THE MONTEREY JET CENTER AUCTION
When Anthony Lago went to Suresnes in September 1933 to salvage Automobiles Talbot-Darracq, he took on a company with massive financial problems and a rather ho-hum range of cars.
The mechanical legacy left by his predecessor Owen Clegg and chief engineer Walter Becchia was staid and pedestrian. The nicest thing that could be said about the cars was that they did no one any harm. Sporty, stylish or chic, they definitely were not. In addition, models had been allowed to proliferate needlessly: too many engine sizes were served up in a bewildering number of chassis lengths and body styles, none of which were selling. One could say that while Talbot could produce a car for every occasion, there was unfortunately not an occasion for every car. Something needed to be done, and quickly.
While the many problems had seemed daunting to Lago’s predecessors, he was not going to let them or anything else stand in his way. Full of confidence, he had just completed the careful construction of the absolute deal of his life with Talbot’s British owners. Now at the age of 40, Lago was a dapper Anglo-Italian gentleman with little in the way of money, but of some sophistication: full of energy and vision for the disintegrating French company that now confronted him. In addition, he was an accomplished wheeler-dealer, who had worked very hard to get where he was.

By late 1932, Automobiles Talbot-Darracq S.A. in Suresnes just outside Paris, which was owned by the British Sunbeam-Talbot-Darracq combine (STD), was on the verge of bankruptcy.
Lago presented himself to the STD board as the “man to the rescue” and was sent from England to look Talbot-Darracq over and make a report as to what could be done. Upon examination of the moribund Talbot factory, Lago found a shambles. Chief engineer and fellow Italian Walter Becchia was on the verge of leaving, and the workers were uncaring and demoralized. The few cars being turned out were poorly put together. But beneath the dust and the cobwebs, Lago could see a plum ripe for the picking. So he went back to England, and instead of recommending liquidation, Lago suggested that he be made managing director of Talbot in France for a two-year period with a put option to buy the company and its holdings at any time at the 1933 value. Not knowing how hoodwinked they were, the STD directors accepted.
Lago then returned to France in the early fall of 1933 to rake the coals out of the fire with that doozy of a contract in his back pocket: potentially it would hand everything over to him if he played his cards right—which he did. The coals were raked out so ruthlessly that Antonio Lago, who in England had changed his name to Anthony, ended up owning Automobiles Talbot-Darracq S.A, once again without paying anyone anything.
When Lago finally exercised his option in 1935, he requested as payment that he might assume an old £500,000 debt that STD still owed the bank due to a loan taken in 1924, with the French factory as collateral. As the debt exceeded the book value of the company as well as that of the real estate, once again the STD directors accepted eagerly. Imagine: not only had Lago become a car maker without a centime to his name, but through this carefully laid out deal, he had also just become STD’s biggest creditor. And that was the devious plan. In 1936, Lago then let Talbot go bankrupt in connection with the great strikes in France. STD couldn’t very well call its remaining debt in with the liquidators, as Lago was first creditor in line, and his £500,000 would wipe the estate clean. In the end, Lago obtained Talbot scot-free.
While conducting these scurrilous financial dealings, he had set about transforming the company.
The plethora of available models, engines and chassis was pared down. Walter Becchia was given the job of redesigning the existing 14-CV six-cylinder engine in order to extract some much-needed extra power. The clunky non-synchronized three-speed gearboxes were supplanted by the advanced four-speed Wilson pre-selector for which Lago so conveniently held the patent rights.
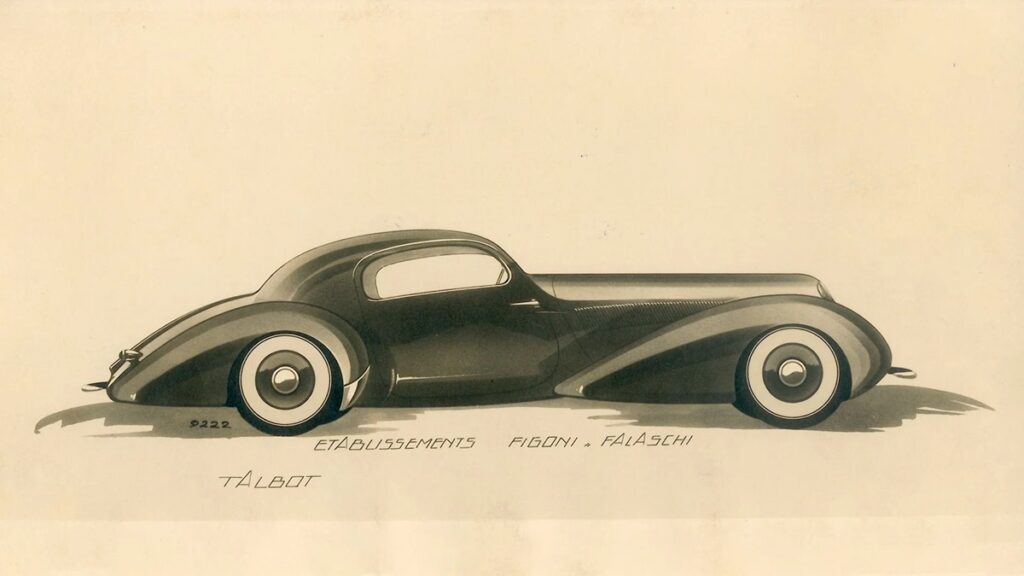
And most important of all, in the summer of 1934, Lago paid a visit to his friend Joseph Figoni and talked him into designing a series of new, lithe and beautifully proportioned bodies to be built at the Talbot factory. As a result, the Talbot stand at the October 1934 Paris Salon featured a new, rakish Talbot prototype cabriolet by Figoni mounted on a 295 cm wheelbase chassis, fitted with a 3-liter engine redesigned by Becchia. It was called the T150 Grand Sport, and it was the talk of the Salon. Then, Lago went racing. Suddenly, Talbots were a hot commodity, and it is no exaggeration to say that the rest is history.
