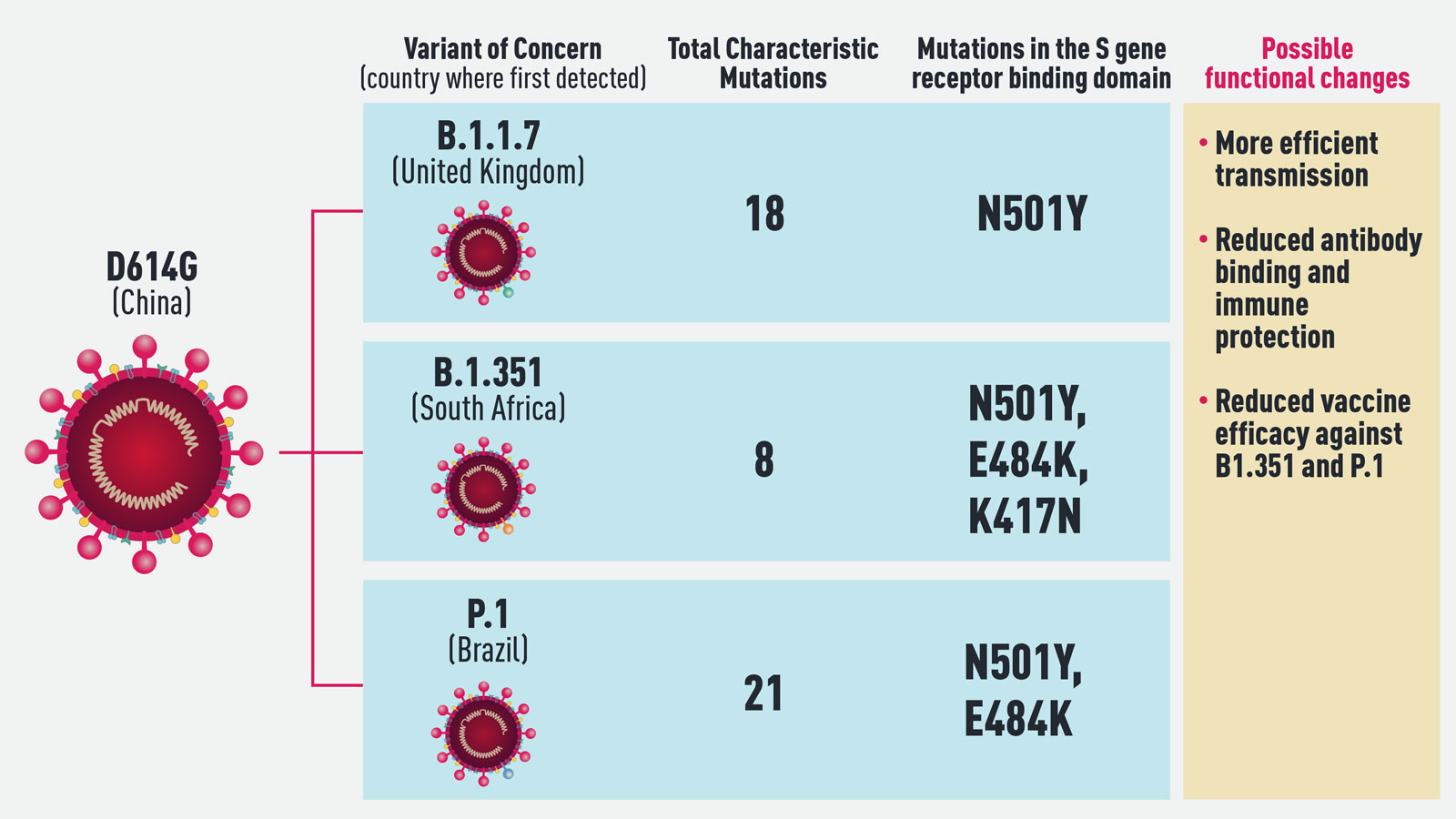
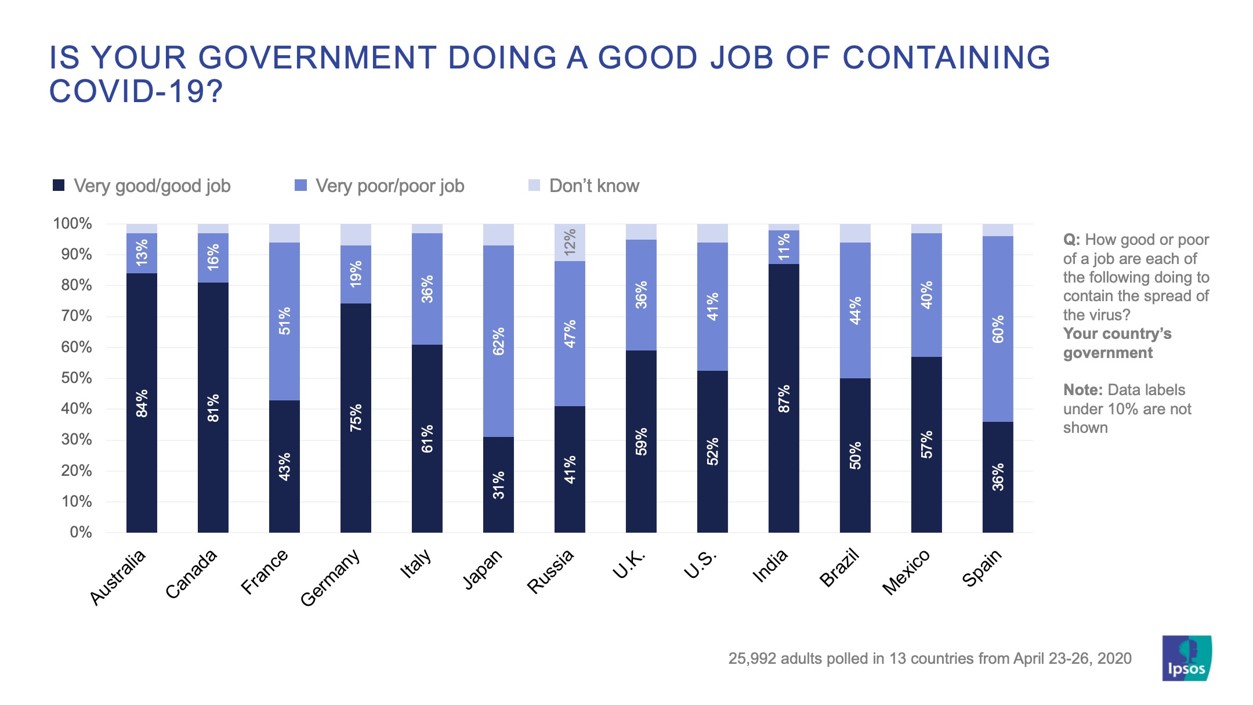
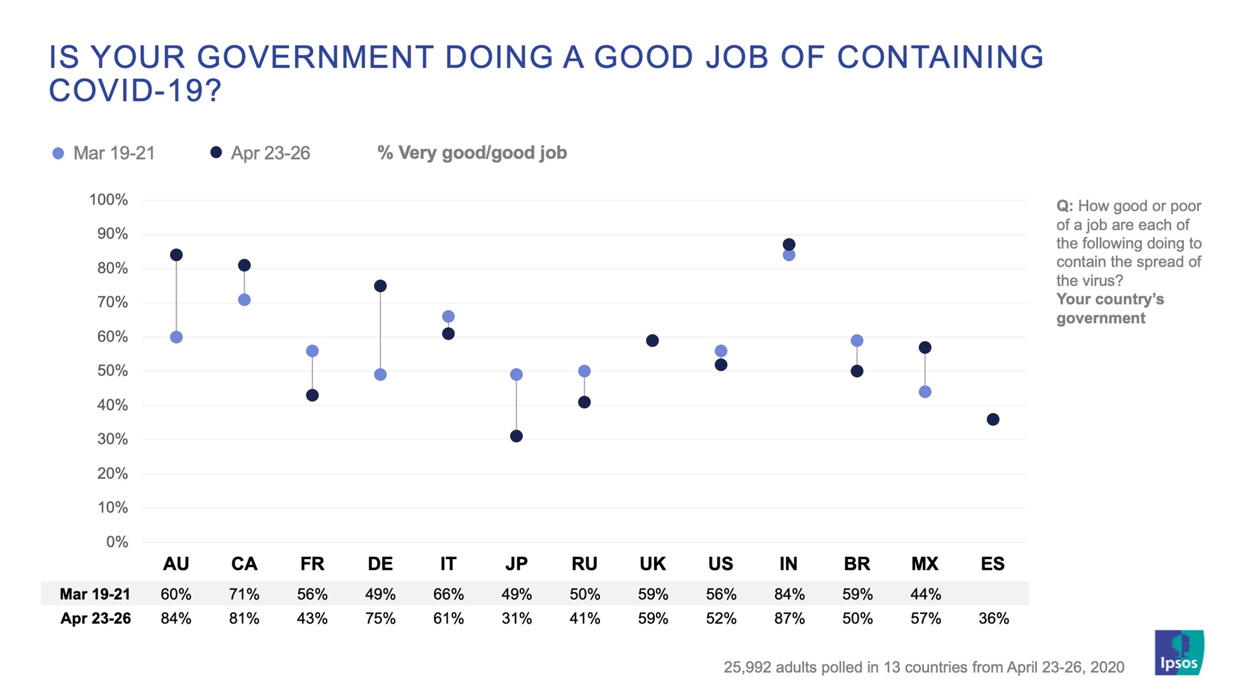
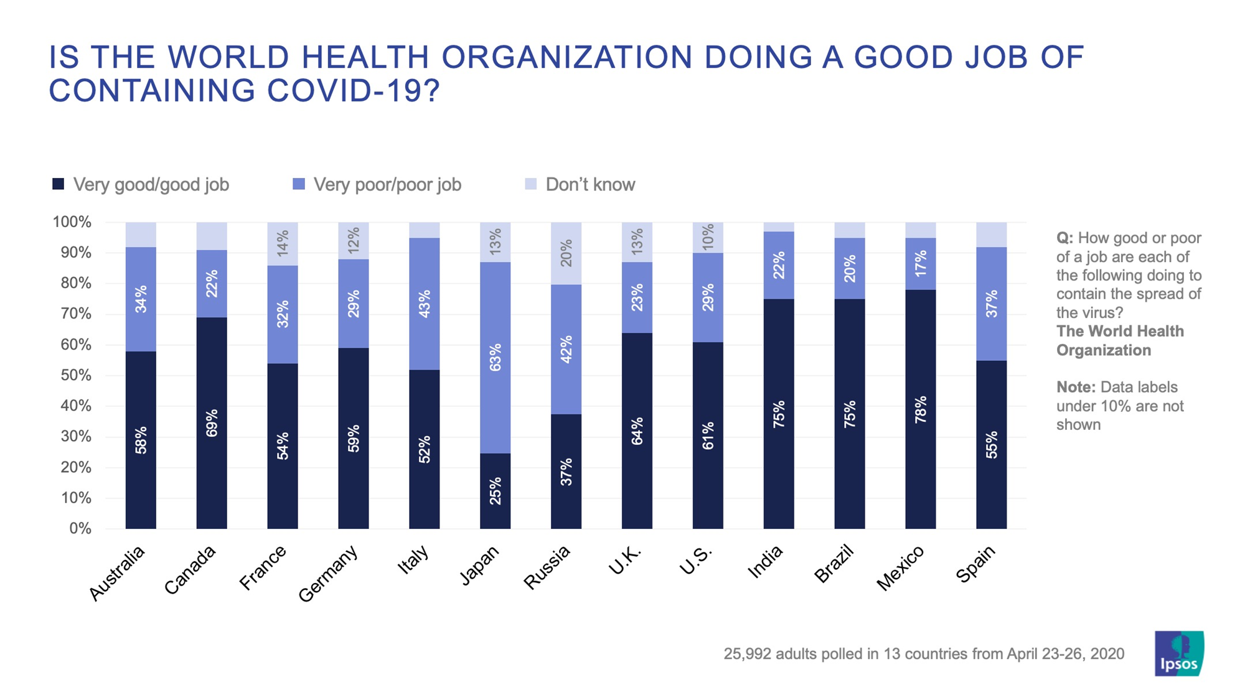
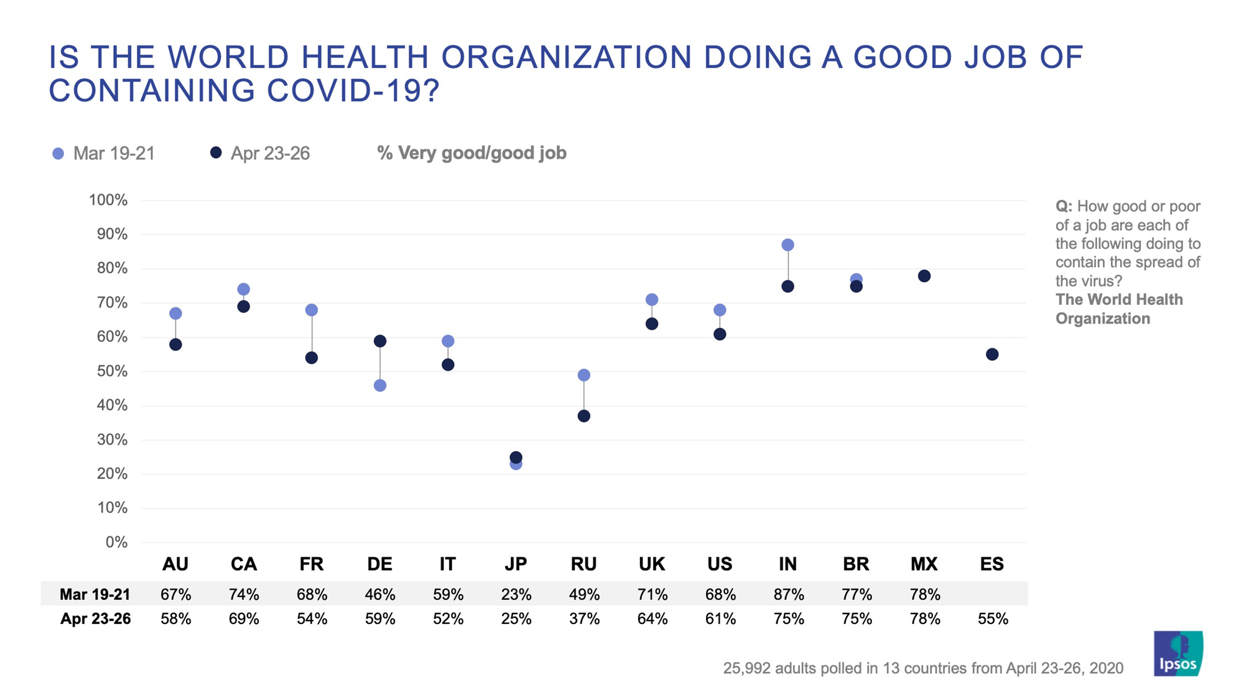
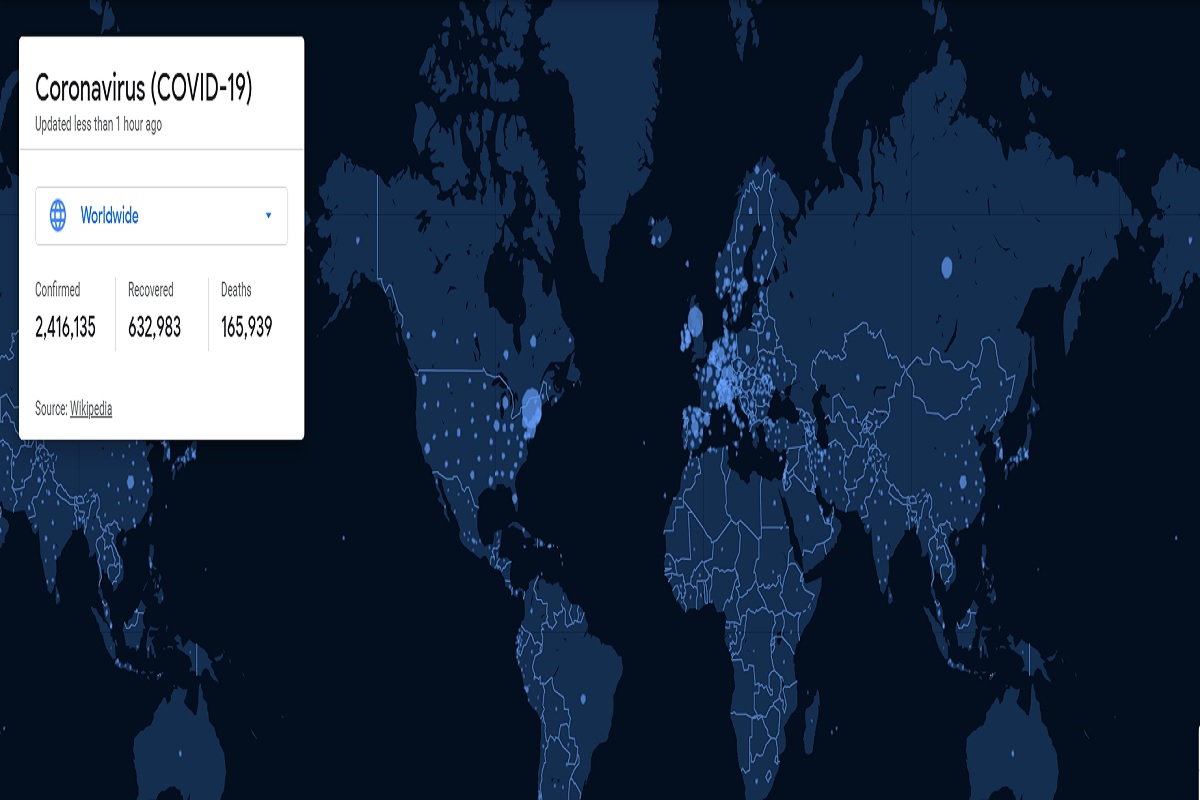
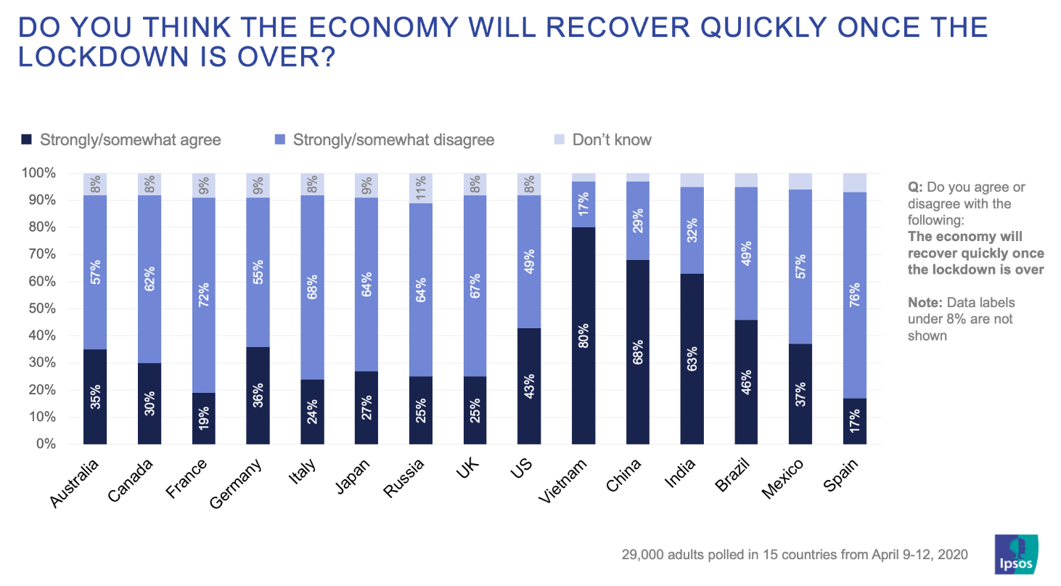
Developing countries (in terms of their income economies) such as Africa are also seeing gains.
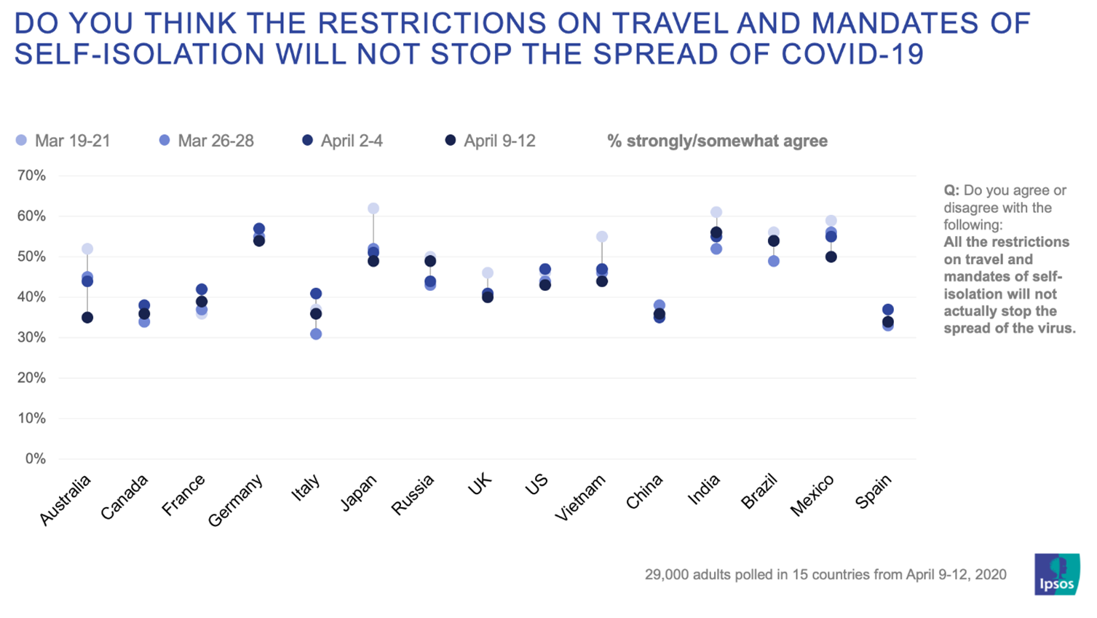
| High-income economies in Europe and Asia-Pacific continue to lead the World Economic Forum Travel and Tourism Index, with the United States, Spain and Japan topping the rankings again. Despite post-pandemic growth, the global tourism sector still faces complex challenges, with recovery varied by region; only marginal overall score improvements since the 2021 edition. Developing economies are making strides – who account for 52 out of 71 economies improving since 2019 – but significant investment is needed to bridge gaps and increase market share. New York, USA, May 2024 – International tourist arrivals and the travel and tourism sector’s contribution to global GDP are expected to return to pre-pandemic levels this