The world needs to cut carbon emissions and fight climate change. This need has caused a huge change in the car industry. Electric vehicles (EVs) are at the forefront. This shift toward electrification is a technological and economic revolution that is changing the way we think about transportation in addition to being an environmental need.

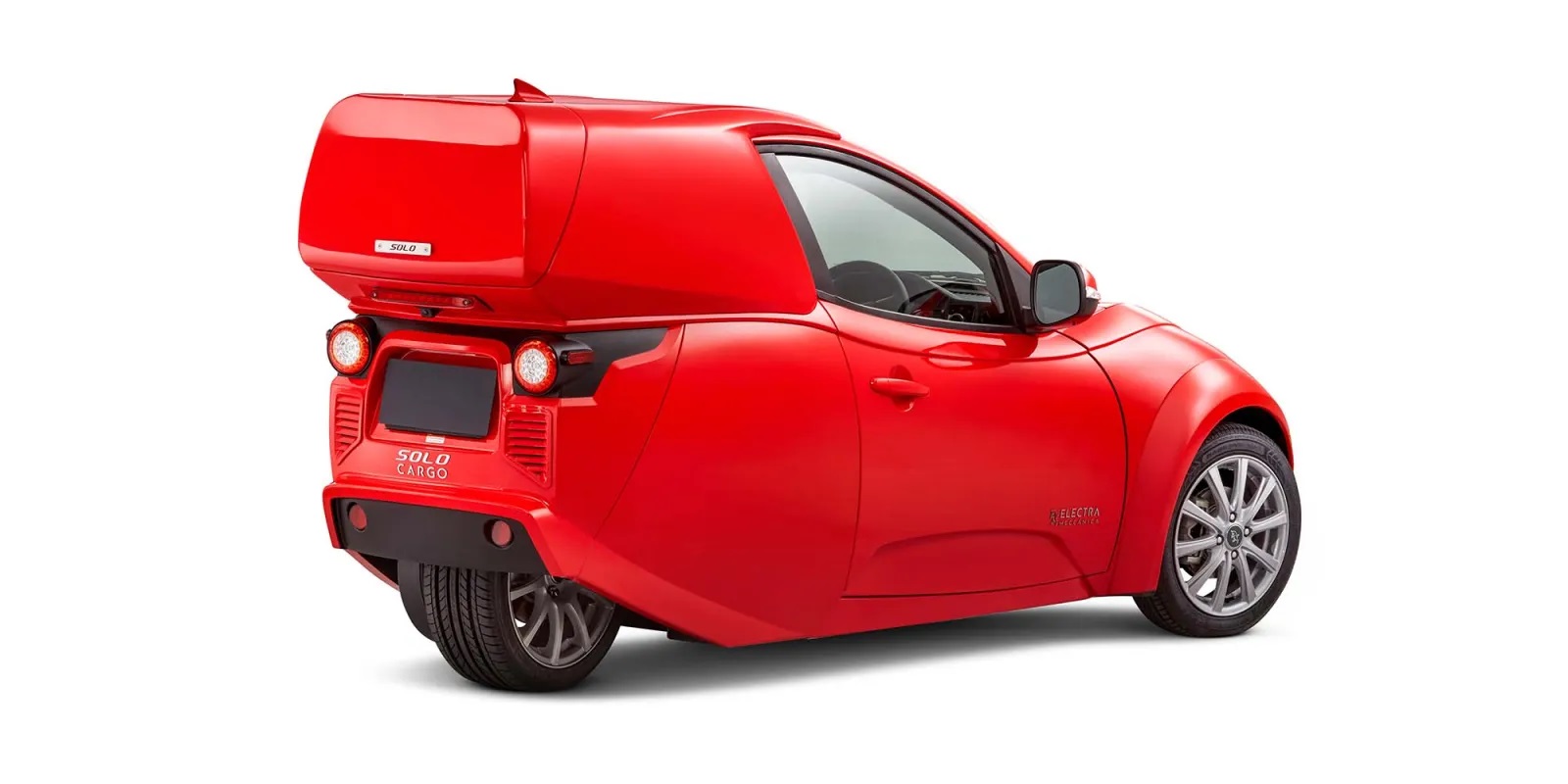
The head-turning Solo EV single seat electric vehicle. Fun and fast.