The T150 C and T150 C-SS Chassis
The T150 Grand Sport remained in production for roughly 18 months. At the October 1936 Salon, Anthony Lago and Walter Becchia presented the fruits of their continued labors in the form of two new and spectacular chassis. The first was an out-and-out sportscar chassis fitted with Walter Becchia’s new 4.0-liter high-performance development of the 3.0-liter six: the Lago T150 C-SS, placed at the very top of the market and only available as a bare chassis for the trade.
In all, less than 30 were made, yet the Lago C-SS would go down in history as one of the great pre-war chassis, on par with the legendary Bugatti 57S and Alfa Romeo 8C 2300. Wheelbase was 265 centimeters, which was identical to the Talbot T150 C GP cars from which the chassis was developed, and it was wide enough to accommodate two-passenger bodies with side-by-side seating.
The second chassis, named the T150 C, was equally formidable as it was mechanically identical to the C-SS, and fitted with the same great engine, but stretched 30 centimeters to a wheelbase of 295 centimeters. The benefits were two-fold. On the one hand, the extra length meant that two rows of seats could be accommodated if a four-to-five-passenger configuration was desired. But more importantly, the longer wheelbase made it possible for coachbuilders to achieve beautiful and harmoniously flowing lines of great elegance—especially on closed bodies with a single bench seat, such as 90034. The engine, gearbox, electrics and suspension specification would remain unchanged for the entire production run.
The construction and layout, as well as the mechanicals, were conventional and represented classic mid-1930s fast-car thinking. Both chassis were low, as the two rails passed under the rear axle and suspension. The engine, gearbox, firewall and suspension components were bolted directly onto the chassis. The steering was worm and nut, and the front suspension was independent with a transverse leaf spring. The live rear axle was suspended by half-elliptic leaf springs, with the suspension mounts on top of the chassis rails.
There was a short transaxle between the engine and the Wilson gearbox, followed by the driveshaft. The gearbox created a hump in the middle of the floor of the cabin just in front of the seats. For repairs and maintenance, the gearbox could be accessed through the floor in the interior of the car. The chassis had a foot operated one-shot lubrication system with a pedal actuated by the driver. The gas tank was a large 120 liter affair mounted on the chassis rails behind the rear axle. The complete T150 C chassis with all components, Wilson gearbox and ancillaries remained relatively light. It was a genuine 100 mph car.

The T150 C-SS and T150 C Engine and Gearbox
Lago’s first brief for Walther Becchia had been the job of developing the 14-CV Talbot six. This engine was bored and stroked to 78 x 104.5 mm, giving 2,996 cc, or 17 fiscal CV, and mounted in a 295 centimeter Talbot chassis. This chassis had already been fitted with an independent transverse leaf front suspension since 1932, which had been patented by Becchia in 1928. Dubbed La Solution Talbot, this suspension gave the chassis the makings of a sports car. The chassis was also given the Wilson gearbox, and the Talbot T150 Grand Sport was born.
For the T150 engine, Becchia designed a new cylinder head with a pent roof that created a nearly hemispherical combustion chamber, inclined valves operated by a single camshaft in the crank case, pushrods and rocker arms. This T150 3-liter put out a very satisfactory 100 horsepower at 4,200 rpm on a 7.4:1 compression ratio with one carburetor, and 110 horsepower with three. It compared well to the 18-CV Delahaye 3.2-liter engine, which Lago saw as his main competition. Whether it was a reflection of the true build costs or Lago’s chronic need for money, the new model carried a peppery price tag. At 78,000 francs, the T150 was not much cheaper than an eight-cylinder Bugatti T57 and a lot more than a six-cylinder 18-CV Delahaye.
Racing was a major motivation driving the development of the new engine. In mid-1935 however, the Automobile Club de France published their new rules for the 1936 season, which stipulated a blown 2.0-liter and an unblown 4.0-liter class. Therefore, in August of 1935, Lago demanded of Becchia that he design a new T150 C racing car from “scratch” for the 4.0-liter formula. Becchia now increased the bore of the 17 CV to 90 mm, but retained the stroke of 104.5 mm. Capacity was increased to 3,988 cc, which equated 23 fiscal CV. The light alloy hemi head remained, and the crank now ran in seven main bearings. In racing trim with three carburetors, power was a considerable 175 horsepower from this normally aspirated engine, permitting a top speed around 210 km/h on the circuits when the chassis was fitted with a light barquette body.
T150 C racers premiered on the French circuits in spring and summer of 1936, while the long and short wheelbase race-derived road-going versions of the 4.0-liter T150 C and T150 C-SS were shown at the October 1936 Paris Salon. In all cases, the “C” was short for Compétition. In the spring of 1937, the long chassis was renamed Lago-Spécial and the short Lago SS. Both featured Rudge knock-off wire wheels and a slightly detuned version of the 23-CV T150 C engine, now putting out 140 horsepower for road use. Lago had entered the Bugatti, Delage and Delahaye market for bespoke, stylish grand routières and sports cars.
