 SUP- Stand up paddling is a popular sport along the Grand River system. image: grandriverrafting.ca
SUP- Stand up paddling is a popular sport along the Grand River system. image: grandriverrafting.ca
Is the water level in the river going to be okay for canoeing or kayaking on any given weekend?
This is a common question that people call the GRCA to ask. It is also an important question. Usually what they mean is ” will there be enough water?”, but occasionally, there is actually way too much water for most people to canoe or paddle safely.
Fly fishermen too need to check river levels so they are safe and don’t get swept off their feet by a strong current.
An angler will likely move to a different area rather than take a chance. As an organization, the GRCA does not make recommendations as to appropriate water flows for recreational activities along the Grand River and its tributaries because there are many variables to consider. Some people have the expertise and training to enjoy high flows that could be fatal to inexperienced and ill equipped paddlers.
Very low flows make for slow going as there may not be enough water for the canoe to float and it may need to be pulled to deeper water at certain times. A skilled paddler will be able to read the water to find the deepest water and will have fewer problems. Some people have a bad day if they have to step out of their boat even once, while others are more tolerant of low flows. That is why there is no definitive answer to this question.
Appropriate water levels are a favorite discussion among paddlers. Those who paddle regularly have their own personal chart, whether it is in their head or on a spreadsheet.
Checking flow information
Many avid river recreation enthusiasts in Southern Ontario bookmark the River Data section of the GRCA’s website and check it when trip planning. This is one of the most visited sections on the GRCA’s website and provides hourly updates on river flows from 39 gauges on the Grand and eight tributaries. Some gauge information is also posted on an Environment Canada website that includes rivers in other parts of Canada, but the GRCA site has data for more gauges from this
watershed.
The main chart here is called the Flow Summary.
Recreational users should pay attention to the column headed “flow.” This one is measured in cubic metres per second or cms. If the rate is 10 cms, that means that 10,000 litres of water is moving past the flow gauge each second at this part of the river. The cms gets bigger as the river moves towards Lake Erie. There are huge changes in river flow due to seasons, weather, ice jams and dam operation.
Compare this to the “summer lowflow” which is the average flow during the dry summer months and you will see in relative terms how much water is flowing down the river. Following this Flow Summary is a list of sections of the rivers and tributaries with graphs. For example, one of the most popular sections of the river for a day trip, Cambridge to Paris, a paddler would check the Galt gauge on the “Middle Grand River“section. The graph will tell you if the level is going up, down, or holding steady. Occasionally a flow gauge does not operate and the information can be inaccurate, so the information is provisional. There is also a River Flow Information line that is updated regularly and can be reached at 519-621-2763, ext. 2511.

Outfitter information
There are several local outfitters in the area and they have cut off levels, when they stop canoe rentals. Canoeing the Grand in Kitchener has a safety section on their website with a five step rating chart for paddling. This scale goes from “Excellent” to “No Go” with five levels, depending on the paddler’s age, skill, expertise and river conditions.
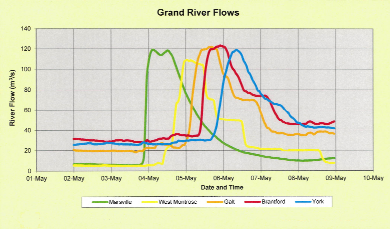
When river flows skyrocket
As the graph above shows, the Grand River may not give much warning of a sudden increase in river flows, which is why the GRCA must sometimes issue high water safety warnings to the public. This is the flow information from the week of May 2 to 9 from a few years ago. Note that it shows heavy rain on Thursday night May 3 in the northern part of the watershed meant flows ballooned from 8 cms to 120 cms within a couple of hours, as the data from Marsville shows. The GRCA issued a warning after the storm. The rainwater gushed down the river and by the afternoon of Friday May 4, flows were dropping at Marsville but skyrocketing at West Montrose. By Saturday May 5, the river flows in Brantford were extreme and then they peaked at York on the southern Grand on Sunday.
A final important note, Dams can make the impact of a rainstorm less severe but they don’t eliminate flooding or high flows.
For the Silo ,Janet Baine, GRCA Communications Specialist

