Fighting against global warming is not popular with consumers today. But the consequences of a changing climate will not necessarily be kinder to the wallet.
If we take the case of three foodstuffs that are particularly consumed for breakfast, namely coffee, chocolate, and orange juice, a combination of unfavourable weather conditions have led to significant decreases in production and very sharp price increases: Lesechos.fr
Brazil, the world’s largest exporter of Arabica, is now increasingly plagued by drought (the latest one has almost dried up tributaries of the Amazon), which, not only affects harvests, but also results in hydroelectric production that has not increased for a decade.
It is again the drought that has penalized Vietnam, the leading exporter of Robusta, the other major variety of coffee grown in the world. In the end, the price of coffee has increased by 70% in one year.
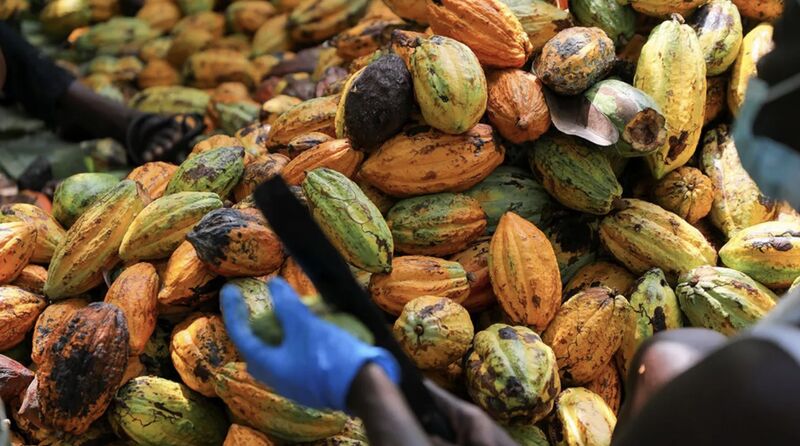
But this is nothing compared to cocoa, whose price tripled over the period, due to unfavorable conditions in Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana, which account for 60% of exported volumes.
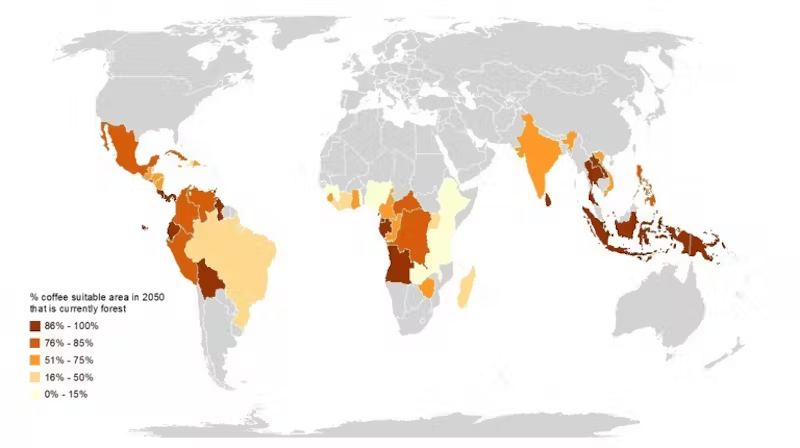
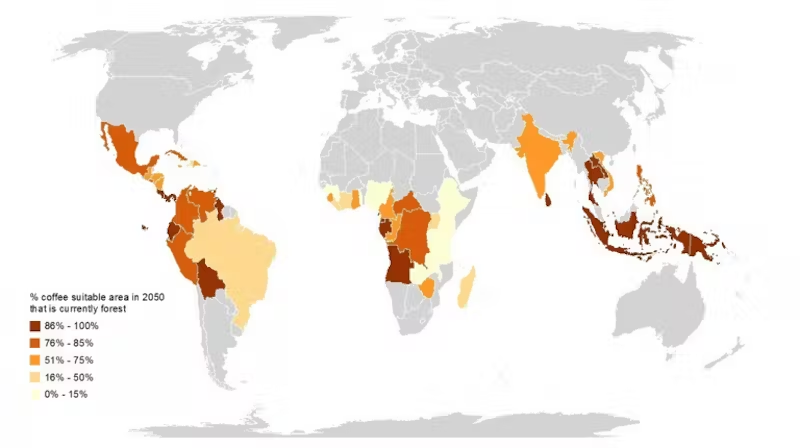
One of the margins for maneuver to lower prices is to increase production, but it is known that, for coffee and cocoa, the expansion of cultivation areas leads to deforestation… which will exacerbate global warming.