By 1939, the Lago SS engine could be ordered in various stages of tune, delivering as much as 200 horsepower for competition and 165 horsepower for road use, which made a top speed of up to 200 km/h possible. This was an absolutely extraordinary figure for a road car at the time. From 1937 through 1939 and the breakout of hostilities, close to 25 T150 C-SS chassis were built, along with approximately 40 to 50 T150 C. Both types were, and are, very rare cars indeed.
Figoni, the Coachbuilder
Guiseppe Herménegilde Louis Figoni was born on 29 December 1892 in a tiny crossroads named Le Moline di Montereggio, about 45 km southwest of Piacenza in the province of Parma in the Emilia-Romagna region. Life was hard, people were poor, and in 1906, like many from northern Italy, the Figoni family emigrated to France to find work. They ended up in Boulogne-sur-Seine, the “Little Italy” of Paris, a working-class suburb far removed from what has now become posh and trendy Boulogne-Billancourt. After having served in the Great War on the Italian side, Joseph was apprenticed as a panel beater, or tôlier, to the well-known coachbuilder Lavocat et Marsaud. In 1923, he opened a modest carrosserie under his own name in Boulogne-sur-Seine.
Sometime around 1931, Joseph became a personal friend of Luigi Chinetti who ran the small and underfunded Alfa-Romeo operation in Paris. In 1932, Chinetti sent the famous racing driver Raymond Sommer to Figoni to have his Alfa-Romeo 8C 2300 chassis 2111018 rebodied to Le Mans specifications. The car won the 1932 race with Chinetti and Sommer at the wheel. For 1933, Sommer’s body was transferred to 8C 2300 chassis 2211109 that then proceeded to win Le Mans once again, driven by Tazio Nuvolari and Sommer. Suddenly, Figoni was the hottest name in French racing circles. Clients became a who’s who of legendary drivers, and for the next three years, the Figoni works virtually became an extension of the French Alfa-Romeo enterprise.
Joseph’s 1934 collaboration with Anthony Lago was another major breakthrough, not only in terms of securing clients that wanted a custom-built Talbot, but also in making the Figoni name world famous—at least in France at any rate. With all this activity, the small Figoni premises were bursting at the seams. Still, profits were not sufficient to allow for necessary expansion, and financial restrictions made it necessary to find an investor. This investor was Ovidio Falaschi, a fellow Italian who became partner in May of 1935. The company was reorganized as the Établissements Figoni et Falaschi, and several surrounding premises were leased so that bodies could now be manufactured at a rate that was a good deal faster than before. It should be noted that Ovidio Falaschi took a strictly financial interest and was not involved in the designs made by the company.
Design 9222
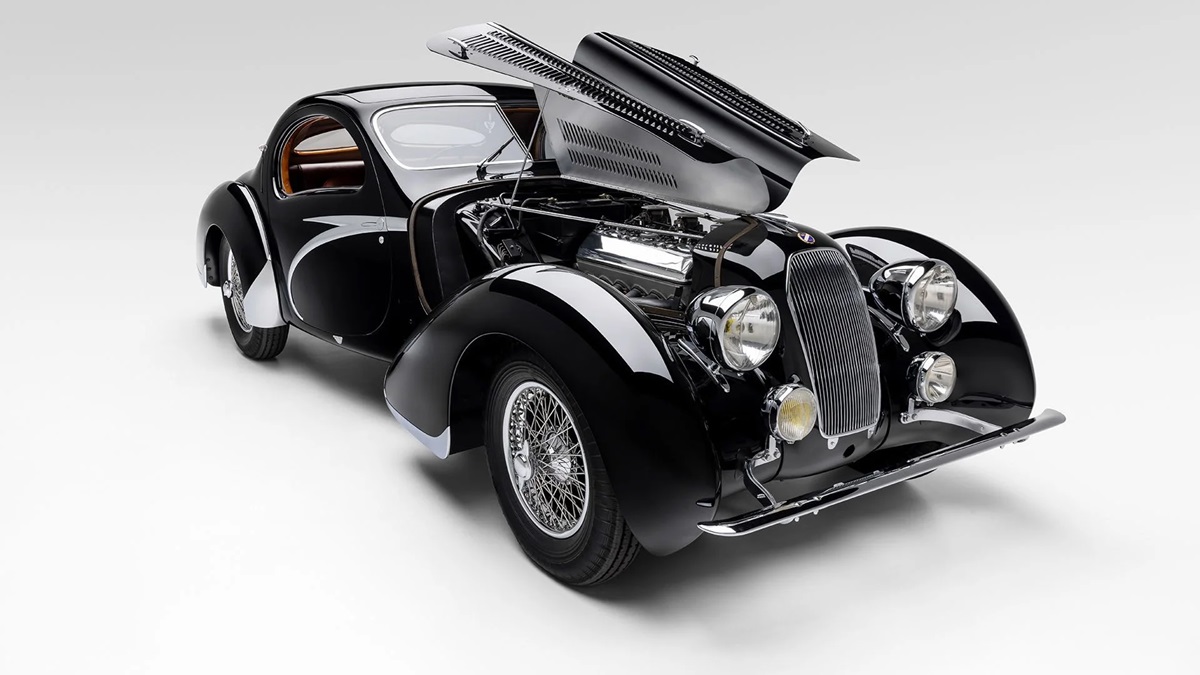
The star, the Figoni design that eclipses all else, remains the streamlined, two-seater coupé body that has become universally known as the Goutte d’Eau, which means water drop in French, now translated as Teardrop. It is a design of such breathtaking beauty that it has become one of the most iconic automobiles of all time. A maximum of thirteen are believed to have been built on the T150 C-SS chassis, two on the T23 Baby 4.0 Liters chassis, and only one T150 C, namely chassis 90034, the subject of this discussion.
