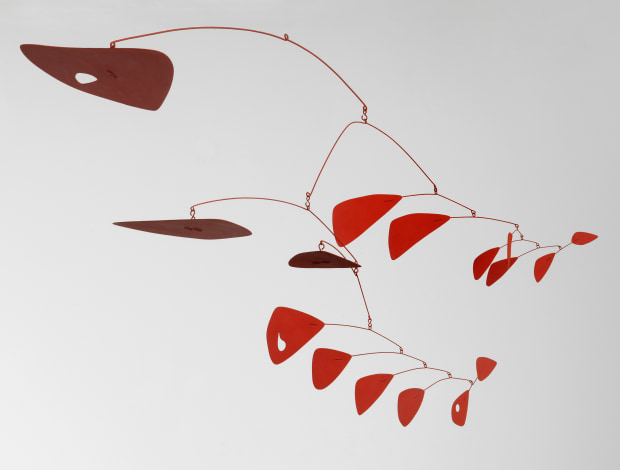
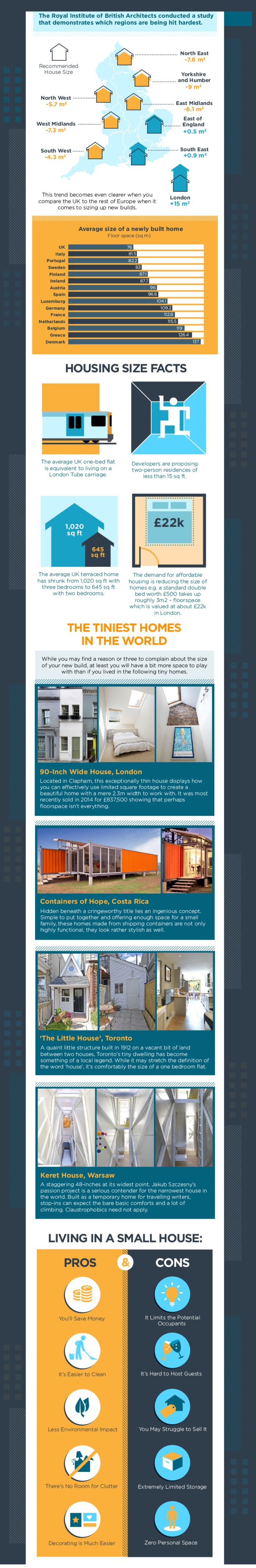
(New York, July, 2024)—This summer, The Metropolitan Museum of Art will present the exhibition Mary Sully: Native Modern, opening July 18, 2024. Born Susan Mabel Deloria on the Standing Rock Reservation in South Dakota, Mary Sully (1896–1963) was a little-known, reclusive Yankton Dakota artist who, between the 1920s and 1940s, produced highly distinctive work informed by her Native American and settler ancestry. The exhibition is part of The American Wing at 100, a series of gallery reinstallations and exhibitions marking the wing’s 2024 centennial.
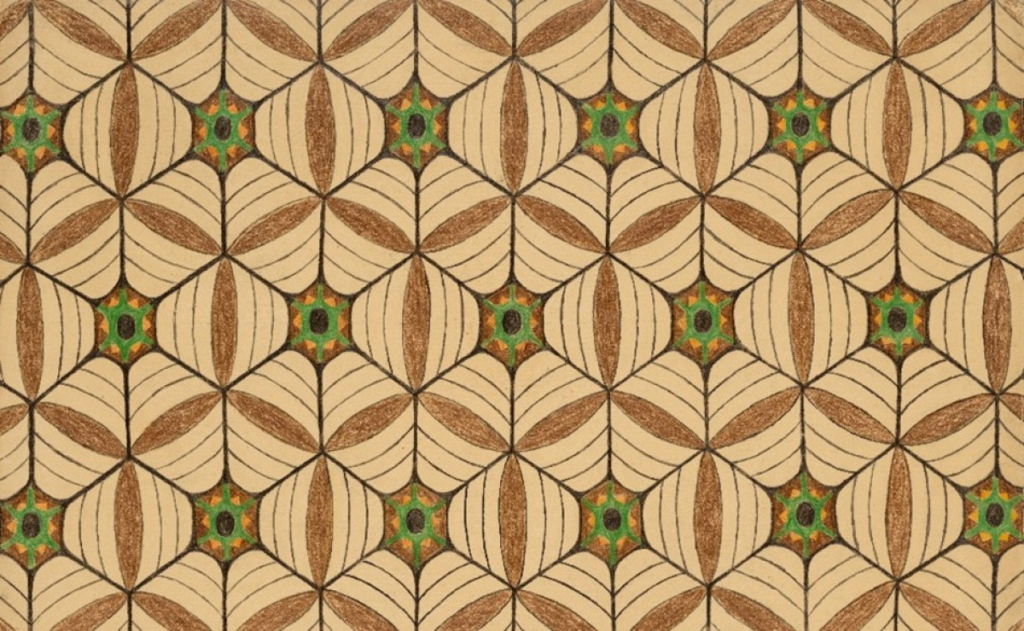


