 |
Rome, Italy, March 2024. The UN’s International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) and the World Food Programme (WFP) have today launched an action plan to work together in fragile contexts — countries simultaneously affected by economic shocks, and extreme weather, in combination with little or no institutional and government capacity to help people cope. The UN agencies seek to leverage the strengths and expertise of each organization to enhance resilience in fragile environments and improve food security for those who need it most. Fragility is a significant barrier to eradicating hunger and poverty. Moreover, frequent and severe extreme weather events are compounding these often-protracted crises worldwide. “We have decades of experience working in fragile contexts, because that is where so many of the rural poor live. But today, the rural environment is changing. It is becoming less predictable. Rapid changes in climate and demographics are making it harder than ever for rural populations to thrive on the land,” said Alvaro Lario, President of IFAD. “This new Action Plan is very exciting because together, we can be more than the sum of our parts,” added Lario. Fragile situations are on the rise and could impact as much as 60 percent of the world’s extreme poor by 2030. Nearly 1 billion people are currently living in such contexts worldwide, according to the International Monetary Fund estimates. “WFP and IFAD teams work in many of the most fragile and challenging regions of the world, where millions of families who live on the frontlines of conflict, climate change and economic turmoil face a daily battle against hunger,” said WFP Executive Director Cindy McCain. “But it doesn’t have to be this way. Combining our expertise, resources and extensive global network, WFP and IFAD will step up our collaboration in key areas, such as food systems and climate resilience, to support sustainable development, peace and progress in the most vulnerable communities.” IFAD and WFP will carry out joint assessments on fragility, integrate smallholder farmers into food assistance programmes, invest in rural communities’ climate resilience, and share logistical capacity, data, analysis and expertise, as well as provide technical and operational support. For instance, IFAD’s investments in sustainable agricultural practices, such as the use of climate-resilient crops and climate insurance, will be combined with WFP’s climate-resilient local infrastructure and