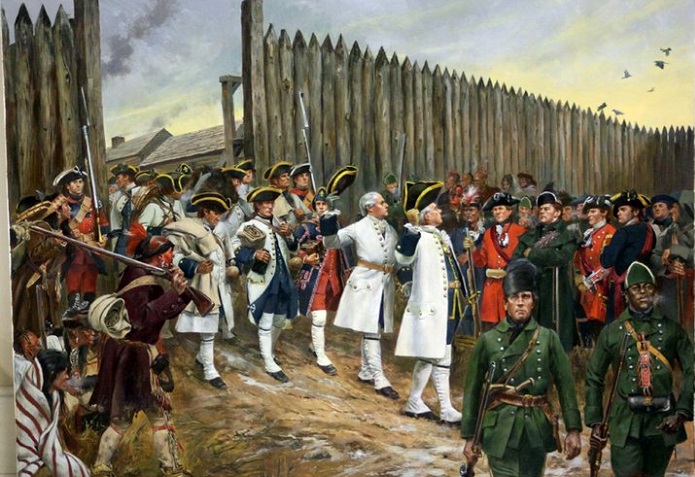
This August we saw the fifth U.S. Civil War re-enactment at Circle G Ranch, east of Cayuga, Ontario. On Sept. 13, re-enactors of the ‘Blue and Grey’ will go to battle in Otterville.
The American Civil War had a tremendous influence on the British North American colonies, and continues to be of mind.
At onset of the Civil War, Canada did not yet exist as a federated nation. When the war broke out in 1861, Canada was still a subject of Great Britain and had maintained an uneasy peace with its American neighbors since the War of 1812.
William Seward, the American Secretary of State during the Civil War, was an annexationist who felt that British North America was destined to become part of the United States. As it became obvious that the North would emerge victorious there was a fear the Union army would turn its eyes north of the border.
Many in the US government were supporters of Manifest Destiny, an ideology that stated America should conquer the continent. Canadians were concerned about the possibility of a US invasion.
The tensions between the United States and Britain, which had been ignited by the war and made worse by the Fenian Raids, led to concern for the security and independence of the colonies, helping to consolidate momentum for Canadian confederation.
In the election of 1864, the Republican Party used annexation as a means to gain support from Irish Americans and the land-hungry.
In 1866, an annexation bill passed in the US House of Representatives stating the United States acquire all of what is now Canada.
The Civil War also had an important effect on discussions concerning the nature of the emerging federation. Many Fathers of Confederation concluded the secessionist war was caused by too much power being given to the states, and thus resolved to create a more centralized federation. It was also believed that too much democracy was a contributing factor and the Canadian system was thus equipped with checks and balances such as the appointed Senate and the power of the British-appointed governor-general.
The guiding principles of the legislation which created Canada, the British North American Act, were peace, order and good government – in stark contrast to the perceived rugged individualism of the neighbours south of the border.
Since 1793, thanks to then Lieutenant-Governor John Graves Simcoe, Upper Canada – now present day Ontario – had banned the importation of slaves.
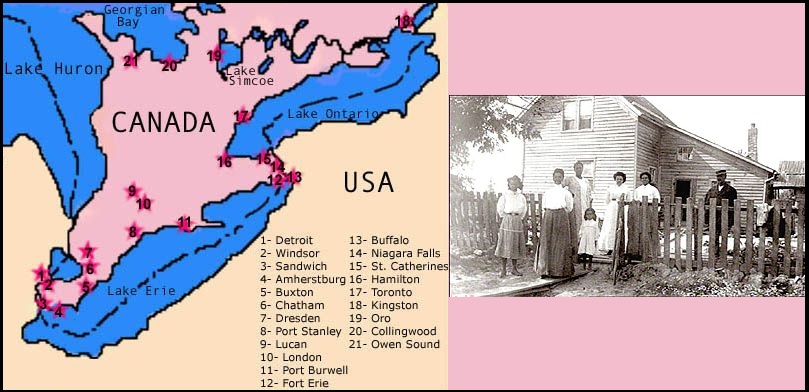
Canadians were largely opposed to slavery, and Canada had recently become the destination of the Underground Railroad.
The Underground Railway was a network of safe houses and individuals who helped runaway slaves reach free sates in the American North or in Canada.
It ran from about 1840 to 1860. It was most effective after the passage of the Fugitive Slave Act in 1850, which enabled slave hunters to pursue runaways onto free soil. It is estimated that about 30,000 reached Canada. Several communities were established in Ontario, including one east of Cayuga, at Canfield.
The Civil War claimed 7,000 Canadians and almost 620,000 US lives.
Between 33,000 and 55,000 men from British North America served in the Union army, and a few hundred in the Confederate army. Five served as generals, and 29 received the U.S. Medal of Honour. For the Silo, Toby Barrett MPP Haldimand-Norfolk.