We tend think of cyborgs as something from the type of ‘horrible future’ depicted in video games and science fiction movies. At least I do, but every once in a while I come across something that reminds me that I am already living in that future. Hate crime against cyborgs may seem like bad fiction, but it has already happened.
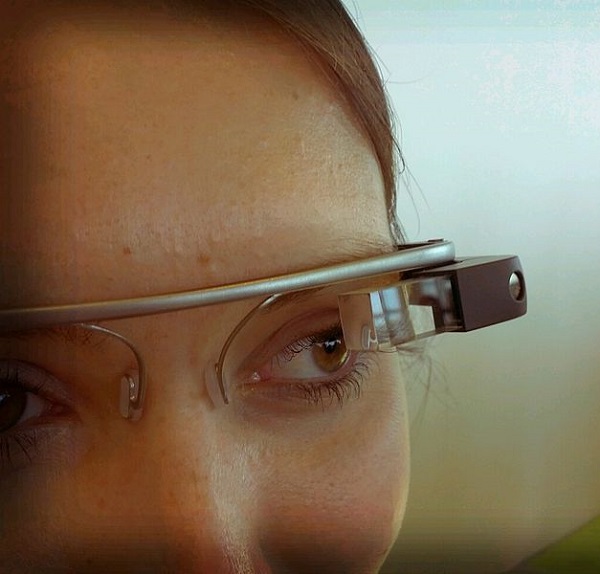
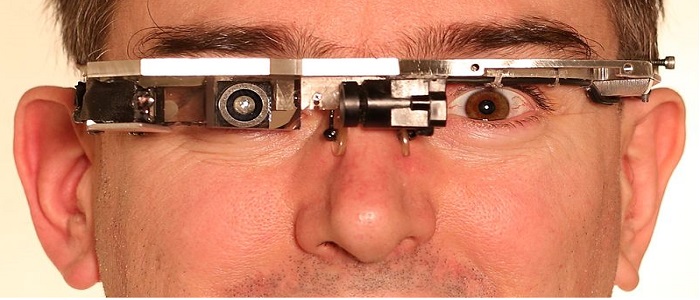
Waaay back in 2012 Toronto cyborg, Steve Mann, claims he was assaulted in a Paris McDonald’s just for wearing his EyeTap. Mann is a professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of Toronto. He is known as the father of wearable computing and is the inventor of the EyeTap, among other things. The EyeTap is an assistive device that can enhance visual information for people who are visually impaired, but can also superimpose extra information on top of the visual scene. For instance, it can overlay infrared heat signatures, measurements, or statistics.
Mann states he was confronted about his EyeTap while in line to order but was left alone after he showed the employee his doctor’s note (something Mann always travels with) which explains exactly what the device is for and why Mann wears it. After eating Mann was surrounded and manhandled by several McDonald’s employees who were concerned that he was filming trade secrets. The employees tore up his doctor’s note and tried to rip off the EyeTap device. However, the EyeTap does not come off without special tools: it cannot just be removed. Although the EyeTap was damaged in the altercation, it managed to capture footage of the employees who assaulted Mann, who was upset but essentially uninjured. McDonald’s consistently denied any wrongdoing in this case despite these images.
But this is just a one-off event right? I suspect that is not the case. In a very real sense, cyborgs are already here. More and more people are turning to the sort of assistive devices that blur the line between human and machine. If you think about it, a cyborg is what you get when you enhance human abilities by adding mechanical elements.
Imagine a deaf person. After a lifetime of being deaf, he gets a cochlear implant allowing him to hear for the first time. His natural abilities have been extended using technology. Another person has a pacemaker that allows her heart to beat in a regular rhythm. Her natural abilities have been extended with technology. Sure, it is not laser hands or a Wi-Fi connection to the hive mind, but it is real and fits the definition.
The Cyborg Handbook estimates that ten percent of Americans qualify as cyborgs in a technical sense. That’s the thing about the future: we are so used to living in it; we forget to be impressed by it. There are also, however, a handful of people who would be considered cyborgs in the traditional sense.
For instance, Steve Mann himself is generally considered a cyborg. Neil Harbisson, artist and cyborg activist is the first person to be legally recognized as a cyborg. Born colour-blind, Harbisson created a head mounted device which turns colour frequencies into sound. He later had a version of this device implanted directly into his skull. With his “Eyeborg” implant Harbisson can now hear colours even into the infrared and ultraviolet spectrum.
Just as more people get closer to being proper cyborgs, more people are starting to push back against what they see as a harmful trend. Stop the Cyborgs is a real group dedicated to preventing a future where privacy is impossible, where we in fact have no expectation of privacy, where surveillance is normalized. It is difficult to argue with that, none of us regular people want to create an Orwellian surveillance state on purpose.

Their second point of contention is much more problematic. Stop the Cyborgs wants to ban or restrict wearable computing devices that can record and upload data, just as an increasing number of people are turning to such devices to manage their tasks of everyday living. They argue that wearable technology blurs the line between human and machine, with the implication of course, that this is a bad thing. They do make a limited exception for people using ‘assistive devices’ as long as the device itself and the data it gathers remain in the sole possession of the individual.
But how do they, and more importantly, how do you determine that on a daily basis? This ‘cyborgs are bad’ mindset is going to lead in a bad direction. With the widespread release of Google Glass this past spring, we are only going to see more integration of people with their computing devices. As the price goes down, a greater number of people are going to adopt wearable technologies.
Stop the Cyborgs seems like a knee-jerk reaction to the introduction of Google Glass, which threatens to normalize an always-on type of surveillance. They even go so far as to suggest that we cannot know if cyborgs are in control of their own implants, or even of their own bodies. But the actual threat is probably much less serious than that.
First, we are already at the point where we could be filmed at any time. Nearly everyone has a video camera in their phone, and most of us are recorded by closed circuit security cameras all day long as we go about our business. If we assume that every person wearing an assistive device is some sort of covert-ops tool of the state, things are going to get ugly very quickly. For instance, Stop the Cyborgs just released a new device called Cyborg Un Plug that prevents cyborgs in your vicinity from connecting with the hive mind, er, internet and uploading video or audio data.
Second, as Steve Mann points out, these cameras can be used by regular people to keep a record of the doings of the state and its agents, like the police. Mann calls this ‘sousveillance’ which essentially means watching from below. Recording and sharing the events of everyday life can allow people to share their personal experiences with others, can provide an alibi when there is alleged wrongdoing, and can make it easier to make power-holders accountable for their actions. These are the real trends to watch for as wearable computing becomes more common. For the Silo, Cathy Greentree.
Supplemental:
http://spectrum.ieee.org/geek-life/profiles/steve-mann-my-augmediated-life