year, driven by the lifting of COVID-19-related travel restrictions and strong pent-up demand, as per the new World Economic Forum travel and tourism study, released today. Topping the 2024 list of economies are the United States, Spain, Japan, France and Australia. The Middle East had the highest recovery rates in international tourist arrivals (20% above the 2019 level), while Europe, Africa and the Americas all showed a strong recovery of around 90% in 2023. These are some of the top findings of the Travel & Tourism Development Index 2024 (TTDI), a biennial report published in collaboration with the University of Surrey, which analyses the travel and tourism sectors of 119 countries around a range of factors and policies. “This year marks a turning point for the travel and tourism sector, which we know has the capacity to unlock growth and serve communities through economic and social transformation,” said Francisco Betti, Head of the Global Industries team at the World Economic Forum. “The TTDI offers a forward-looking window into the current and future state of travel and tourism for leaders to navigate the latest trends in this complex sector and sustainably unlock its potential for communities and countries across the world.” Post-pandemic recovery The global tourism industry is expected to recover from the lows of the COVID-19 pandemic and surpass the levels seen before the crisis. This is largely being driven by a significant increase in demand worldwide, which has coincided with more available flights, better international openness, and increased interest and investment in natural and cultural attractions. However, the global recovery has been mixed. While 71 of the 119 ranked economies increased their scores since 2019, the average index score is just 0.7% above pre-pandemic levels. Although the sector has moved past the shock of the global health crisis, it continues to deal with other external challenges, from growing macroeconomic, geopolitical and environmental risks, to increased scrutiny of its sustainability practices and the impact of new digital technologies, such as big data and artificial intelligence. In addition, labour shortages are ongoing, and air route capacity, capital investment, productivity and other sector supply factors have