History of Electric Vehicles
Contrary to popular belief, the idea of electric automobiles is not very new. The origins of electric vehicles (EVs) may be traced to the early 1800s when European and American inventors started experimenting with battery-powered cars. The 1890s saw the introduction of the first useful electric vehicles.
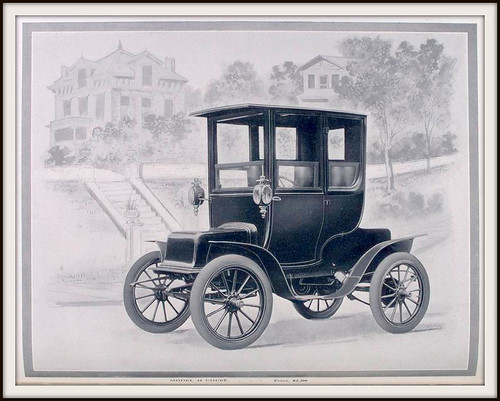

1909 Babcock Electrics – Model 10 Coupé; Price, $ 2,200. – Babcock Electric Carriage Company, Buffalo, New York.
They were competitive with gasoline-powered cars up until the 1920s because of their silent operation and lack of harmful exhaust fumes. But, electric cars started to lose to gasoline cars. This was due to the mass production of gasoline cars, a movement ignited by Henry Ford’s Model T and the discovery of big oil deposits. Meanwhile, the conversation around modern advancements and regulatory changes in various sectors, including automotive and sports, continues to evolve.
A pertinent example of such evolution is the shift in the sports betting landscape, as detailed in insightful sources like this legal sports betting blog.
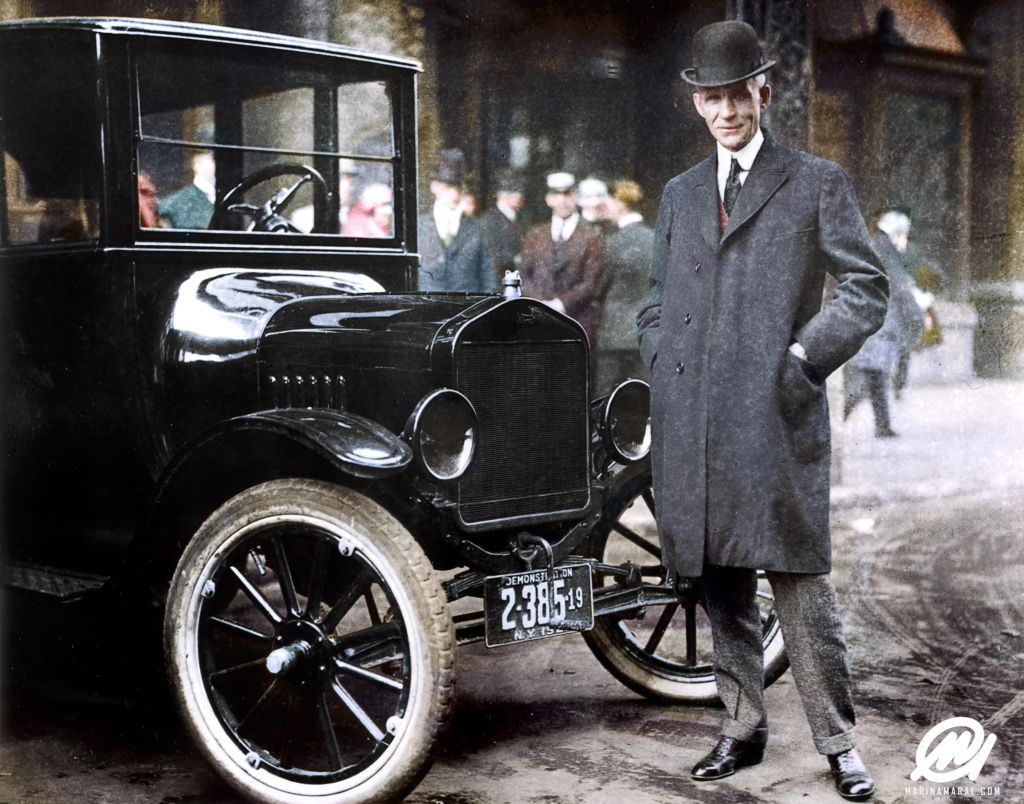

Henry Ford in 1921 with his Model T.
