Potter Box
Definition:
Is it ethical for media streaming companies, such as Spotify, to take advantage of IP loopholes, which are known to negatively impact artist revenues?
Values:
>Balance & Fairness
>Legal Values
Loyalties:
a. Duty to service
b. Duty to subscribers
c. Duty to shareholders
d. Duty to Intellectual Property
e. Duty to Art & Commerce
Principles:
Aristotle’s Mean: “Moral virtue is a middle state determined by practical wisdom.” Virtuous people will arrive at a fair and reasonable agreement for the legitimate claims of both sides somewhere in the middle of two extreme claims.The two sides must negotiate a compromise in good faith. “Generally speaking,in extremely complicated situations with layers of ambiguity and uncertainty, Aristotle’s principle has the most intellectual appeal.”
BASIC CONCEPT:
Negotiated compromise.
>>Streaming Media Company
For the Purpose of analyzing an isolated streaming media company, Spotify will be examined through the lens of the potter box. Spotify is a streaming service with cross-platform availability that specializes in music, and generates income from its 20 million premium and 75 million free users, respectively. Spotify boasts an extensive catalogue for free and for a nominal fee. Spotify’s extensive catalogue is made possible due to established agreements between various record labels and media companies. Agreements that are known to negatively affect artists, while benefiting both Spotify & Record labels, plague the music industry. Payout deals between Spotify and record companies range from royalty payout to equity deals.
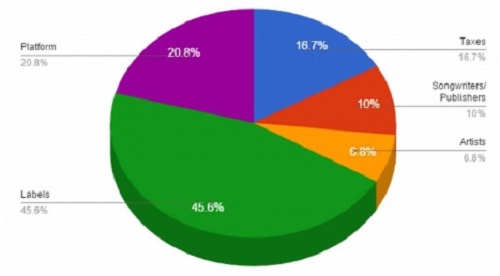
Spotify does not want to make adjustments to the model of its free service, because if their users are not able to find it on Spotify, they will utilize other streaming services such as youtube, which is likely to have the content. They have identified this free offering as being their driving force for getting new subscribers to the service. New subscribers that turn into increased revenue for record labels, as 70% of revenue from $10 per month subscriptions and advertisements are paid to record labels, artists, and song publishers.
>>Artists—Influence: Art/Media Creators
The Artists on Spotify collectively stream over 30 million songs across 58 different markets. Despite collectively making up a heart from which Spotify thrives, Artists receive 6.8% of streaming revenue, the smallest share of the pie.
Artists receive 10.9% of the post tax payout between artists, labels, and songwriters/publishers. Many artists including Adele, Taylor Swift, the Beatles, and Coldplay have opted for keeping music off of Spotify.
Spotify does not have direct agreements with most artists. The streaming company has agreements with labels, whom are responsible for not only securing licenses to music, but to are also responsible for payouts to artists. So essentially, Spotify pays labels, and the label is empowered with payout to artists. The problem is not that Spotify refuses to fairly pay for royalties; it is the trickling down of payment from labels to the respective artists. Spotify has wholesale access to music catalogues from record labels, which makes it hard to fairly split royalty payments amongst artists that are under contractual agreements with respective label.
Even with leaked contract between Spotify and Sony Music available, it is still unclear how much of payouts to record labels actually get to the hands of the artist. It is clear that Sony Music is getting a hefty payout annually, but the question is still whether or not these hefty payouts are passed on to the artists.
>>Major Record Companies
The music catalogue on Spotify is mostly populated by content from major record labels that include Sony Music, Universal Music Group, EMI, Warner Music, Merlin, and The Orchard. Self-published artists as well as artists from independent labels also help makeup Spotify’s catalogue.
Record companies have begun to further question Spotify’s free model since Taylor Swift and other artists have proactively opposed Spotify’s extensive free offerings to users. Streaming consumers of music increased by 54% between 2013 and 2014 according to the Nielsen SoundScan. Major record companies are often made better deals, which disproportionately disadvantage independent artists and labels.