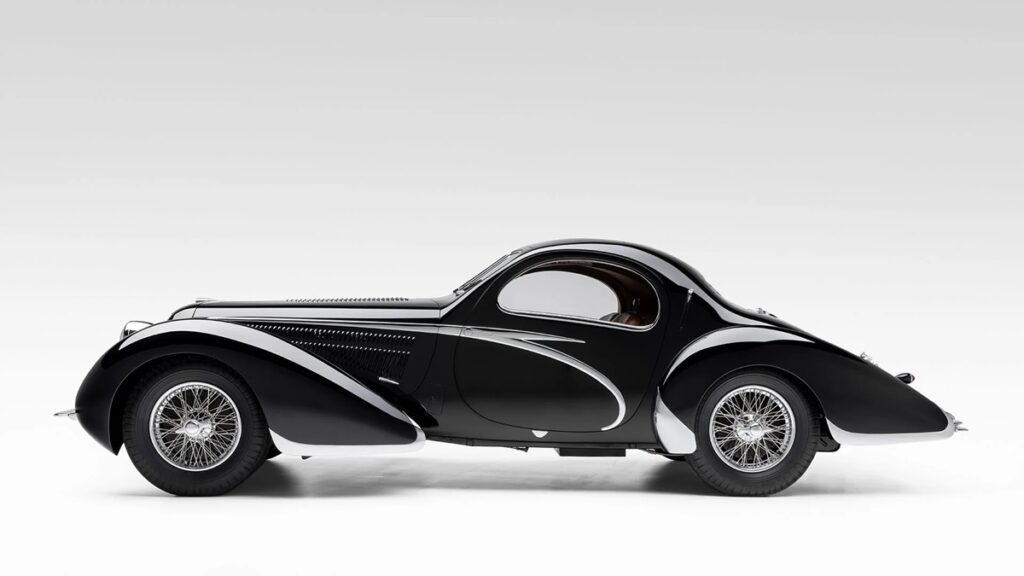

Yet it is a body that more than 85 years after its inception, and despite its age, is instantly recognizable to automotive enthusiasts all over the world. It is one of the very few designs that is aesthetically correct, balanced and in equilibrium from any angle. This absolute harmony of line is a rare achievement indeed, and one that the Goutte d’Eau shares with only a minute number of other automotive design statements that are equally famous and universally revered, such as the “coffin-nosed” Cord 810, the Ferrari 250 GT California Spyder, the Lamborghini Miura or the first series Jaguar E-Type. Exalted company indeed.
Interestingly, it was the media who gave the Goutte d’Eau its name. While no one will dispute that it was fitting, the design was simply called a Faux Cabriolet by Figoni, and this in spite of the fact that the style has no elements that relate to the look of a classic (faux) cabriolet. Two versions existed of Figoni’s basic faux cabriolet design, a fastback and a notchback, which makes definitions even more confusing: the designations Coupé Amérique or Modèle New York were used indiscriminately by Figoni for the fastback, named so because it was first shown at the 1937 New York Auto Show, and Coupé Jeancart for the notchback as an industrialist named Jeancart bought the first body constructed to this style.
There were three Jeancart designs: no. 9220 with enclosed fenders front and rear, 9221 with exposed front wheels and enclosed rear wheels with fender skirts, and 9222 with no fender skirts and all four wheels exposed. On T150 C chassis 90034 the wheels are exposed, and it was therefore bodied to design 9222 and not 9221 as has been stated elsewhere.
Enter Antoine Schumann
In 1925, Luigi Chinetti was working as a mechanic for the Alfa-Romeo racing team. Like Anthony Lago, he was unhappy with the rise of fascism in Italy. After the team had completed its racing efforts in France and was on the cusp of returning to the home country, Chinetti decided to stay. As mentioned above, he then worked out of the premises Alfa-Romeo had established in Paris in the rue Marbeuf, just off the Champs-Élysées, which led him to sell an 8C 2300 to up-and-coming race driver Raymond Sommer. Chinetti had the car rebodied to Le Mans regulations by Figoni, and being the consummate wheeler-dealer that he was, he secured the position as Sommer’s co-driver in the 1932 Le Mans race which they won.