The Rise of Modern Electric Vehicles
Concerns over pollution, climate change, and the depletion of fossil fuels drove the late 20th and early 21st century interest in electric automobiles. Battery technology today has greatly improved. This is especially true for lithium-ion batteries. They have greatly increased the range of electric vehicles (EVs). It has also reduced the time required to charge them. This has positioned EVs as a viable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars.
Benefits of Electric Vehicles
Environmental Impact
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is the primary advantage of electric cars (EVs). Air pollution is significantly decreased by EVs because they produce no exhaust emissions, in contrast to ICE cars. Furthermore, when renewable energy sources are incorporated into the electrical grid, the overall environmental impact of electric vehicles will decrease, making the system greener overall.
Economic Advantages
Individuals and the overall economy can both profit financially from electric vehicles. For a given distance, the cost of charging an electric vehicle is typically less than that of gasoline. Additionally, EVs require less maintenance because they have fewer moving components than ICE cars. In macroeconomics, switching to electric cars can improve energy security. It does so by reducing reliance on imported oil.
Technological Innovation
With cutting-edge technologies like regenerative braking, which recovers energy lost during braking, electric vehicles are frequently at the forefront of automotive technology. The cars have sophisticated entertainment systems. They connect with smart gadgets. They are more connected than regular cars.
Challenges Facing Electric Vehicles
Charging Infrastructure
Infrastructure for charging EVs is convenient and readily available, which is one of the biggest obstacles to their adoption. Although there has been a lot of development, each location has a very different density of charging stations. Cities are better connected than rural areas. This can cause “range anxiety” in people considering electric vehicles.
Battery Technology and Range
Even with the tremendous advancements in battery technology, many consumers are still concerned about range. The best electric cars can go as far as gas cars. But, the average user may not afford the expensive long-range versions. Also, a vehicle’s range and resale value may drop. This may happen because the battery’s performance worsens over time.
Initial Cost
Even though EVs have reduced running expenses, they may cost more to buy initially than equivalent ICE cars. Although prices have been continuously declining, the high cost of batteries is the main cause of this pricing disparity.
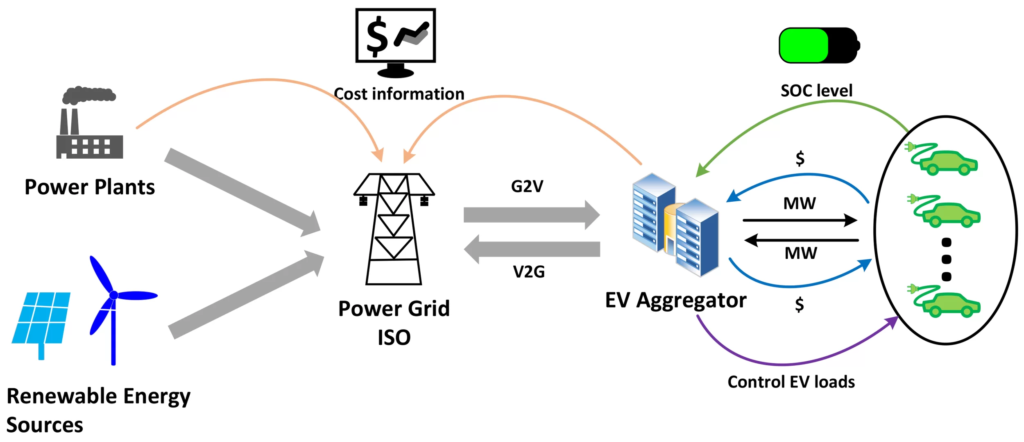
The Integration of Electric Vehicles into Smart Grids
With the increasing number of electric vehicles on the road, integrating them into smart grids offers a revolutionary way to improve energy efficiency and lower transportation’s carbon footprint. Smart grids provide a dynamic framework for the integration of EVs into the larger energy ecosystem by using digital technology to monitor and control the transportation of power from all sources of generation to satisfy the various electrical demands of end-users.
