary care, and infrastructure, cetaceans still suffer intensely in captivity and exhibit surprisingly high mortality rates.Please help protect dolphins and whales in the wild where they belong, by pledging to never visit facilities that imprison them.”
The list was selected from over 60 facilities from southern Canada to Mexico where almost 1,000 whales and dolphins are held captive for public display. “Forcing an orca to live in solitary confinement while hoarding so many beluga whales is Marineland’s tragic dichotomy, and a horrific example of cetacean captivity. It plumbs the depths in its exploitation of intelligent and sensitive animals,” said In Defense of Animals President, Dr. Marilyn Kroplick. “Even with the most modern technology, veterinary care, and infrastructure, cetaceans still suffer intensely in captivity and exhibit surprisingly high mortality rates.Please help protect dolphins and whales in the wild where they belong, by pledging to never visit facilities that imprison them.”