not kept up with the increase in demand. This imbalance, worsened by global inflation, has increased prices and service issues. TTDI 2024 highlights Out of the top 30 index scorers in 2024, 26 are high-income economies, 19 are based in Europe, seven are in Asia-Pacific, three are in the Americas and one (the United Arab Emirates) is in the Middle East and North Africa region (MENA). The top 10 countries in the 2024 edition are the United States, Spain, Japan, France, Australia, Germany, the United Kingdom, China, Italy and Switzerland. The results highlight that high-income economies generally continue to have more favourable conditions for travel and tourism development. This is helped by conducive business environments, dynamic labour markets, open travel policies, strong transport and tourism infrastructure, and well-developed natural, cultural and non-leisure attractions. Nevertheless, developing countries have seen some of the greatest improvements in recent years. Among the upper-middle-income economies, China has cemented its ranking in the top 10; major emerging travel and tourism destinations of Indonesia, Brazil and Türkiye have joined China in the top quartile of the rankings. More broadly, low- to upper-middle-income economies account for over 70% of countries that have improved their scores since 2019, while MENA and sub-Saharan Africa are among the most improved regions. Saudi Arabia and the UAE are the only high-income economies to rank among the top 10 most improved economies between 2019 and 2024. Despite these strides, the TTDI warns that significant investment is needed to close gaps in enabling conditions and market share between developing and high-income countries. One possible pathway to help achieve this would be sustainably leveraging natural and cultural assets – which are less correlated with country income level than other factors – and can offer developing economies an opportunity for tourism-led economic development. “It’s essential to bridge the divide between differing economies’ ability to build a strong environment for their travel and tourism sector to thrive,” said Iis Tussyadiah, Professor and Head of the School of Hospitality and Tourism Management at the University of Surrey. “The sector has big potential to foster prosperity and mitigate global risks, but that potential can only be fully realized through a strategic and inclusive approach.”  