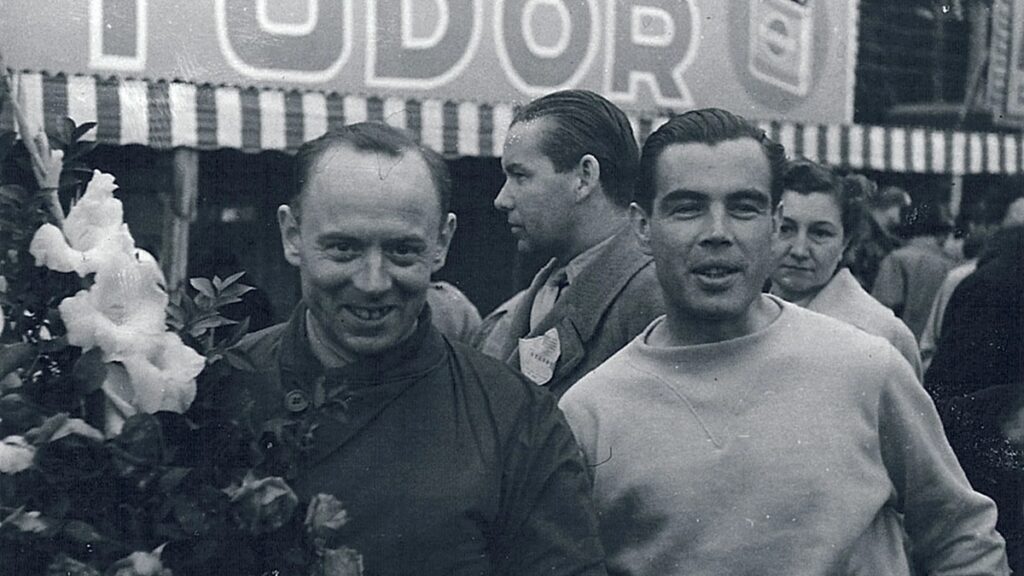

This marked the beginning of a lifelong friendship between Luigi Chinetti and Joseph Figoni. After he left Alfa-Romeo, Chinetti became a sales agent for Talbot-Lago, and Joseph Figoni gave Chinetti the exclusive rights for France to sell Talbot-Lago chassis fitted with teardrop bodies by Figoni et Falaschi. As a result, it was Luigi Chinetti who sold 90034 to wealthy banker and gentleman racer Antoine Schumann for the princely sum of 165,000 francs.
The car was delivered to Schumann in Paris in January 1939. Antoine Marc Philippe Jacques Schumann was born on November 26, 1905, in the home of his parents who lived in an imposing building at no. 5 rue Beaujon in the 8th arrondissement of Paris. It was a family of means. Antoine’s father, Robert Schumann, was a banker, and his mother Alice, née Lehmann, also came out of a banking family. Antoine’s birth certificate was witnessed by Paul Jaillot and Gaston Grainger, both employees of the bank: it was in the cards that baby Antoine would eventually follow in everyone’s footsteps and enter the world of finance.
Antoine married Eliane Louis-Dreyfus on April 13, 1929. It may well have been true love, but the marriage certainly buttressed the coffers of the young couple, as the Louis-Dreyfus family was equally well-to-do. Charles Louis-Dreyfus, Elaine’s father was a shipping merchant, while her grandfather was a banker, a former member of parliament and a recipient of the Croix de Guerre, a military decoration given for valor during World War I.
Important for this discussion, however, is that by this marriage, Antoine Schumann became brother-in-law to Pierre Louis-Dreyfus, as he was Eliane’s younger brother. Pierre was already a repeat customer of the Figoni and making his mark as a gentleman racer. Soon Antoine shared his passion for fast cars.
But before that, Pierre Louis-Dreyfus and Antoine Schumann had become their own racing team, a secretive privateer racing duo that would garner fame in French racing circles. As gentleman racers they desired no publicity surrounding their names. In addition, daredevil antics on the tracks could reflect negatively on their careers in business, and as a result they camouflaged themselves with a number of pseudonyms. However, since these pseudonyms were in the nature of acronyms, it is moot whether many, if any, were actually fooled.
As he was more active over the years than Antoine Schumann, Pierre Louis-Dreyfus had more than one of these assumed names. When racing alone or with other co-drivers, he used the acronym Heldé, which was a transcription of the French pronunciation of the initials of the Louis-Dreyfus surname: LD. But when Pierre and Antoine raced together, the duo facetiously called themselves Ano (Pierre) and Nime (Antoine) for driver and co-driver, a play on Anonime, which means Anonymous in French.
As this daring duo they raced at Le Mans in a Bugatti Type 43 in 1931, an Alfa Romeo 8C 2300 LM in 1932 and a Talbot T150 C in 1939—not with outstanding results unfortunately as they were forced to retire on all three occasions. But that is the nature of gentleman racing. You are up against factory-sponsored teams, and it is the sportsmanship, the participation and the thrill of the race that is the essence of it all. It can therefore come as no surprise that Antoine Schumann was a connoisseur of fast road cars too. This included a massive 5-liter Bugatti Type 50 that was sold by the Bugatti factory to him on February 19, 1932.
Luigi Chinetti sold Talbot-Lago chassis 90034 to Antoine Schumann in September 1938. It was delivered that same month to the Figoni et Falaschi works at no. 14 rue Lemoine in Boulogne-Billancourt. The Carrosserie assigned body order number 738 to the build, and this number can be found stamped on body parts of the car. Perhaps Schumann bought the car for himself as a consolation prize of sorts, as by this time, his marriage to Eliane was on the rocks: they were divorced on 12 November 1938 by order of the civil court. He ended as the second of her four husbands. If this was his motivation for buying 90034, one may say that Antoine Schumann certainly knew how to defuse bad feelings!
