 The Great Lakes are one of the world’s most important natural resources – holding one fifth of the world’s fresh surface water, home to more than 150 species of fish, and vital to the economy of Ontario and neighbouring U.S. states. But several kilometres from Lake Michigan lurks a threat that could change the Great Lakes forever. The fish known as Asian carp could wipe out native fish species, devastate sport and commercial fisheries, and cause far-reaching changes to the Great Lakes ecosystem.
The Great Lakes are one of the world’s most important natural resources – holding one fifth of the world’s fresh surface water, home to more than 150 species of fish, and vital to the economy of Ontario and neighbouring U.S. states. But several kilometres from Lake Michigan lurks a threat that could change the Great Lakes forever. The fish known as Asian carp could wipe out native fish species, devastate sport and commercial fisheries, and cause far-reaching changes to the Great Lakes ecosystem.
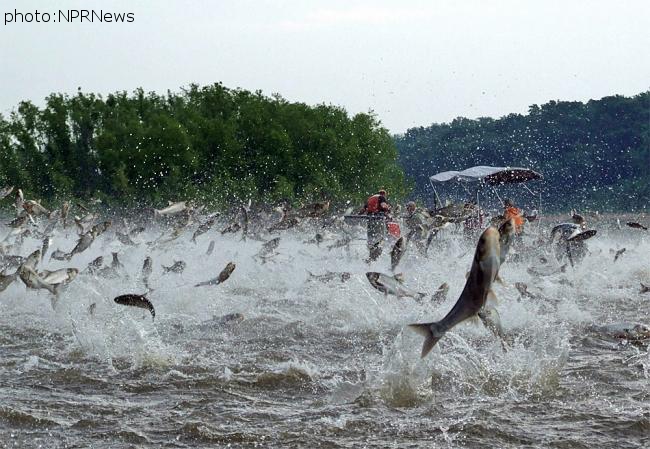
If you need proof of the danger to the Great Lakes, take a look at the Mississippi River Basin. After escaping from aquaculture ponds in the southern U.S. in the 1970s and 80s, Asian carp have spread steadily northward. In parts of the Mississippi and other rivers, invasive, voracious Asian carp have crowded out native fish and make up as much as 90 per cent of all fish by weight. Only electric barriers in a canal near Chicago are currently keeping the fish out of Lake Michigan.
The need for a coordinated plan to fight Asian carp led the Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources, with support from the Department of Fisheries and Oceans Canada, to host a “table-top exercise” in March. The exercise simulated an incident where Asian carp get into Ontario waters. The aim was to test if the agencies involved are ready to respond quickly and effectively.
“Preventing Asian carp from spreading into the Great Lakes is the most cost-effective control measure we’ll ever have,” says Ontario Minister of Natural Resources Linda Jeffrey. “This exercise was about making sure all the agencies involved work together, and identifying areas where we’re vulnerable.”
For the March exercise, participants rehearsed how they would respond IF an accident on a bridge over the Thames River in southwestern Ontario caused a truckload of live Asian carp to be dumped in and near the river. It was a timely choice – only a week earlier a fish importer had been fined $50,000 for trying to truck 1,800 kilograms of live Asian carp across the Windsor/ Detroit border to sell in the Greater Toronto Area. It’s illegal to possess live Asian carp in Ontario.
The term “Asian carp” includes four species – bighead, silver, grass and black carp. The bighead and silver carp currently pose the biggest threat. They weigh up to 45 kilograms and can grow to more than a metre long. As filter feeders that can eat 20 per cent of their body weight a day in plankton, they’re able to grow and multiply faster than native species. In some areas in the U.S. carp populations are doubling every year.
Silver carp are also a hazard to people on the water. When disturbed by boat motors, the fish jump as much as two metres out of the water. Boaters and water skiers on the Illinois River have already been hit and injured.
Canadian and U.S. experts agree that Asian carp would thrive in the Great Lakes, and that quick action is the only way to prevent Asian carp from spreading if they are found in the Great Lakes Basin.
During the table-top exercise, local MNR staff described how they would place nets upstream and downstream to catch and identify fish in the river, test the fish to find out if they could reproduce, and confirm if the river habitat was suitable for Asian carp. The agencies involved also had to decide if any local species at risk might be harmed by the control measures, and keep governments, partners, the public and the media informed.
“Ontario’s recreational fishery contributes $500 million to the province’s economy each year, our commercial fishery is worth up to $215 million a year, and the Great Lakes ecosystem is priceless,” says Minister Jeffrey. “With so much at stake, we have to be prepared.” For the Silo, Lacey Williamson.

Ontario invests $850,000 in Invasive Species Centre Funding to support management and advance scientific research in the fight against invasive species
SIMCOE – The Ontario government is investing $850,000 in the Invasive Species Centre to support ongoing research and management of invasive species across the province.
The Invasive Species Centre, based out of Sault Ste. Marie, brings together government, academic, industry and Indigenous communities and organizations to conduct invasive species research, response planning, management and habitat restoration.