Executives at major record label such as Universal Music and Warner Music have made statements about the extensive free offering of its licensed music is not sustainable long-term. It was suggested that there needs to be a more clear differentiation between content available to free and premium users. Bjork has suggested that Spotify should not allow access for certain content right when it comes out, but should allow for content to go through certain rounds of monetization before ending up on Spotify, similar to Netflix’s rollout method for its content. Major record labels are currently in the process of renegotiating agreements, and are mostly pushing for adjustments to free service offered.
Their goal is to have the “freemium” model disappear as time persists.
What is the current policy?
A legal agreement between Sony, the second largest record company in the world, and Spotify recently leaked, which further intensifies questions about fair payouts for artists. The contract confirmed that major record companies benefit from the success of the streaming service Spotify. The contract details advance payments of over $40 million, with a $9 million advertising credit. Sony has declined to comment on the leaked contract, as it was illegally obtained. Labels routinely keep advances for themselves according to an industry insider.
The leaked contract detailed agreements between Sony Music and Spotify, but not between Sony Music and artists. Such fruits of private agreements don’t necessarily trickle down to the artist, because in most cases they are not even aware of an under the table deal unless a leak has occurred. Unstated under the table deals are not ethical, because artists do not benefit from funds received on account of their intellectual property. The International Music Managers Forum urges European and American authorities alike to use the Sony leak as an example of why more transparence is necessary.
Artists are not being fairly compensated for use of their intellectual property.
Streaming companies have established a revenue arrangement with major Record Companies that often does not favor artists. The obvious shortfalls with existing policy include the lack of transparency when it comes to agreements between record labels and Spotify. There are no systems of checks and balances for ensuring that labels adequately and fairly share Spotify revenue with artists. There needs to be a streamlined system that puts everything on the table in clear view, for fair agreements between artists, label, and streaming company to be arrived at. Current policy also allows Spotify to take up to 15% off the top from revenue generated from ad sales.
What needs to be changed?
Spotify seems to be fairly paying for royalties, but the flow of cash does not always get to the artists. Substitute apps; try to compete with Spotify, by challenging the freemium model. Other apps such as Tidal aim to provide audience with exclusive content that they won’t find anywhere else. The problem is that apps such as Tidal market themselves as a music-streaming app by the artists for the artists. Nowhere in that equation is the interest of the average potential consumer considered. Artists may receive more money per stream, but the service is double the price of Spotify. Record companies, and artists alike, are moving away from Spotify’s freemium model. The digitization of music is not the problem, as most artists and labels generally trust certain digital services such as itunes, because it translates into revenue for artists with no veil or strings attached. Extensive free offerings seem to be the major issue that involved parties have with Spotify, but it is the only thing that drives traffic according to Spotify. The freemium offerings need to be changed in some way, but in a way that is non-disruptive to Spotify’s commerce. Since Spotify pays its fair share of royalties, a more streamlined agreement between record labels and artists should be established and transparent, as should deals made between Spotify and record labels.
Major record labels need to stop double dipping. Not only do they receive cash advances & royalties, but they also benefit from Spotify’s overall revenue stream as they have equity in Spotify of up to 18%. Billboard magazine interviewed two dozen record executives and they agreed that they were confused as to what Spotify was replacing, whether being a substitute for sales or piracy. Examples of setting limitations of the freemium service have showed signs of slowing down subscription growth rate. Spotify has stated that if artists are not fairly compensated from stream revenue, then it is a result of recording contracts and or label accounting practices. Some major record labels are fine with Spotify using their music to build business, because of their equity; they are looking ahead for profit from a future IPO. The artists would not benefit in the same manner, despite their content being the driving force for the app in the first place.
Scenarios
In a time of changing platforms and distribution methods, consumer trends has undoubtedly been in transition. The radio still accounts for an estimated 35% of music consumption, followed by CD consumption at 20%, free streaming at 19%, and paid streaming at 1%. Multichannel consumers, mostly millennia’s, account for 66% of music consumers. A multichannel consumer may pay for a streaming subscription, and make a physical and/or a virtual music purchase. The most common multichannel consumption combination is free streaming coupled with CD listening which accounts for 49% of multichannel listeners, followed by free streaming coupled with music downloads which accounts for 44%. Millennia’s are also known to engage in both free streaming and downloading.
