Cybercriminals are constantly attempting to exploit vulnerabilities that affect as many people as possible to maximize their profit opportunities.
According to the recent Atlas VPN team findings, Google and Microsoft accumulated the most vulnerabilities in the first half of 2021. Although not all exposures can cause critical damage, hackers could exploit some of them for severe attacks.

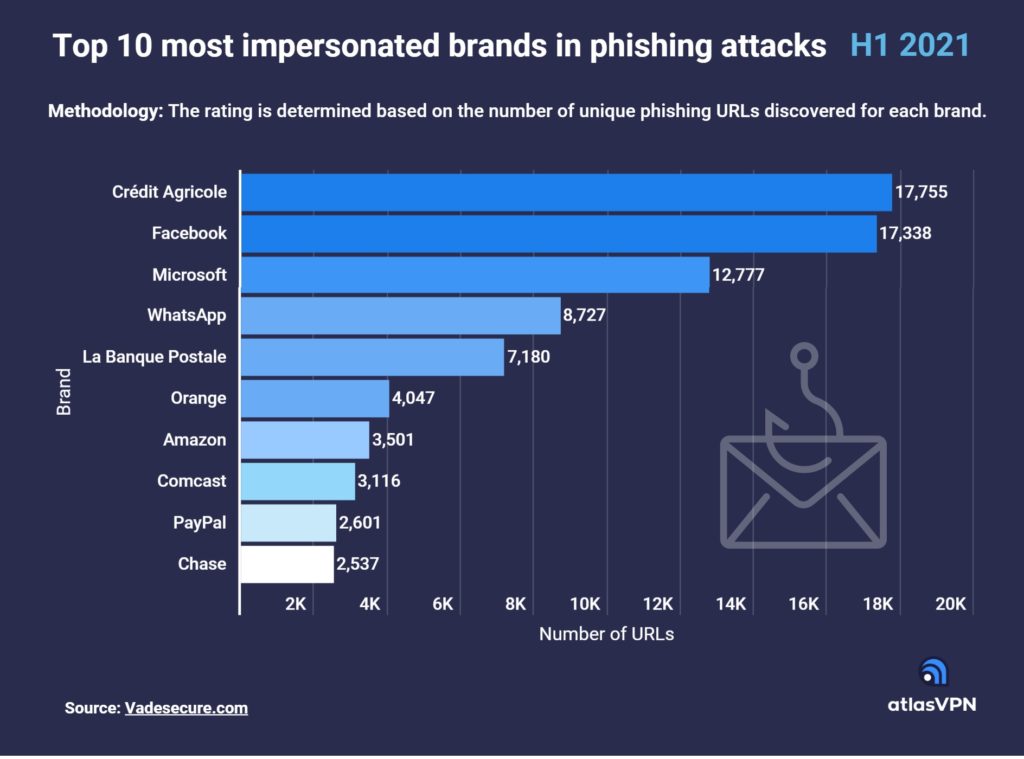
Google had 547 accumulated vulnerabilities throughout the first half of 2021. Exploiting Google products like Chrome is popular among cybercriminals. Next up, the second most exposures were found in Microsoft products — 432. State-sponsored threat actors from China abused Microsoft Exchange Server vulnerabilities to carry out ransomware attacks.

Oracle registered 316 total vulnerabilities in the first six months of 2021. Usually, the exploits are found in Oracle WebLogic Server, which functions as a platform for developing, deploying, and running enterprise Java-based applications.
Networking hardware company Cisco accumulated 200 vulnerabilities. Lastly, the producer of software for the management of business processes SAP had 118 exploits in total. Cybersecurity writer and researcher at Atlas VPN William Sword shares his thoughts on Microsoft and Google vulnerabilities: “Exploiting vulnerabilities in Google or Microsoft products allow cybercriminals to probe millions of systems. While the tech giants are doing a fair job of keeping up with exploits and constantly updating their software, people and organizations need to follow suit and keep up with the updates to prevent further exploitation.”
Vulnerability tiers
Exploits that can be turned into a severe attack get more attention from cybercriminals and companies themselves to fix the flaw as soon as possible. In the first half of 2021, there were 1,023 vulnerabilities found with a risk tier of 10.
One of the exploits that applied to such a tier is CVE-2021-22986, with a score of 9.8. National Vulnerability Database (NVD) issued risk tier 9 to 927 vulnerabilities. At this tier, exploit CVE-2021-28111 stood out with a score of 8.8. NVD recorded most vulnerabilities at a risk tier of 8 — 2,164. A notable exploit was CVE-2021-24092, with a score of 7.8. Finally, NVD recorded 501 vulnerabilities at risk tier 7. While second-most vulnerabilities — 1,765 — were found at tier 6.