This monograph provides for the first time a combined overview of all classes of metal body armour from the European Bronze Age in a holistic perspective, combining discussion of both traditional typo-chronologies and aspects of manufacture and use.
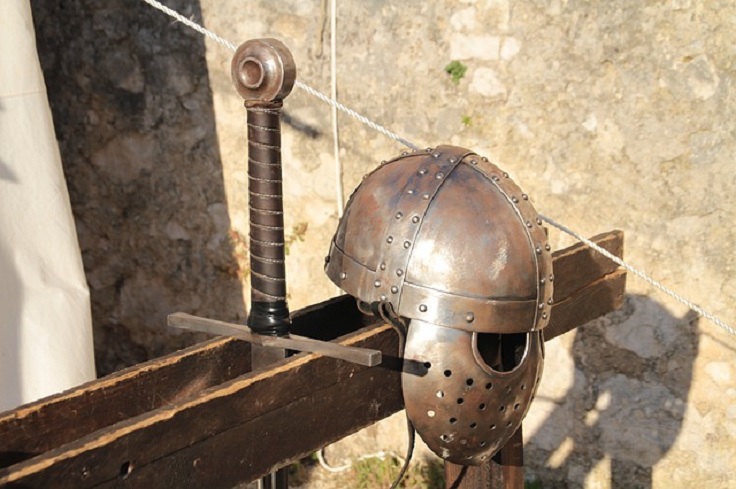
The earliest metal body armour recovered comes from Dendra, Greece, and dates to the first half of the 15th century BC.
However, the majority of metal body armour, including helmets, cuirasses and greaves, derives from the European Late Bronze Age, c. 1200–950 BC. This armour has been found from Iberia in the west to Cyprus in the east, and from Sicily in the south to Denmark in the north, as well as in the Near East. It thus derives from a wide geographical study area. Nevertheless, only around 30 cuirasses, 75 greaves and 120 helmets have so far been recovered.
The development, manufacture and use of this metal body armour across Europe remains unclear, even after more than a century of research. Earlier studies were largely concerned with typo-chronological aspects of this armour, whilst topics such as manufacturing techniques, efficacy and technological observations were rarely addressed.

This volume therefore brings together both traditional artefact and metallurgical studies, as well as reconstructions of manufacturing techniques, technological developments and innovations and use-wear analysis. The monograph also provides much-needed detail concerning material characterisation, in the form of alloy composition and microstructure analysis of a significant sample of the original finds.
Combining the results of this with the study of the manufacturing techniques and use-wear traces, a better understanding of how this armour was both produced and used is achieved. I have documented, studied and analysed all accessible helmets, greaves and cuirasses in eastern Europe as well as a number of examples from western Europe, significantly increasing the quantity of body armour studied and analysed in detail. The publication contains the whole spectrum of known body armour currently recovered, as well as including ‘new’ finds from auctions or private collections, which have previously been overlooked.
The present volume offers a holistic artefact study of European Bronze Age body armour, its manufacture and usage. It serves as a basis for further experimental studies into the production and utility of bronze helmets, cuirasses and greaves, which will deliver further important insights in … View full abstract For the Silo, Marianne Modlinger.