Mitigating future global challenges According to the World Economic Forum’s 2024 Global Risks Report, the travel and tourism sector faces various complex risks, including geopolitical uncertainties, economic fluctuations, inflation and extreme weather. Balancing growth with sustainability also remains a major problem, due to high seasonality, overcrowding, and a likely return of pre-pandemic emissions levels. The report also analyses persistent concerns about equity and inclusion. While the tourism sector offers a major source of relatively high-wage jobs, particularly in developing countries, gender parity remains a major issue for regions such as MENA and South Asia. Despite these challenges, the sector can play a significant role in addressing them. To achieve this, decision-makers should prioritize actions such as leveraging tourism for nature conservation efforts; investing in skilled, inclusive and resilient workforces; strategically managing visitor behaviour and infrastructure development; encouraging cultural exchange between visitors and local communities; and using the sector to bridge the digital divide, among other policies. If managed strategically, the travel and tourism sector – which has historically represented 10% of global GDP and employment – has the potential to emerge as a key contributor to the well-being and prosperity of communities worldwide. About the Travel and Tourism Development Index 2024 The 2024 edition of the TTDI includes several improvements based on newly available data and recently developed indicators on the environmental and social impact of travel and tourism. The changes made to the 2024 Index limit its comparability to the previously published TTDI 2021. This year’s report includes recalculated 2019 and 2021 results, using new adjustments. TTDI 2024 reflects the latest available data at the time of collection – end of 2023. The TTDI is part of the Forum’s broader work with industry communities actively working to build a better future enabled by sustainable, inclusive, and resilient industry ecosystems. |

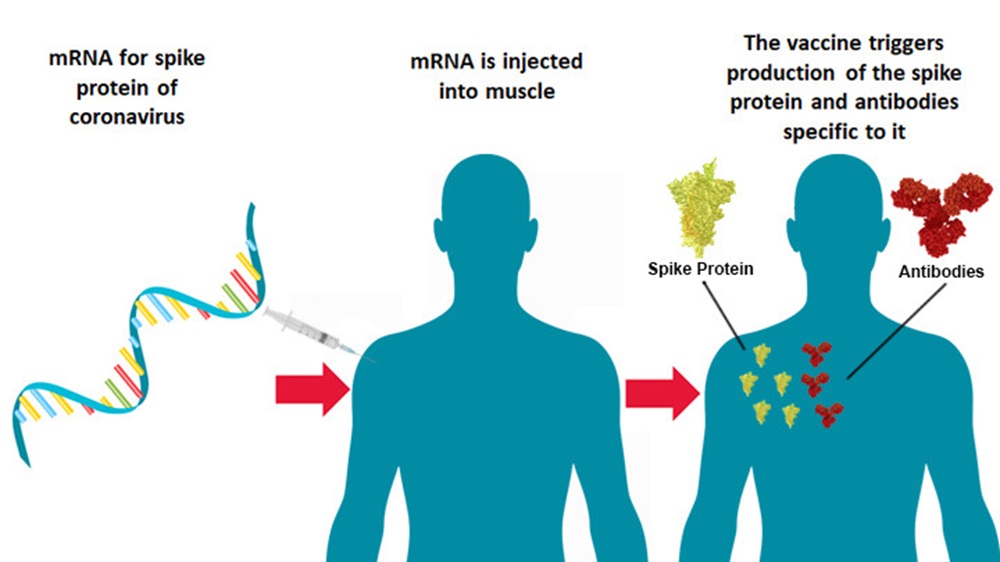









 Graphic design: Sarah Markes/WCS.