Image: Mary Sully (Dakota, 1896–1963). Alice (detail), ca. 1920s–40s. The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, Purchase, Morris K. Jesup Fund and funds from various donors, 2023
The exhibition is made possible by the Barrie A. and Deedee Wigmore Foundation.
“This compelling exhibition celebrates how Mary Sully’s cultural sensibilities influenced her unconventional body of work,” said Max Hollein, The Met’s Marina Kellen French Director and Chief Executive Officer. “Sully translated her life and experiences into a unique graphic language, culminating in an intensely creative perspective from which to consider Indigenous cultures and imagery.”
This first solo exhibition of Sully’s groundbreaking production highlights recent Met acquisitions and loans from the Mary Sully Foundation, works that call into question traditional notions of Native American and modern art.

The Met Fifth Avenue. 82nd Street New York, NY, 10028
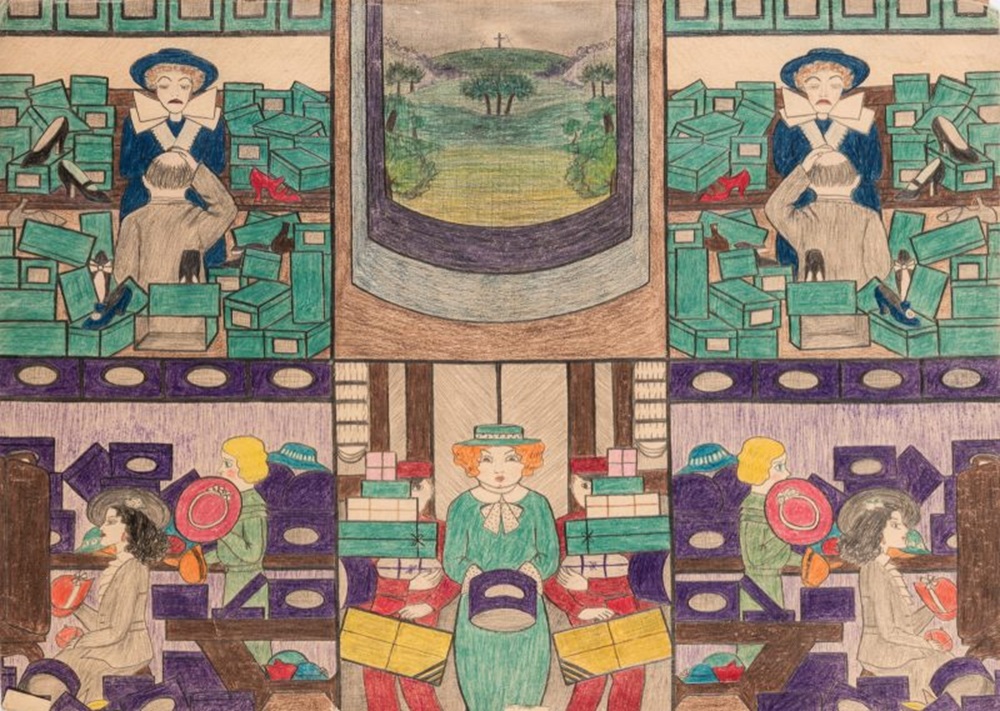
Working without patronage, in near obscurity, and largely self-taught, Sully produced approximately 200 intricately designed and vividly colored drawings in colored pencil, graphite, and ink on paper that captured meaningful aspects of her Dakota community mixed with visual elements observed from other Native nations and the aesthetics of urban life. Euro-American celebrities from popular culture, politics, and religion inspired some of her most striking works, which she called “personality prints”—abstract portraits arranged as vertical triptychs.
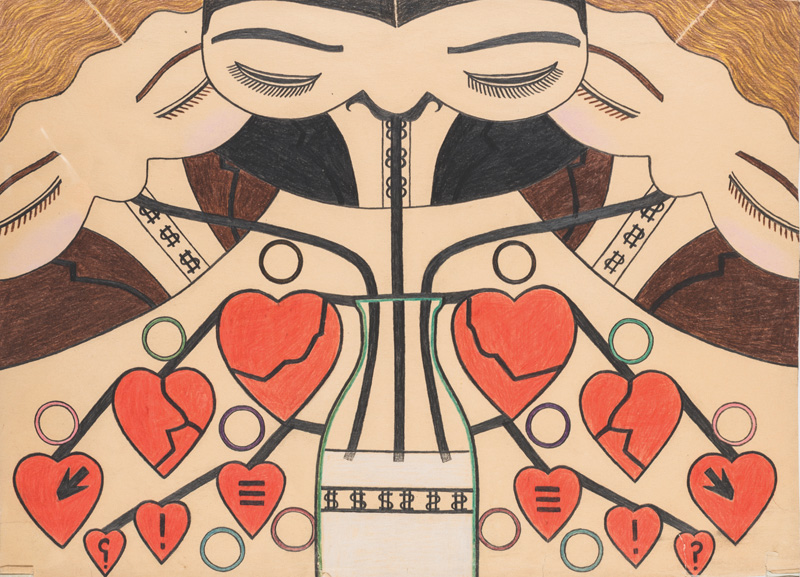
Panel from Titled Husbands in the USA by Mary Sully (1896–1963), 1927–1945. Colored pencil on paper, 12 7/8 by 18 inches. None of Sully’s pieces are dated, but it is estimated that they were all created between 1927 and 1945. Except as noted, all objects illustrated are in the collection of Philip J. Deloria. via themagazineantiques.com
Featuring 25 rarely seen Sully compositions—primarily her “personality prints”—as well as archival family material and other Native American items from The Met collection, the exhibition offers a fresh and nuanced lens through which to consider American art and life in the early 20th century.
Sylvia Yount, Lawrence A. Fleischman Curator in Charge of the American Wing, said: “We’re thrilled to present Mary Sully: Native Modern as a special feature of the department’s 100th anniversary in 2024. Born of particular Native and Euro-American cultural entanglements, Sully’s work is highly relevant and resonant for the American Wing, The Met’s historic department of a broadly defined American art by diverse makers, with a deepening concentration of work by women and artists of color.”