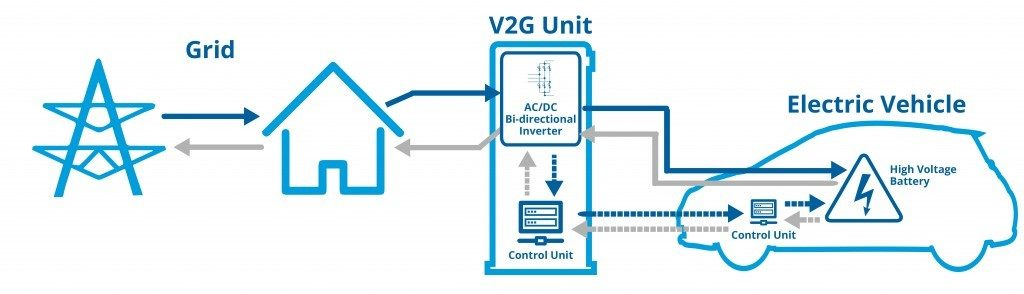
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology
V2G technology lets electric vehicles talk to the power grid. They use it to absorb and return electricity. V2G is crucial to this integration. This feature allows EV owners to sell extra energy from their car’s battery to the grid during peak hours. They can also charge their vehicles during off-peak hours. Power demand is lower then and rates are lower. This two-way energy exchange can help stabilize the grid. It is especially useful as the use of renewable energy grows. Renewable energy sources are often intermittent.
Enhanced Energy Storage
For grid operators, electric vehicles can serve as a useful resource by effectively serving as mobile energy storage units. Utilities can boost the use of renewable energy sources, decrease the need for peaking power plants, and better manage supply and demand by utilizing the combined storage capacity of thousands of electric vehicles. This increases the electrical grid’s efficiency and makes EVs more sustainable by tying their operation more tightly to renewable energy sources.
Smart Charging
The capacity to regulate how long an electric car takes to charge depends on a number of variables, including the owner’s needs, the condition of the grid at the time, and the availability of renewable energy sources. This process is known as smart charging. Smart charging can help by ensuring that vehicles charge at the best times for the grid and the consumer. It can reduce the impact of rising EV demand on the grid.
The Future of Electric Vehicles
There are a lot of exciting developments in store for electric cars shortly. Battery technology is advancing. This progress should make EVs cheaper and available to more people. In addition, electric vehicles will be more practical for daily usage. This is due to the growth of the charging infrastructure. It is being driven by both public and private investment.
Around the world, governments are putting in place policies to help the shift to electric vehicles. These policies include investments in infrastructure for charging, incentives for EV purchases, and tighter pollution standards for internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. The EV industry will grow fast. It will be fueled by these rules and by growing consumer knowledge and concern for the environment.
Also, nearly every big automaker has announced plans to increase the number of electric vehicles in their lineup. This shows how much the industry is embracing electrification. Customers will gain from this competition’s increased innovation and cost-cutting measures.
In summary, electric cars promise a cleaner, more sustainable transportation future, marking a significant turning point in the history of the automobile industry. Even though there are still obstacles, the future is clear. Electric vehicles (EVs) will be crucial. They are key to the global effort to fight climate change and reduce our reliance on fossil fuels. Electric vehicles will play an even bigger role in our lives as technology develops and the globe shifts more toward renewable energy sources, changing not only the way we drive but also the way we live.
Featured image: Electrameccanica Solo EV