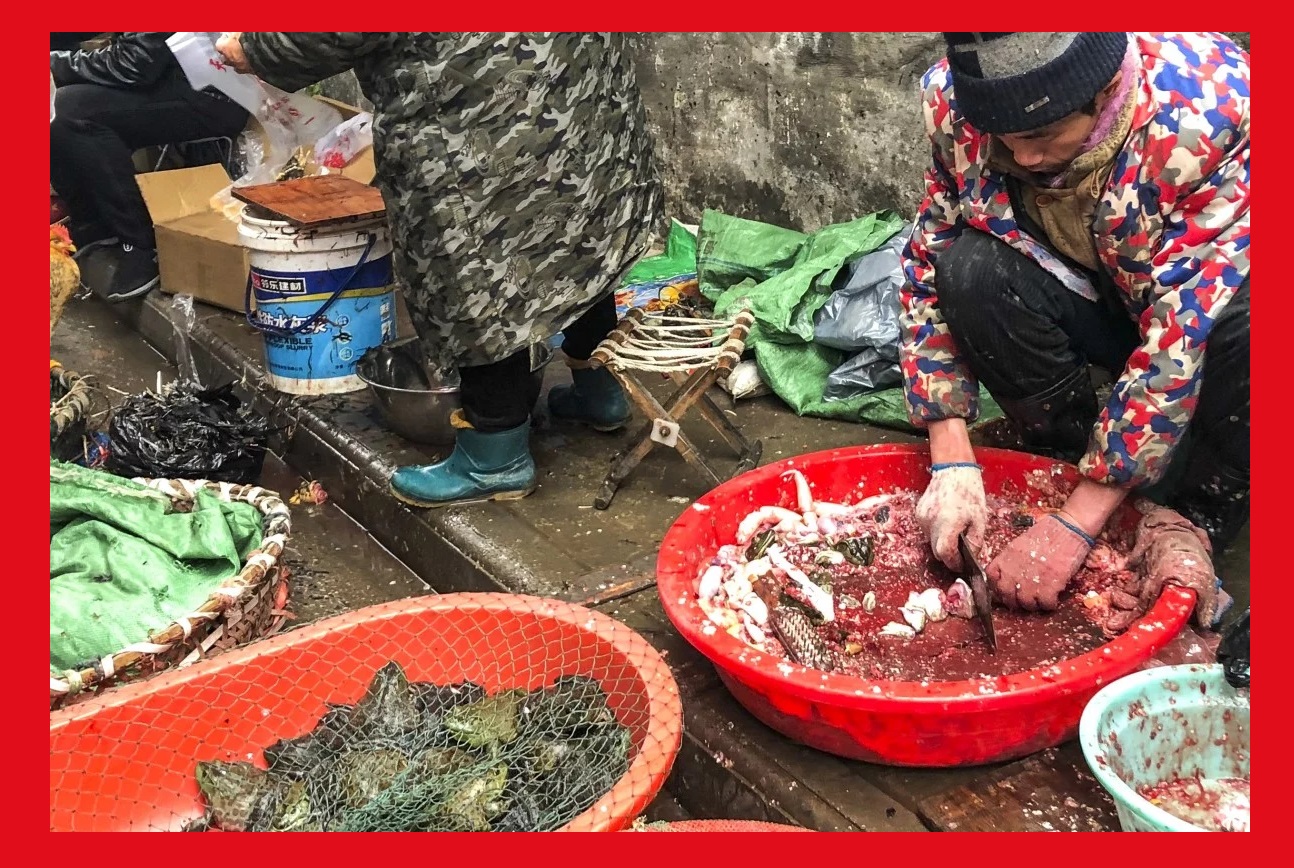
Graphic design: Sarah Markes/WCS.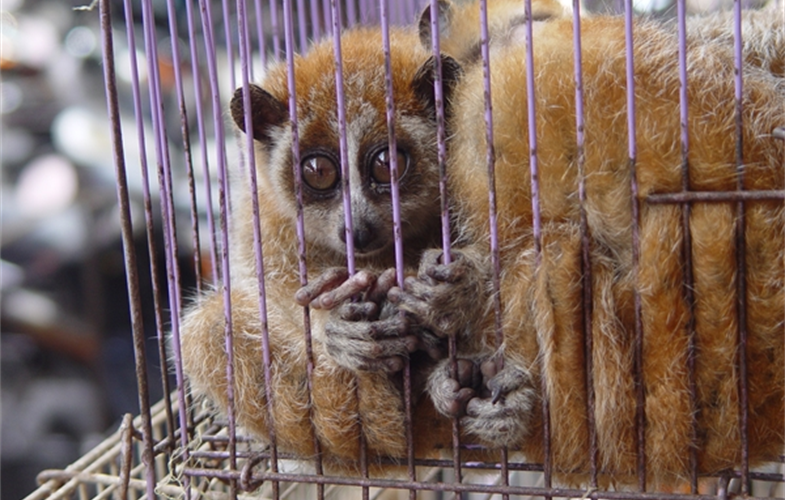 The conditions of so-called “wet markets” are ideal for incubating new diseases and bolster their transmission. Photo credit: Elizabeth L. Bennett/WCS
The conditions of so-called “wet markets” are ideal for incubating new diseases and bolster their transmission. Photo credit: Elizabeth L. Bennett/WCS