A recent OECD report finds that low and middle income earners have seen their wages stagnate and that the income share of middle-skilled jobs has fallen. Rising inequality has led to concerns that top earners are getting a disproportionate share of the gains from global “openness and interconnection”. During a Summer 2017 meeting of OECD, employment outlook revealed that job polarization has been “driven by pervasive and skill-biased technological changes.
Founded in 1945, the United States Council for International Business (USCIB) builds awareness among business executives, educators and policy makers around issues related to employment, workforce training and skills enhancement. CMRubinWorld spoke with USCIB President and CEO Peter M. Robinson, who serves as a co-chair of the B20 Employment and Education Task Force, through which he helped develop recommendations to the G20 leaders on training for the jobs of the future. Robinson also serves on the board of the International Organization of Employers, which represents the views of the business community in the International Labor Organization.
“I think the guiding principle for government should be to protect and enable/retrain the worker, not protect the job. Policy makers and educators should focus on making sure that workers are as equipped as possible to transition to new opportunities” Peter Robinson.
Peter, welcome. How severe do you believe jobsolescence will be over the next 20 years? How big will the challenge be to offset it and maintain a growing workforce?
I really don’t think the overall effect will be as dramatic as some people fear, at least for the medium-term as far as we can tell. There is an over-hype factor at play, but the consequences still deserve serious attention. For one thing, so many of the jobs in the United States, Canada and other advanced economies are in the service sector, and involve interacting with other people. Despite all the advances in AI, we are still a long way off from robotic nurses or home health aides. Overall, history tells us that at least as many new jobs are created as are displaced by technological innovation, even though transitions can be difficult in some sectors and localities, and as long as upskilling takes place.
“The biggest threat is that our educational institutions won’t be able to keep pace with new skills demands.” — Peter Robinson

What do you think are the biggest obstacles facing college grads today trying to enter the workforce?
I actually think the greatest obstacles are faced by those who don’t make it to university or some form of higher education beyond high school (a four-year degree is not the right path for everyone). A 2014 Pew survey found that among workers age 25 to 32, median annual earnings of those with a college degree were $17,500 greater than for those with high school diplomas only. Obviously, everyone at whatever educational level needs to keep their skills sharp, and governments should join with employers and educators to instill better life-long learning. But there are far fewer established paths toward long-term employment at a middle-class level of income for those who don’t graduate from college. A greater emphasis on vocational education and apprenticeships would help. We strongly support the work being done by United States Secretary of Labor Acosta to promote apprenticeships.
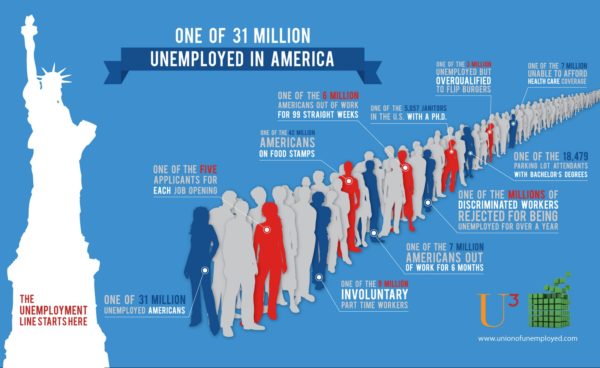
Given that machines are in the process of stripping white collar workers from their jobs, what kind of skills are key manufacturing and service industries going to need from new employees?
I think the premise of your question is overstated. We’re all being told that our jobs are doomed by robots and automation. But the OECD estimates that only nine percent of jobs across the 35 OECD nations are at high risk of being automated, although of course even 9% can be generative of social difficulties. But there is an established track record across history of new technologies creating at least as many new jobs as they displace. Usually these new jobs demand higher skills and provide higher pay. The biggest threat is that our educational institutions won’t be able to keep pace with new skills demands.
“It is becoming clear that Versatility matters, in a constantly changing world, so Jim Spohrer’s IBM model of a “T-shaped” person holds true: broad and deep individuals capable of adapting and going where the demand lies.” — Peter Robinson

In an economy with a significant on-demand labor force, what competencies will these workers need to compete?
There are two types of competencies that will be needed: “technical” – or in other words, related to deep knowledge of a specific domain, whether welding or optogenetics; and “transversal,” which applies to all occupations. Those are described by the Center for Curriculum Redesign as skills (creativity, critical thinking, communication, collaboration), character (mindfulness, curiosity, courage, resilience, ethics, leadership) and meta-learning (growth mindset, metacognition).
How will managerial skill requirements change as a result of major structural changes that are likely, including human replacement by machines and growth of the on-demand economy?
OECD’s BIAC surveys of 50 employer organizations worldwide has shown that employers value not just Skills as described above, but also Character qualities as well. Further, it is becoming clear that Versatility matters, in a constantly changing world, so Jim Spohrer’s IBM model of a “T-shaped” person holds true: broad and deep individuals capable of adapting and going where the demand lies.

“We often hear about the need for more STEM education. But I think there is an equal need for a greater emphasis on the humanities and the arts, for their intrinsic value as well as for developing skills and character qualities.” — Peter Robinson
What central changes in school curricula do you envision, both at the secondary school and college levels?
We often hear about the need for more STEM education. But I think there is an equal need for a greater emphasis on the humanities and the arts for their intrinsic value as well as for developing skills and character qualities as described above. As David Barnes of IBM wrote recently, these skills are more durable and are also a very good indicator of long-term success in employment.
How can the evolving changes in competencies required for employment be effectively translated into school curricula? Where are the main opportunities to enable this? e.g. Assessment systems? Business/Education collaboration? Curriculum change?
I’d go back to something else David Barnes said: We need much stronger connections between education and the job market, in the form of more partnerships among employers, governments and education institutions. Everyone needs to step up and create true partnerships. No one sector of society can address this alone. OECD’s BIAC has also documented employers’ wishes for deep curricular reforms to modernize content and embed competencies in order to meet today’s market needs.
What role should government play in ensuring citizens receive a quality and relevant education given the challenges that lie ahead?
I think the guiding principle for government should be to protect and enable/retrain the worker, not protect the job. Policy makers and educators should focus on making sure that workers are as equipped as possible to transition to new opportunities as these develop, and on ensuring that businesses have the freedom to pivot and adopt new technologies and business processes.
 For the Silo, C.M. Rubin. C. M. Rubin is the author of two widely read online series for which she received a 2011 Upton Sinclair award, “The Global Search for Education” and “How Will We Read?” She is also the author of three bestselling books, including The Real Alice in Wonderland, is the publisher of CMRubinWorld and is a Disruptor Foundation Fellow.
For the Silo, C.M. Rubin. C. M. Rubin is the author of two widely read online series for which she received a 2011 Upton Sinclair award, “The Global Search for Education” and “How Will We Read?” She is also the author of three bestselling books, including The Real Alice in Wonderland, is the publisher of CMRubinWorld and is a Disruptor Foundation Fellow.