Evidence
During the first quarter of 2014, Pharrell Williams garnered 43 million Pandora streams, which only paid him $2,700 as a songwriter. A statement from Pandora indicates that all rights holders were paid upwards of $150,000 within the first 3 months, and that the real issue is the financial dispute between labels and publishers. Pandora also indicated in the statement that labels are free to split royalties between themselves and artists, however they see fit. Clearly there needs to be more transparency for the cash flow between streaming company, label, and the artist.
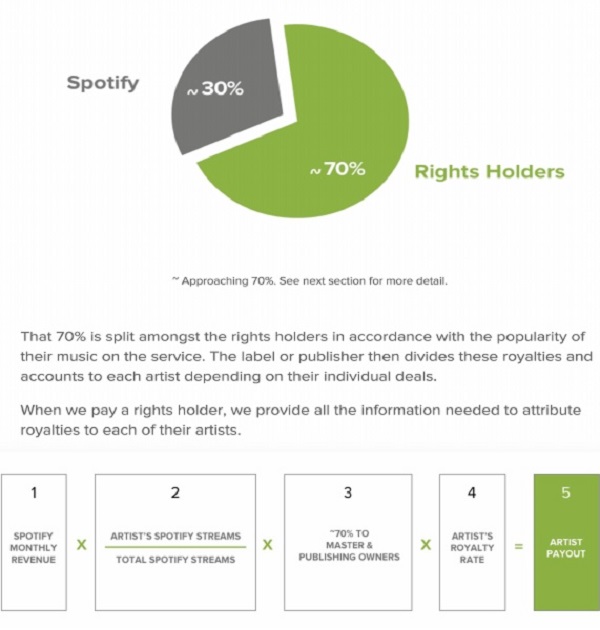
Spotify returns 70% of its revenue to rights holders, with information about each artist to aid in the royalty split process. Streaming companies are engaged in fair due diligence where payment of royalties are concerned. The evidence is as follows:
Actionable Policy
The music industry needs a streamlined agreement between streaming companies, record labels, publishers, and artists. It is imperative that there is increased transparency, especially where cash flow is concerned. Artists should be able to see all cash and data exchanged between streaming company and label. Royalty holders need to publicly split funds amongst themselves and artists. Record labels need to be accountable to both their artists and streaming company, because an artist that feels swindled can create bad blood between the artist and the label and/or the artist and streaming company.
Recommendation
>>Actionable
1. Artists are cut into equity deals based on audience pull to streaming service per qtr
>>Streaming Services should provide analytics with specific data to aid audience pull observation for given artists
2.Major Labels are transparent with cash flow of compensation from Streaming Companies
Is it ethical for media streaming companies, such as Spotify, to take advantage of IP loopholes, which are known to negatively impact artist revenues?
Judgment:
It is ethical for streaming services to take advantage of IP loopholes, which are known to negatively impact artist revenues. Music platform are changing, and as such, better agreements need to be drafted to complement this change. Streaming companies have shown the numbers, and they are paying for royalties, which is essentially paying for the use of the music in their catalogue. Music streaming is an emerging market, which record companies themselves are invested in. The common mode of music monetization is moving away from CD sales, and that is undeniable. Music downloads take up a lot of data, so streaming is the most practical way for consumers to enjoy their music.
The freemium model of Spotify should not be eliminated, but it should certainly be reconsidered, or at least limited in music access. Premium, new, and sought after music should not be as accessible as music that has already exited the promotion stage. Their needs to be some sort of compromise between record labels and Spotify, to better differentiate between premium content and freemium content. Spotify does not want to compromise the availability of its music on either platform, and labels reserve right to pull any of their artists from Spotify as they wish. Spotify should do a better job differentiating free content from premium content, it’s only fair. Spotify should not compromise to the point that it becomes impractical, but should compromise in a way that is cost-effective for all parties. If this were to be attained, streaming companies, record labels, and artists would be happy, circumventing social dilemma. Jordan Muthra The New School University, M.A., Media Studies, Graduate Student
Click here to read PDF version: The_Ethics_of_Streaming_Music