If you want good health, a long life and to feel your best well into old age, the No. 1 most important thing you can do is strength-training, says Dr. Brett Osborn, author of “Get Serious, A Neurosurgeon’s Guide to Optimal Health and Fitness,”
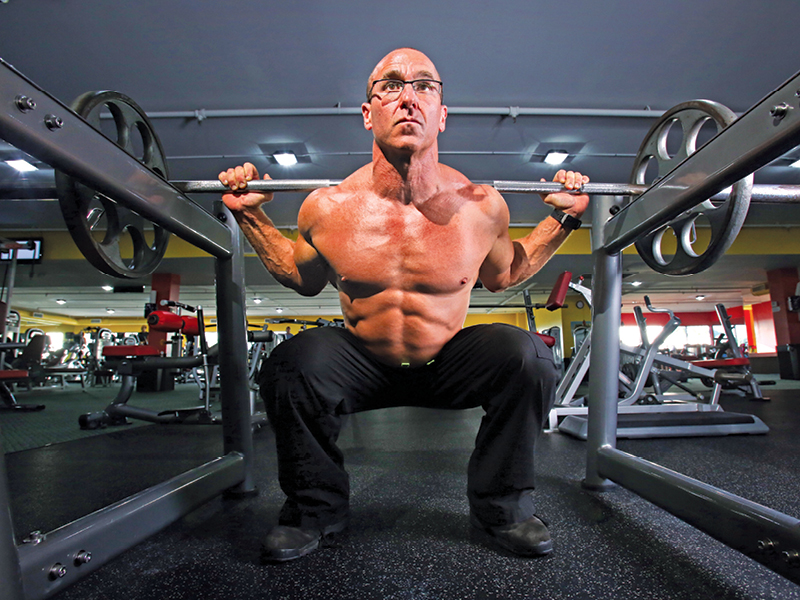

“Our ability to fight off disease resides in our muscles,” Dr. Osborn says. “The greatest thing you can do for your body is to build muscle.”
He cites a large, long-term study of nearly 9,000 men ages 20 to 80. After nearly 19 years, the men still living were those with the most muscular strength. (BMJ, formerly British Medical Journal, 2008).
Muscle is all protein – “nothing but good for you,” Dr. Osborn says.
Fat, however, is an endocrine organ, meaning it releases hormones and other chemicals. When a person has excess fat, he or she also has a
disrupted flow of excess biochemicals, which can increase insulin resistance and boost risk factors for stroke and high blood pressure, among other problems.
“Increased cytokines, an immune system chemical, for example, are associated with increased risk for cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Osborn says. “You’re only as old as your arteries!” Strength-training has health benefits for everyone, he adds, no matter their size. “Some fat is visceral fat – it’s stored around the organs and it’s even more dangerous than the fat you can see,” he says. “People who look thin may actually be carrying around a lot of visceral fat.”
So, what’s the workout Dr. Osborn recommends?
“Back to basics,” he says. “These five exercises are the pillars of a solid training regime.”
• The squat is a full-body exercise; it’s the basic movement around which all training should be centered. Heavy squats generate a robust hormonal response as numerous muscular structures are traumatized during the movement (even your biceps). Standing erect with a heavy load on your back and then repeatedly squatting down will stress your body inordinately – in a good way — forcing it to grow more muscle.
• The overhead press primarily activates the shoulders, arm extenders and chest. Lower body musculature is also activated as it counters the downward force of the dumbbell supported by the trainee. From the planted feet into the hands, force is transmitted through the skeletal system, stabilized by numerous muscular structures, most importantly the lower back.
• The deadlift centers on the hamstrings, buttocks, lumbar extensors and quadriceps, essentially the large muscles of your backside and the front of your thighs. As power is transferred from the lower body into the bar through the upper body conduit, upper back muscles are also stressed, contrasting with the squat, which is supported by the hands. Deadlifts are considered by some to be the most complete training exercise.
• The bench press mostly targets the chest, shoulders and triceps; it’s the most popular among weightlifters, and it’s very simple – trainees push the barbell off the lower chest until the arms are straight. This motion stresses not only the entire upper body, but also the lower body, which serves a stabilizing function. This provides a big hormonal response and plenty of bang for your buck.
• The pull-up / chin-up stress upper body musculature into the body. A pull-up is done when hands gripping over the bar; a chin-up is where hands are gripping under the bar. Nine out of 10 people cannot do this exercise because most simply haven’t put in the effort. It’s also been called a “man’s exercise, which is nonsense,” he says. There are no gender-specific exercises. Women, too, should aspire to enjoy the health benefits entailed with this pillar.
“There are no secrets to a strong and healthier body; hard work is required for the body that will remain vital and strong at any age,” Osborn says. “Always practice proper form and safety. Otherwise, the result will be the opposite of your goal, an injury.”