“We recognize the importance of prevention, early detection, response, and eradication of invasive species for our natural environment and the people of Ontario,” said John Yakabuski, Minister of Natural Resources and Forestry.
“With this investment we are prioritizing research and response strategies to prevent long-term impacts to our land, lakes, rivers, and economy,” said Toby Barrett, MPP for Haldimand-Norfolk. “We believe the Invasive Species Centre is in the best position to protect our ecosystems province-wide.”
The ministry will continue to work with conservation partners to coordinate prevention, management, and research activities to help address this serious threat while promoting public education on the negative impacts of invasive species.
“The Invasive Species Centre is committed to working together to find efficiencies in the fight against invasive species and thanks the Government of Ontario for its support and commitment to protecting our natural spaces and economy,” said Bob Lambe, President, Invasive Species Centre Board of Directors. “The Made-in-Ontario Environment Plan recognized that preventing invasive species is the single most effective and least costly method to manage invasive species. In fact, for every dollar spent on coordinated multi-jurisdictional prevention activities, $3 in mitigation, regulatory and depletion costs can be avoided if only one such pest is prevented from establishing.”
QUICK FACTS
· The Made-in-Ontario Environment Plan commits to protecting our natural environment from invasive species by working with partners like the Invasive Species Centre and using tools to prevent, detect and respond to invasions.
· Since 2008, Ontario has invested over $15 million in the Invasive Species Centre.
· This year, the Ontario government is investing over $2 million in invasive species programs and education.
· Ontario is the only jurisdiction in Canada that has standalone invasive species legislation. The Invasive Species Act provides legislative tools to prohibit and restrict certain invasive species and carriers that facilitate the movement of invasive species
_______________________________________________________________________________
For more information, contact MPP Toby Barrett at 519-428-0446 or toby.barrett@pc.ola.org Please mention The Silo when contacting.
A possible Great Lakes Asian carp invasion?
By MPP Toby Barrett
Our Great Lakes are facing challenges – we see the impact of low water and high phosphorus levels, and, more recently, have become aware of the potential devastating impact stemming from the threat of an Asian carp invasion.
The overwhelming concern with Asian carp – bighead carp and the jumping silver carp- is the threat they pose as they compete with native fish for food; fish like ciscos and perch, which in turn are food for lake trout and pickerel. These native species support a multi-billion dollar sport and commercial fishery.
Asian carp have no natural predators, and have explosive reproductive capacity. Consuming a quarter of their body weight each day, Asian carp monopolize the food source of many other fish and aquatic life forms.
There are several possible routes for Asian carp to reach the Great Lakes. One is the Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal which connects the Mississippi River system with Lake Michigan. While an electrical barrier is in place, carp DNA has been detected beyond the barrier. Another is Eagle Marsh, a 716-acre tract southwest of Fort Wayne, Indiana.
This presents a short-cut directly into Lake Erie.
The Port Dover Harbour Museum recently hosted a talk by David Frew of Mercyhurst College in Erie, Pennsylvania, on the potential Asian carp/Eagle Marsh link to the Great Lakes
As David Frew explained, concerns remain despite $200,000 being spent on a 10-foot-high, 1,177-foot-long chain-link fence bisecting Eagle Marsh to stop Asian carp. Many have cast a skeptical eye as fence-openings allow the free flow of water, as well as fish eggs. The fence does not prevent seagulls from eating carp eggs, flying over the fence, and depositing eggs on the other side.
Of concern locally, according to a Geological Survey review, is the fact that Lake Erie stands to suffer the most devastating impact from an Asian carp invasion.
Jeff Reuter, Director of Ohio Sea Grant, noted recently in the Toledo Blade, “if the carp get in, there’s no doubt that in Lake Erie we will have more carp that the other four great lakes combined.” The article went on to warn: “It would be a disaster of biblical proportion.”
Five bighead carp have been individually collected between 1995 and 2003 in western Lake Erie – although a reproducing population does not exist.
There’s ongoing concern Asian carp could also access the Great Lakes through live bait, or through retail transport of live Asian carp, resulting in accidental or intentional release into the Great Lakes watershed. Ontario’s Ministry of Natural Resources proposes the gutting of imported carp to make sure they’re dead. On January 7th, MNR posted an Asian carp evisceration discussion paper on the Environmental Registry.
Comments are strongly supportive of only allowing eviscerated Asian carp into Ontario. Over the years, Ontario, Quebec and the eight Great Lakes states have cooperated to tackle problems. In 1972, the U.S. and Canada signed the Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement, in part, to stop the spread of invasive species by developing and implementing early detection and rapid response initiatives.
The cost of this invader in the Great Lakes is too great to ignore – proposed environmental legislation for the Great Lakes doesn’t seem designed to head off the threat. An aggressive initiative is needed -working with the U.S. – to address the pending Asian carp invasion. Toby Barrett MPP Haldimand-Norfolk