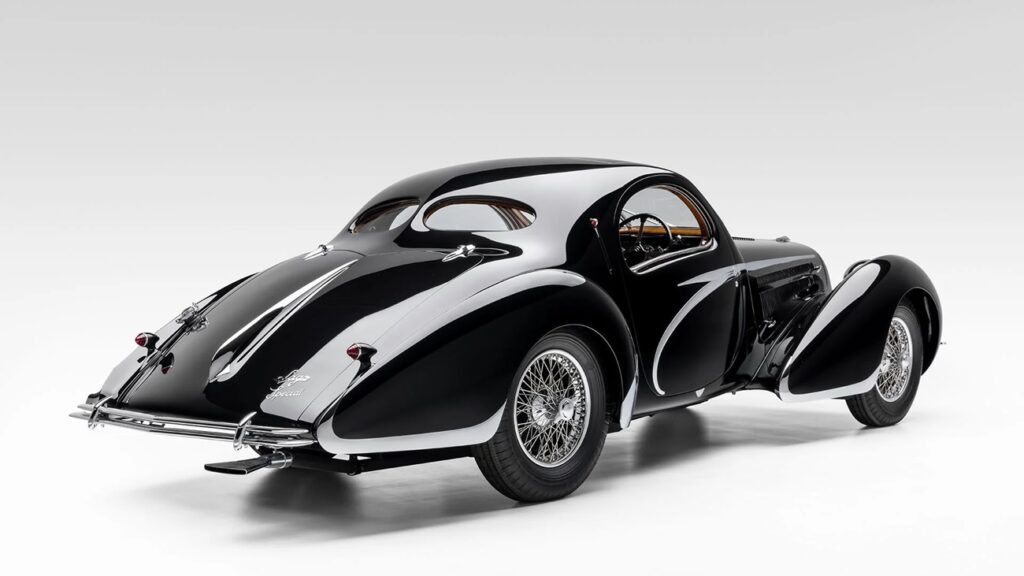
For this very special chassis, Schumann selected Figoni et Falaschi design no. 9222, which with its open rear fender style was a good deal more sporting than the enclosed rear fender of design 9221. But while sportsmanlike, 9222 is nevertheless a style which in many ways remains the most elegant and tasteful of all Joseph Figoni’s streamlined efforts in the late 1930s. Features that link the exquisite body on chassis 90034 to the other Teardrops built by Figoni include the split windshield, integrated doorhandles, the smooth execution of the grille and front fender tips, the double row of side louvers on the hood, as well as the judicious use of chromed scallops.
The extra 30 centimeters of wheelbase compared to the T150 C-SS chassis made it possible for Joseph Figoni to create smooth, flowing lines of unparalleled harmony which in their execution were simply captivating to the eye. The length of the hood and the front fenders were much the same as the proportions used on the shorter chassis, but the notchback of the Jeancart greenhouse was subtly refined and the rear deck was transformed into a long delicately sloping tail that was a masterclass in balance and proportion. Longer, lower and wider than its siblings, the sporting stance of the T150 C Jeancart coupé is unparalleled. No one could be in any doubt that 90034 was a fast car.
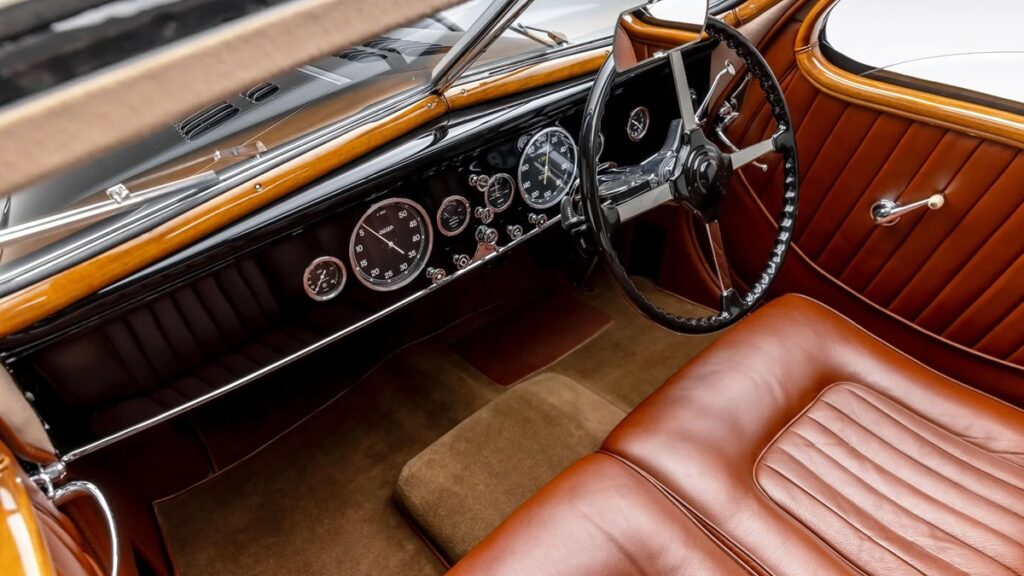

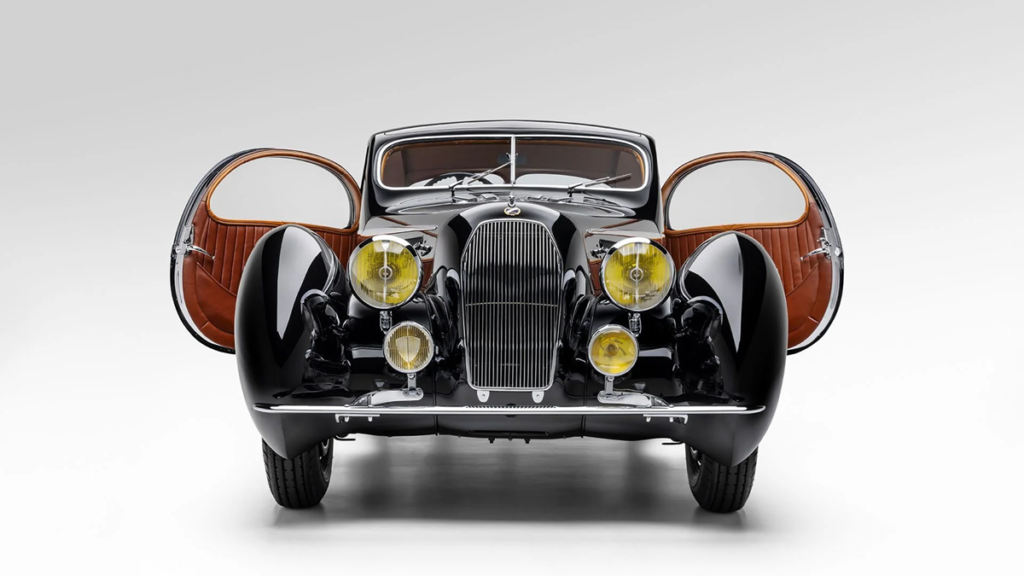
As a true appreciator of fine cars, Schumann had Figoni incorporate a number of bespoke details that were special orders. The livery was specified as bleu “Tango” irisée noire, which was a metallic dark blue with a black tinge, a very expensive selection as metallic paints were rare and costly to make at the time. Traces of this original dark blue may still be found behind the dashboard and inside the glovebox. The three-abreast seat was upholstered in Havana (tobacco) leather with matching wood on the door cappings. The dash was fitted with a full set of Jaeger instruments with black dials and painted in body color, while the carpets and headliner were in a delicate shade of gray. Special curtains in Havana leather were made for the rear window.
Bespoke details to the body included free-standing headlights. The enclosed headlights seen on most Teardrops provided poor light for night driving, and a number were in fact modified by their early owners, simply because they couldn’t see properly in the dark. In addition, the body received a full sliding sunroof, detachable rear fenders, a Lago Spéciale script on the rear deck and opening rear windows to improve airflow in the cabin. Most importantly, however, Schumann specified a graceful, chromed sweep spear on the body side, a unique styling enhancement that was used on a number of Figoni designs in this period but was absent on design 9222. This started as a beltline at the trailing edge of the radiator shell, ran along the edge of the hood and then swept down in a supple curve along the side of the door, only to double back on itself at the sill. Pure aesthetic genius.