Portion of Mary Sully’s The Indian Church (around 1938-45)Collection of Philip J. Deloria

Bottom of Sully’s The Indian Church (c. 1938-45)© Collection of Philip J. Deloria via theartnewspaper.com
About Mary Sully
As a great-granddaughter of the successful 19th-century portraitist Thomas Sully (1783–1872), Susan Deloria expressly adopted the name of her mother, Mary Sully (1858–1916), daughter of Alfred Sully (1820–1879) and the Dakota woman Susan Pehandutawin (dates unknown), an artist in her own right. Deloria grew up in a distinguished family of Dakota leaders. Her sister Ella Cara Deloria (1889–1971), with whom she primarily lived, was a linguistic ethnographer trained by the esteemed Columbia University anthropologist Franz Boas. Her nephew, Vine Deloria, Jr. (1933–2005), was an author, theologian, historian, and activist for Native American rights. And her great-nephew, historian Philip J. Deloria, is the author of Becoming Mary Sully: Toward an American Indian Abstract (University of Washington Press, 2019), the only scholarly investigation of her art and life.
Related Presentation in Art of Native America Installation
In late June, the American Wing unveiled a new rotation of works by Native American artists focusing on intergenerational knowledge and their critical role as knowledge keepers. These include recent acquisitions by contemporary basket makers Jeremy Frey (Passamaquoddy) and Theresa Secord (Penobscot), in addition to painter Rabbett Strickland (Red Cliff Ojibwe).
Credits and Related Content
Mary Sully: Native Modern is curated by Patricia Marroquin Norby (P’urhépecha), Associate Curator of Native American Art, and Sylvia Yount, Lawrence A. Fleischman Curator in Charge of the American Wing.
The exhibition is conceived in partnership with the Mary Sully Foundation and the Minneapolis Institute of Art.
Featured image– Mary Sully, “Good Friday” From Philip J. Deloria, “Becoming Mary Sully; Toward an American Indian abstract” (Seattle, University of Washington Press: 2019) ISBN 978-0-295-74504-6. Courtesy University of Washington Press.



 Florence Henri (1893 – 1982)Composition18 ½ x 12 ½ inchesGouache on paper Monogrammed F.H. and dated 1926 lower right
Florence Henri (1893 – 1982)Composition18 ½ x 12 ½ inchesGouache on paper Monogrammed F.H. and dated 1926 lower right George Pearse Ennis (1884 – 1936)Forging a Gun Tube #146 x 37 inches, 1918 Signed lower right
George Pearse Ennis (1884 – 1936)Forging a Gun Tube #146 x 37 inches, 1918 Signed lower right Daniel Ralph Celantano (1902-1980)Long Beach8 x 10 inchesOil on artist boardSigned lower leftTitled in pencil, verso
Daniel Ralph Celantano (1902-1980)Long Beach8 x 10 inchesOil on artist boardSigned lower leftTitled in pencil, verso Harold Haydon (1909 – 1994)History of the US Postal Service21 x 25 inchesoil on canvas, c. 1938
Harold Haydon (1909 – 1994)History of the US Postal Service21 x 25 inchesoil on canvas, c. 1938