- Following Indonesia, the Philippines joins the World Economic Forum’s Blue Carbon Action Partnership to safeguard crucial coastline ecosystems in South-East Asia.
- Mangroves and other littoral biospheres provide a critical buffer against climate change globally, but environmental degradation is putting them under threat.
- Momentum builds at COP28 for the conservation and restoration of these critical blue carbon ecosystems, for the benefit of people, nature and the climate.
- Learn more about the World Economic Forum’s work at COP28 here.
Dubai, United Arab Emirates, December 2023 – The Government of the Philippines’ Department of Environment and Natural Resources announced yesterday at COP28 that it is joining the World Economic Forum’s Blue Carbon Action Partnership to accelerate the restoration and conservation of coastal ecosystems.
South-East Asia is home to almost one-third of mangroves globally, with nearly 20% of the world’s mangroves in Indonesia alone.
Blue carbon ecosystems such as mangroves, seagrasses and salt marshes store up to five times more carbon per acre than tropical rainforests and have been receiving greater attention in recent years. Yet, these ecosystems are under threat of destruction. These important carbon sinks also provide support for livelihoods, food security, shoreline protection and habitat for numerous.
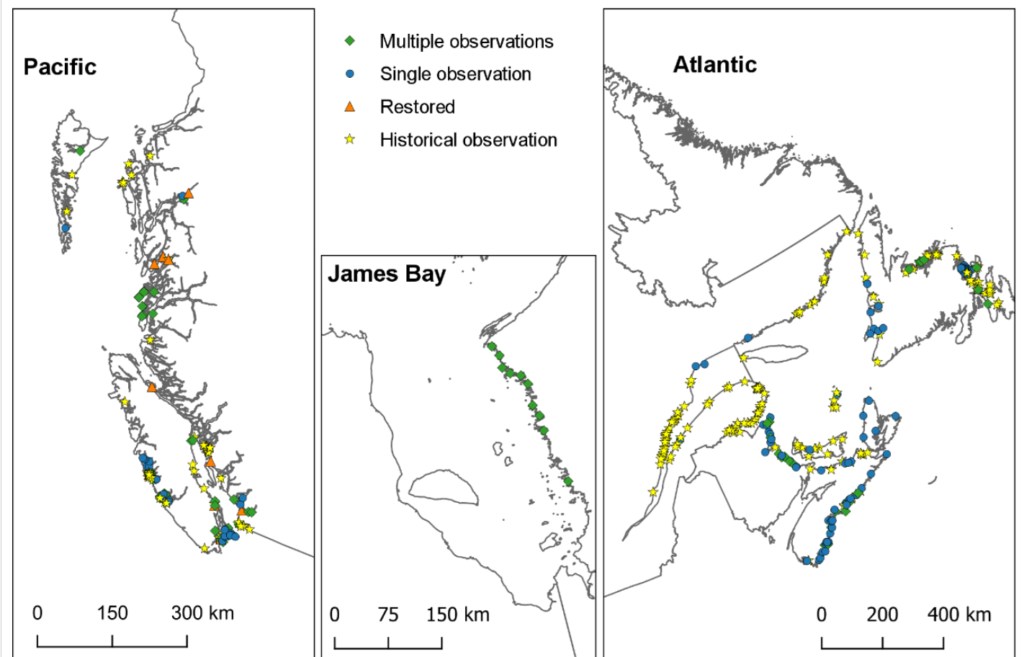
Eelgrass (seagrass) distribution on Canada’s sea coastlines are under threat.
Source: Environment and Climate Change Canada (2020).
The importance of eelgrass to ecosystems was shown after a widespread wasting disease outbreak along the Atlantic coast of North America in the 1930s resulted in a 90% loss of eelgrass. It is estimated that populations of migratory Brant geese along the Atlantic coast, which rely heavily on eelgrass outside the breeding season, declined by as much as 90%. Declines of clams, lobsters, crabs, scallops, cod and flounder were also reported following the loss of eelgrass.
Eelgrass beds are highly productive and several studies have indicated that eelgrass beds contribute to the sequestration of “blue carbon” in marine sediments, providing a valuable ecosystem service in coastal areas.
“Coastal ecosystems such as mangroves are critical to life in the ocean and to those who live alongside it. Increasingly, we are also recognizing their vital role to buffer us against the worst effects of the climate crisis,” said Alfredo Giron, Acting Head of the Ocean Action Agenda and Friends of Ocean Action at the World Economic Forum. “When blue carbon benefits are recognized and valued by governments and businesses, who commit and invest in the restoration of mangrove, seagrass and salt marsh ecosystems around the world, everybody wins – people, nature, climate and ultimately, the planet.”
The newly launched National Blue Carbon Action Partnership in the Philippines will convene, coordinate and support implementation to scale high-quality blue carbon action, representing nearly 700 billion metric tons of carbon sequestered in mangroves and seagrasses in the country.
“The Philippines, endowed with rich biodiversity and extensive coastlines, is home to vast blue carbon ecosystems. We look forward to working with the Blue Carbon Action Partnership to facilitate the inclusive, whole-of-society approach to developing a shared ambition for blue carbon, community resilience, inclusive development and unlocking the Philippines’ potential to provide nature-based climate solutions for the rest of the world whilst supporting our programs for protected areas and preparing the country for participating in the new blue economy,” said Antonia Loyzaga, Secretary of the Department of Environment and Natural Resources of the Philippines.
The Philippines partnership is the second to be launched after an agreement last year with the Government of Indonesia, which has also strengthened its partnership agreement with the World Economic Forum at COP28 and is preparing to launch its National Blue Carbon Action Partnership secretariat. Combined, the Philippines and Indonesia house 4 trillion tons of carbon in their blue carbon ecosystems, which is the carbon equivalent of over 11 trillion of barrels of oil consumed.
There is increasing demand for blue carbon ecosystem restoration and conservation to attain the multifaceted benefits these ecosystems provide, including food security, support for livelihoods, coastal protection and carbon storage. Working with its government partners, the Blue Carbon Action Partnership can support connecting finance with countries that have established policies to receive blue carbon ecosystem investment.
“The ocean is our largest buffer in tackling the climate crisis and it plays an essential role in climate change mitigation, resilience and adaptation as well as regulating the global weather system. It is encouraging to see the ocean gaining increasing prominence as a natural resource for accelerated climate action,” said Giron.