Antoine Schumann was able to enjoy his jewel of a car until the Nazi invasion of France which began in May 1940. The Schumann family was Jewish, and Antoine was forced to either leave France or face deportation to German concentration camps. As so many other cars during the Nazi Occupation, the striking Talbot-Lago was squirreled away as it would have been one of the first cars the Occupiers would have expropriated for their own use without compensation. Antoine fled to Egypt, took a pilot’s license and joined the French Resistance.
There, he flew for the Compagnie de l’Air au Moyen-Orient, a squadron operating out of Cairo that fought Nazi Field Marshal Erwin Rommel’s Deutsches Afrika Korps and participated in the Battle of Tobruk. From 1943, Antoine Schuman served under François Dumont in the air force of the Forces Françaises Libres, the Free French Forces. For his bravery during the war, Schumann was made an Officer of the Legion of Honor and awarded the Croix de Guerre. On April 18, 1947, he married Jeanine Constantinovitch, and on June 25, 1948, for reasons unknown, he changed his last name to Saville. At seven in the morning on August 15, 1956, Antoine Schuman died as Antoine Saville in his apartment at no. 16 rue Paul Valéry in the 16th arrondissement of Paris. He was 50 years old.
Frédéric Damman and the 24 Hours of Spa
Paris was liberated on August 19, 1944, but fighting continued in Europe until Germany surrendered unconditionally on May 7, 1945. It is not known when Antoine Schumann returned to France, but it seems that he kept 90034 until sometime in late 1946 or early 1947. Paul Frère, the late racing champion and noted automotive journalist, remembered seeing 90034 in Brussels in 1946 or 1947 where it was for sale with the Garage Masuy, located in the rue de Stassart, close to the Porte de Namur in downtown Brussels. The car was apparently in nigh on perfect condition, which is consistent with the fact that it had been laid up during the War and had not seen much use since its delivery in January of 1939.
Sometime in 1947, chassis 90034 was purchased by Frédéric (a.k.a. Freddy) Damman, owner of the Magasins Butch clothing stores which provided him with the wherewithal to finance his hobbies as amateur pilot and race driver. 90034 received registration 2536, and Damman had the car repainted in gray, after which he prepared it for participation in the 1948 Belgian Grand Prix, Les 24 Heures de Spa, which took place on July 10 and 11. Chassis 90034 was entered in the 4-liter category and given race no. 92. With Damman and co-driver and mechanic Constant Debelder at the wheel, the car placed first and won its class—an impressive result for a nine-year-old car.