services. Ethiopia, Haiti, Mozambique, Pakistan, South Sudan, Sudan, Yemen and Zambia are the initial countries for collaboration to address fragility and food insecurity in addition to geographic areas across the Sahel and Pacific islands. The action plan aims at maximizing impact, being responsive to dynamic challenges, and focuses on tackling some of the main drivers of fragility. The partnership also builds upon the broader collaboration of the three Rome-based UN food and agriculture agencies, including the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), which was reinforced with a new five-year partnership agreement signed last August during a joint visit to South Sudan. Being able to work in fragile contexts is a priority for IFAD’s next three-year cycle (2025-2027), as the UN Fund plans to reach 100 million rural people. FAO, IFAD and WFP cover a spectrum of work that spans from humanitarian responses to emergencies and shocks, to resilience and development activities, aligning with the 2030 Agenda. The Rome-based agencies are working together on agri-food systems transformation, nutrition, gender equality and women’s empowerment, resilience-building, youth, and climate change to achieving maximized impact and delivering tangible value added to countries and populations. The United Nations World Food Programme is the world’s largest humanitarian organization saving lives in emergencies and using food assistance to build a pathway to peace, stability and prosperity for people recovering from conflict, disasters and the impact of climate change. Follow us on X, formerly Twitter, via @wfp_media |
For the Silo, Julie Marshall.
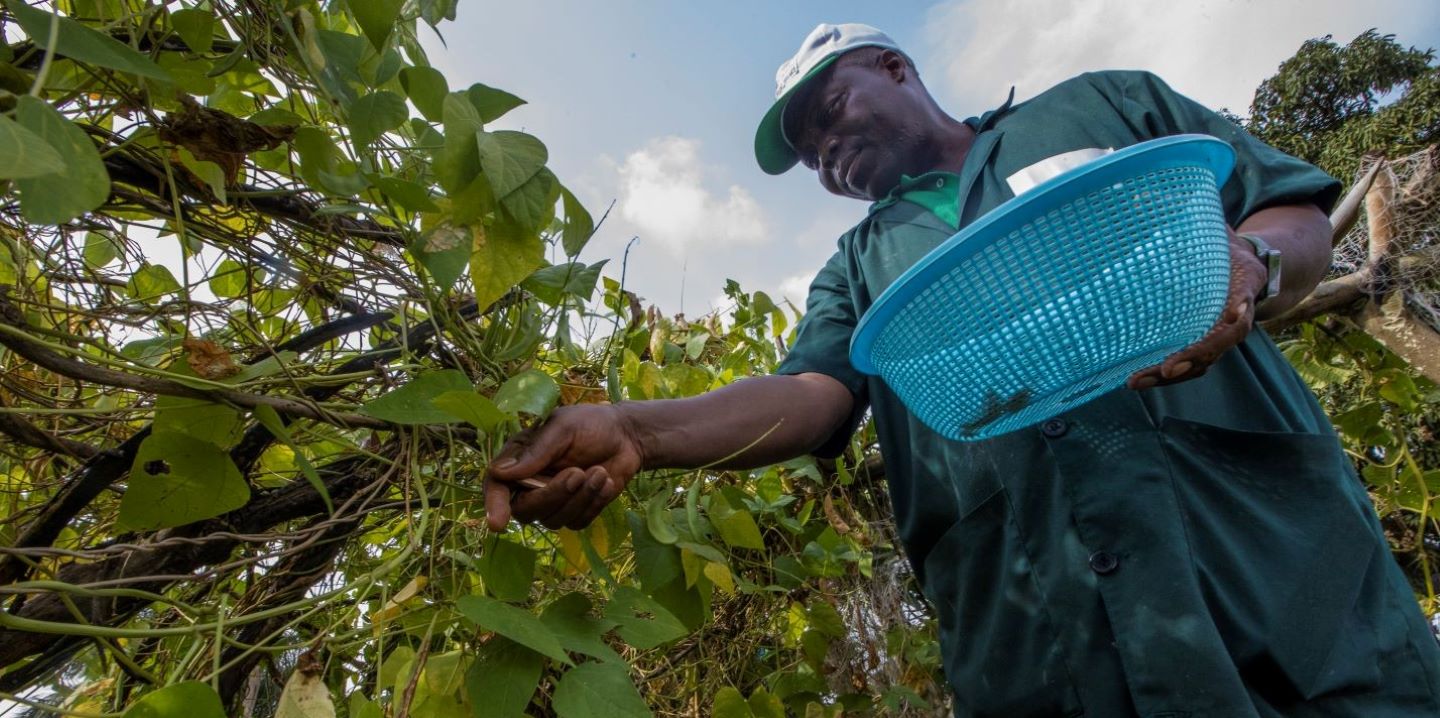
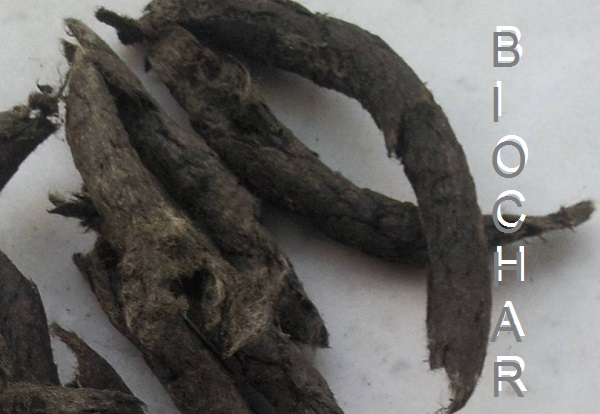


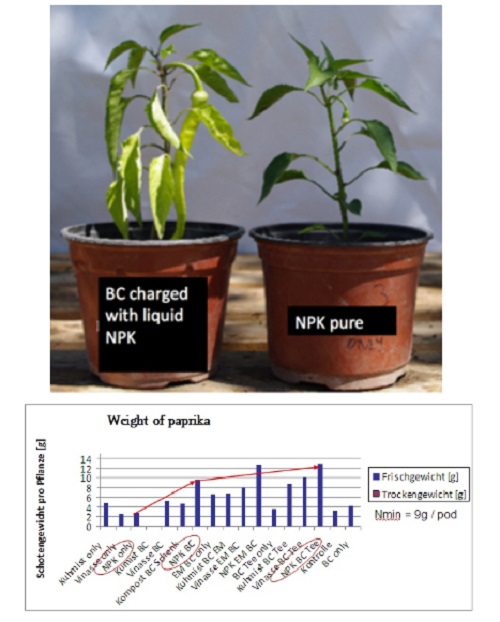


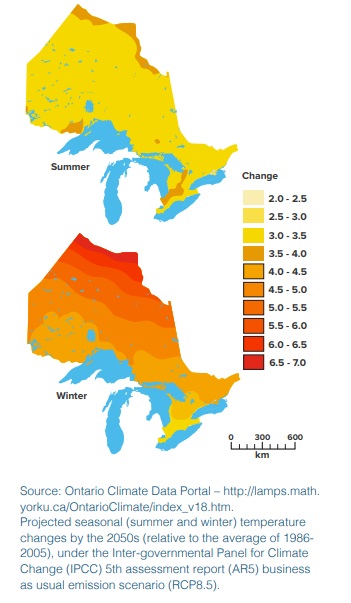 Milder winters and hotter summers create a paradise for insect and plant diseases. Are you getting more tick and mosquito bites? Lyme disease and West Nile virus, and other mosquito and tick-borne diseases, have been moving northward as our part of the world warms. And with increasing temperatures and phosphorus loads, many have taken notice of
Milder winters and hotter summers create a paradise for insect and plant diseases. Are you getting more tick and mosquito bites? Lyme disease and West Nile virus, and other mosquito and tick-borne diseases, have been moving northward as our part of the world warms. And with increasing temperatures and phosphorus loads, many have taken notice of