More coffee and chocolate?
Let’s drink orange juice! Unfortunately, the situation is not much more favorable for this citrus fruit. The table shows the drought in Brazil, the world’s largest exporter of oranges, but also a parasite that has led Florida’s production to be divided by 4.
Energy abundance, which started in a stable climate, has radically changed our consumption habits of exotic products in a few decades, allowing for long-range mass transport, and increasing crop yields.
Today, an orange, a chocolate bar or a cup of coffee have become commonplace products. But it doesn’t take a rocket scientist to understand that deglobalization (which will be a reality with a greatly reduced supply of hydrocarbons) and climate change will trigger an evolution that will go more or less far in the other direction.
Another not easy question in perspective! For the Silo, Jean-Marc Jancovic.

Lutter contre le réchauffement climatique n’a pas la faveur du consommateur aujourd’hui. Mais les conséquences d’un climat changeant ne seront pas nécessairement plus clémentes pour le porte-monnaie.
Si l’on prend le cas de trois denrées particulièrement consommées au petit déjeuner, à savoir le café, le chocolat, et le jus d’orange, une conjonction de conditions météo défavorables ont conduit à des baisses significatives de production et des augmentations très fortes de prix : Lesechos.fr
Le Brésil, premier exportateur mondial d’Arabica, est désormais en proie de plus en plus souvent à la sécheresse (la dernière en date a quasiment mis à sec des affluents de l’Amazone), laquelle, non contente d’affecter les récoltes, a aussi pour conséquence une production hydroélectrique qui n’augmente plus depuis une grosse décennie.
C’est encore la sécheresse qui a pénalisé Le Vietnam, premier exportateur de Robusta, l’autre grande variété de café cultivée dans le monde. A l’arrivée, le prix du café a augmenté de 70% en un an.
Mais ce n’est rien à côté du cacao, dont le cours a triplé sur la période, à cause de conditions défavorables en Côte d’Ivoire et au Ghana, qui totalisent 60% des volumes exportés.
Une des marges de manoeuvre pour faire baisser les prix est d’augmenter la production, mais il est connu que, pour le café et le cacao, l’expansion des zones de culture engendre de la déforestation… qui va exacerber le réchauffement climatique.
Plus de café et de chocolat ? Buvons du jus d’orange ! Malheureusement, la situation n’est pas beaucoup plus favorable pour cet agrume. On retrouve dans la tableau la sécheresse au Brésil, premier exportateur mondial d’oranges, mais aussi un parasite qui a conduit la production de Floride à être divisée par 4.
L’abondance énergétique, qui a démarré dans un climat stable, a radicalement changé nos habitudes de consommation de produits exotiques en quelques décennies, en permettant les transports de masse à longue portée, et l’augmentation des rendements des cultures.
Aujourd’hui, une orange, une tablette de chocolat ou une tasse de café sont devenus des produits banals. Mais il ne faut pas être grand clerc pour comprendre que la démondialisation (qui sera une réalité avec un approvisionnement en hydrocarbures fortement diminué) et le changement climatique vont enclencher une évolution qui ira plus ou moins loin dans l’autre sens.
Encore une question pas simple en perspective ! Pour le Silo, Jean-Marc Jancovic.