Freddy Damman’s daughter has recounted that it was love at first sight when he first spotted 90034 in the Garage Masuy showroom. There is no reason to doubt this, as it turned out to be a very long love affair on Damman’s part: he kept 90034 for 32 years until July 17, 1979, a few months after its 40th “birthday”, when he finally parted with his cherished Talbot-Lago in a private sale. His daughter said that Damman owned many cars over the years, only retaining one or two important cars at a time. This included a number of exotic Ferraris, but it was always 90034 that was the keeper, the car that stayed behind when the time came to buy something new. The Talbot was simply the car he loved the most.
Moving On
The lucky buyer in July 1979 was Gaston Garino who had worked at the Hispano-Suiza factory in Bois-Colombes. In the early 1950s, Garino purchased an old garage in Puteaux where he specialized in keeping Hispanos on the road. By 1979, Garino had partnered with M. Lerouvillois, and the enterprise had become a dealer in high-end classics. 90034 was registered 1551-HN-92 by Garino, using the chassis identity of T150 C-SS chassis no. 90121, a Pourtout-boded car, on the registration document. This subterfuge may have been performed for customs reasons. Chassis number 90121 was an obscure car at the time as it was not finished until October 1944 after the French Liberation and had been exported to the USA in 1953.
On May 14, 1980, and still using the identity of 90121, chassis 90034 was re-registered 543-DAL-75 and sold to film producer and businessman Michel Seydoux, a famous early French collector in Clausonne in the Alpes-Côte d’Azur region. The car was auctioned by Poulain-Le Fur on December 16, 1981, and passed from Seydoux to Yves Rossignol, an avid motoring enthusiast of little means. Once again, 90034 received a new registration, namely 1938-KB-13. Rossignol kept 90034 for 23 years. During that time, the car received a two-tone black and burgundy livery but was subsequently repainted in a single shade of black. Importantly, it remained unmolested and complete, and had never received an actual restoration. In 1998, thanks to the help of the Talbot Club and its President Dominique Dupont, the original identity of 90034 was re-established.
In 2004, Antoine Rafaëlli, the legendary author of Memoirs of a Bugatti Hunter, contacted Toby Ross, another car sleuth, telling him that he had seen a Teardrop in Marseille some years back, and that it belonged to someone called Yves Rossignol. They located Rossignol in a garage in Nice where he was making security bars for windows. A friendship was established, and eventually, Rossignol agreed to sell.
Yves Rossignol described himself as an “Adventurer”. In the past he had been the young boyfriend of Madame Coty of Coty Perfumes. At some point, she bought the Talbot for him at a Paris auction which can only have been the Poulain-Le Fur auction. He later married a lady from Columbia and spent time in South America. At some point, “La Noire” as he called 90034, was shipped to South America, where Rossignol used it. It starred in a long-forgotten film and Rossignol had a photo of the car being rowed across a lake on a wooden raft.
At some point, Rossignol and the car returned to France—he sans wife. She had gotten fed up with him being penniless. By the time Toby Ross was negotiating with Rossignol, La Noire was hiding in plain sight in a car museum close to Geneva airport. Toby Ross went to see it, took some poor-quality photos in the gloomy museum and set about selling it. In July 2004, chassis 90034 sold to Marc Caveng of 135 Route de Chêne, Chêne Bougeries, a collector-dealer based in Geneva, Switzerland, who repaired the engine head, renewing the valves. Yves Rossignol took his payout and went back to live with his wife in Columbia. In 2005, Caveng sent 90034 to auction in Monterey, where it sold to the late John O’Quinn.
90034 was then sent to RM Auto Restorations in Blenheim, Ontario, Canada for a comprehensive restoration. The body was refinished in a deep luminous black, while the original tobacco leather was renewed in the same shade and the original wood trim was kept and refinished. The car was extraordinarily complete, so virtually all body panels remain original. The engine and mechanicals were fastidiously reconditioned. After the passing of John O’Quinn in October 2009, chassis 90034 was sold to its current owner in August 2010 at the Monterey auctions.
For the past fourteen years, this deeply historic automobile with its ground-breaking coachwork of timeless beauty has been part of and curated by an important collection on the West Coast of the United States. This is the singular motorcar that is being offered. Highly original and authentic, in beautifully restored condition, it has a continuous and unbroken history of ownership since its inception in September 1938 when ordered by Antoine Schumann. Many years after the fact, Paul Frère remembered the unique engine and exhaust note he heard when this Talbot-Lago blasted by at the 1948 24 Hours of Spa. This is a car that makes memories, a car that stays with you. One word from Cole Porter’s famous song for the Grace Kelley, Frank Sinatra and Big Crosby film High Society sums up Talbot-Lago Teardrop chassis 90034: Unforgettable. For the Silo, Caroline Cassini.
- Ordered new by gentleman race driver and banker Antoine Schumann as a replacement for his Bugatti Type 50
- Sold to Schumann by Luigi Chinetti for the sum of 165,000 francs
- The only Figoni Teardrop Coupé built on the T150 C Lago Spéciale chassis
- Special-order body with unique features specified by Schumann
- Class winner at the 1948 Belgian Grand Prix, the 24 Hours of Spa
- Known provenance with ownership by prominent French collectors
- An outstanding design icon of remarkable and enduring beauty
Chassis No. 90034
Chassis No. 90034
Figoni et Falaschi Design No. 9222
1938 Talbot-Lago T150 C Lago Spéciale Teardrop Coupé by Figoni et Falaschi
Auction Sale Estimate: $6,500,000 usd – $8,500,000usd/ $8,900,000cad – $11,600,000cad
